OpenCV 学习(Hough 变换提取直线)
OpenCV 学习(Hough 变换提取直线)
在机器视觉应用中,我们经常要提取图像中的各种特征,最基本的特征就是图像中的线条、拐角等。这篇笔记就来讲讲如何提取图像中的直线。这里使用的方法叫做 Hough 变换。
Hough 变换这个名称最早是在 Richard Duda 和 Peter Hart 两人于 1972 年合写的发表于 Comm. ACM 文章 《Use of the Hough Transformation to Detect Lines and Curves in Pictures》 中提出的。 大家可能会好奇,这俩人没一个叫 Hough,为啥这个变换叫 Hough 变换呢。这还要追溯到更早的年代,1962 年 Paul Hough 申请了一个美国专利,专利的名称叫做 《Method and means for recognizing complex patterns》,这个专利中提出了 Hough 变换基本方法。不过 1962 年那时还没有所谓的机器视觉这个学科,计算机也不是一般人能见到的。所以这个专利并没有受到特别的重视。 Richard Duda 和 Peter Hart 不知是如何翻到这个 10 年前的专利,并敏锐的发现了它的价值,并将其用于机器视觉领域。从此就有了大名鼎鼎的 Hough 变换。
关于 Hough 更详细的历史发展大家可以参考:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hough_transform
Hough 变换的原理介绍也可以参考上面的 wiki。简单的说 Hough 变换采用的是一种证据收集的方式,遍历一幅图像上所有的直线位置,哪条直线上的特征点(证据)更多,哪条直线就更可能是我们希望找到的直线。
这里不准备详细介绍Hough 变换的原理。但是Hough 变换如何表示图像中的直线还是要介绍的。否则,我们都不知道如何使用获得的结果。
Hough 变换时,我们采用参数方程来表示直线。
ρ 的几何含义是直线到图像原点的距离。 θ 是直线的法向方向与 x 轴的夹角。 θ=0 表示的是垂直的直线,例如下图中直线 1。 θ=π/2 表示的是水平的直线,例如下图中直线 5。 θ 的取值范围是 0 到 π 。由于限制了 θ 的取值范围, ρ 既可以为正也可以为负。比如下图中直线2, θ=0.8π , ρ 为负。
OpenCV 中提供了两个Hough变换提取直线的函数。
- cv::HoughLines 函数
- cv::HoughLinesP 函数
下面分别介绍。
cv::HoughLines 函数
这个函数采用最原始的Hough 变换来计算直线的位置。
void HoughLines( InputArray image,
OutputArray lines,
double rho, // rho 的步长
double theta, // 角度步长
int threshold, // 阈值
double srn=0,
double stn=0 );输入图像必须是单通道的。输出的直线存在一个
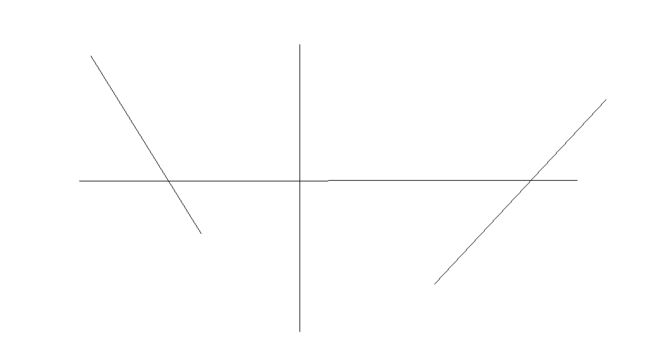
std::vector首先给出一个简单的测试图片。这个图片上有四条直线。没有其他的干扰物体。这属于最基本的情形。
下面是个测试代码。
#include
#include
#define PI 3.14159265358979
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
cv::Mat image = cv::imread("c:\\test.png");
cv::Mat contours;
cv::cvtColor(image, contours, cv::COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
cv::bitwise_not(contours, contours);
//cv::Canny(image, contours, 155, 350);
std::vector lines;
cv::HoughLines(contours, lines, 1, PI/180, 180);
//cv::imshow("cany",contours );
