OpenCV——人脸识别模型训练(2)
在之前的博客OpenCV——人脸识别数据处理(1)之中,已经下载了ORL人脸数据库,并且为了识别自己的人脸写了一个拍照程序自拍。之后对拍的照片进行人脸识别和提取,最后我们得到了一个包含自己的人脸照片的文件夹s41。在博客的最后我们提到了一个非常重要的文件——at.txt。
一、csv文件的生成
当我们写人脸模型的训练程序的时候,我们需要读取人脸和人脸对应的标签。直接在数据库中读取显然是低效的。所以我们用csv文件读取。csv文件中包含两方面的内容,一是每一张图片的位置所在,二是每一个人脸对应的标签,就是为每一个人编号。这个at.txt就是我们需要的csv文件。生成之后它里面是这个样子的: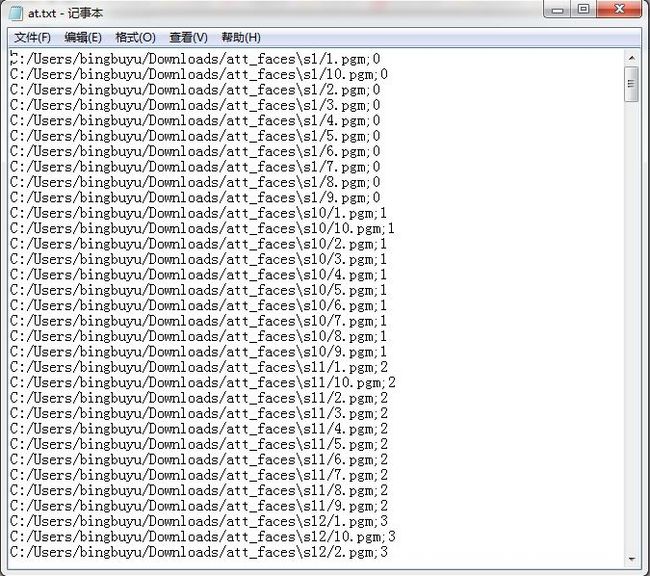
前面是图片的位置,后面是图片所属人脸的人的标签。
要生成这样一个文件直接用手工的方式一个一个输入显然不可取的,毕竟这里有400多张图片。而且这种重复性的工作估计也没人想去做。所以我们可以用命令行的方式简化工作量;或者用opencv自带的Python脚本来自动生成。
命令行方式是这样的。比如我的数据集在C:\Users\bingbuyu\Downloads\att_faces文件夹下面,我就用下面两行命令: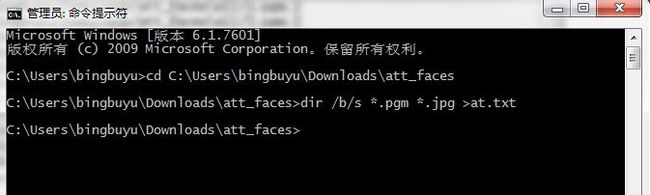 然后数据集文件夹下面就多出了一个at.txt文件,但是现在是只有路径没有标签的。像下面这样:
然后数据集文件夹下面就多出了一个at.txt文件,但是现在是只有路径没有标签的。像下面这样: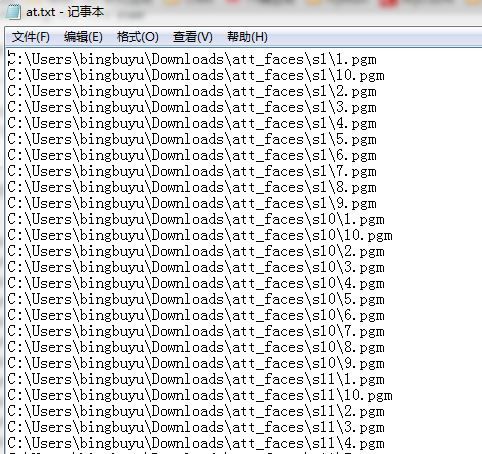
标签需要手动敲上去。。。也挺麻烦的。
好在opencv教程里面为我们提供了自动生成csv文件的脚本。路径类似这样:F:\opencv\sources\modules\contrib\doc\facerec\src\create_csv.py。我不知道怎么用命令行参数的形式运行Python脚本,所以只能把代码里面的BASE_PATH手动的改成自己的数据集路径,改完大致是这样:
#!/usr/bin/env python
import sys
import os.path
# This is a tiny script to help you creating a CSV file from a face
# database with a similar hierarchie:
#
# philipp@mango:~/facerec/data/at$ tree
# .
# |-- README
# |-- s1
# | |-- 1.pgm
# | |-- ...
# | |-- 10.pgm
# |-- s2
# | |-- 1.pgm
# | |-- ...
# | |-- 10.pgm
# ...
# |-- s40
# | |-- 1.pgm
# | |-- ...
# | |-- 10.pgm
#
if __name__ == "__main__":
#if len(sys.argv) != 2:
# print "usage: create_csv "
# sys.exit(1)
#BASE_PATH=sys.argv[1]
BASE_PATH="C:/Users/bingbuyu/Downloads/att_faces"
SEPARATOR=";"
fh = open("../etc/at.txt",'w')
label = 0
for dirname, dirnames, filenames in os.walk(BASE_PATH):
for subdirname in dirnames:
subject_path = os.path.join(dirname, subdirname)
for filename in os.listdir(subject_path):
abs_path = "%s/%s" % (subject_path, filename)
print "%s%s%d" % (abs_path, SEPARATOR, label)
fh.write(abs_path)
fh.write(SEPARATOR)
fh.write(str(label))
fh.write("\n")
label = label + 1
fh.close() 然后运行这个脚本就可以生成一个既有路径又有标签的at.txt了。
二、训练模型
现在数据集、csv文件都已经准备好了。接下来要做的就是训练模型了。
这里我们用到了opencv的Facerecognizer类。opencv中所有的人脸识别模型都是来源于这个类,这个类为所有人脸识别算法提供了一种通用的接口。文档里的一个小段包含了我们接下来要用到的几个函数:

OpenCV 自带了三个人脸识别算法:Eigenfaces,Fisherfaces 和局部二值模式直方图 (LBPH)。这里先不去深究这些算法的具体内容,直接用就是了。如果有兴趣可以去看相关论文。接下来就分别训练这三种人脸模型。这个时候就能体现出Facerecognizer类的强大了。因为每一种模型的训练只需要三行代码
Ptr<FaceRecognizer> model = createEigenFaceRecognizer();
model->train(images, labels);
model->save("MyFacePCAModel.xml");
Ptr<FaceRecognizer> model1 = createFisherFaceRecognizer();
model1->train(images, labels);
model1->save("MyFaceFisherModel.xml");
Ptr<FaceRecognizer> model2 = createLBPHFaceRecognizer();
model2->train(images, labels); 当然在这之前要先把之前图片和标签提取出来。这时候就是at.txt派上用场的时候了。
//使用CSV文件去读图像和标签,主要使用stringstream和getline方法
static void read_csv(const string& filename, vector在模型训练好之后我们拿数据集中的最后一张图片做一个测试,看看结果如何。
Mat testSample = images[images.size() - 1];
int testLabel = labels[labels.size() - 1];
"white-space:pre"> //。。。。这里省略部分代码。。。。。。。。
// 