std::vector::const_iterator it= lines.begin();
while (it!=lines.end())
{
float rho= (*it)[0]; // first element is distance rho
float theta= (*it)[1]; // second element is angle theta
if (theta < PI/4. || theta > 3.*PI/4.)// ~vertical line
{
// point of intersection of the line with first row
cv::Point pt1(rho/cos(theta), 0);
// point of intersection of the line with last row
cv::Point pt2((rho - image.rows * sin(theta))/cos(theta), image.rows);
// draw a white line
cv::line( image, pt1, pt2, cv::Scalar(255), 1);
}
else
{ // ~horizontal line
// point of intersection of the
// line with first column
cv::Point pt1(0,rho/sin(theta));
// point of intersection of the line with last column
cv::Point pt2(image.cols, (rho - image.cols * cos(theta))/sin(theta));
// draw a white line
cv::line(image, pt1, pt2, cv::Scalar(255), 1);
}
++it;
}
cv::imshow("", image);
return a.exec();
}
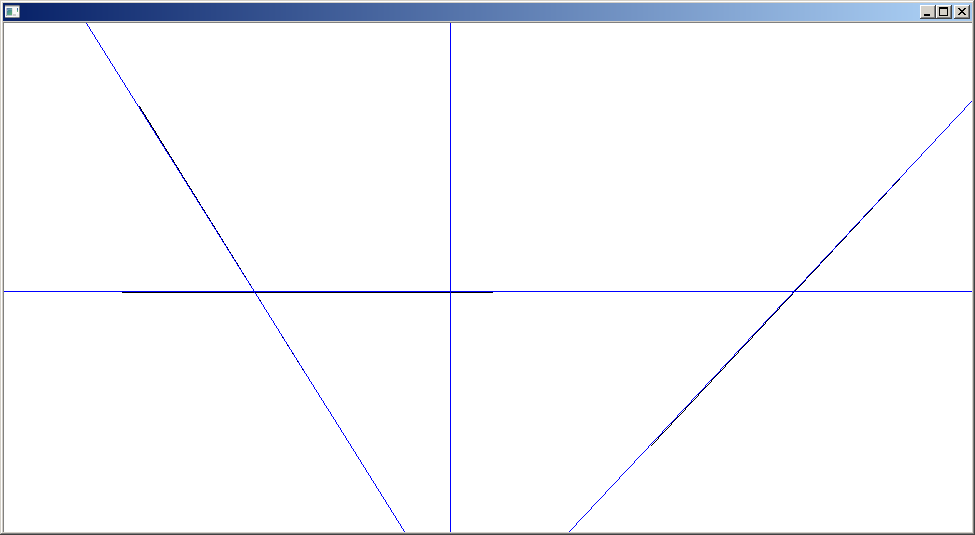
这几条线找的还是蛮准的。
cv::HoughLinesP 函数
与 cv::HoughLines函数不同, cv::HoughLinesP 函数可以提取线段。
输出的直线存在一个
std::vector中。
cv::Vec4i 的四个整数分别是线段的起点和终点坐标。
void HoughLinesP( InputArray image,
OutputArray lines,
double rho, // rho 的步长
double theta, // 角度的步长,单位是度
int threshold, // 阈值
double minLineLength=0, // 线段的最小长度
double maxLineGap=0 ); // 线段之间的最小距离下面把 HoughLinesP 函数封装到一个类中。
class LineFinder
{
private:
cv::Mat img; // original image
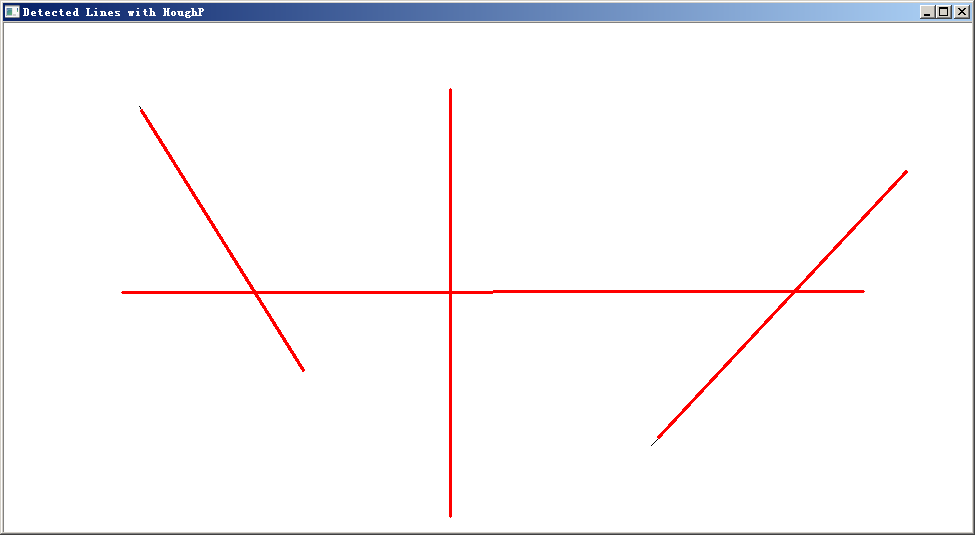
std::vector用这个类实现图中线段的检测。
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
cv::Mat image = cv::imread("c:\\test.png");
cv::Mat contours;
cv::cvtColor(image, contours, cv::COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
cv::bitwise_not(contours, contours);
//cv::Canny(image, contours, 155, 350);
LineFinder finder;
// Set probabilistic Hough parameters
finder.setLineLengthAndGap(100, 20);
finder.setMinVote(80);
// Detect lines and draw them
std::vector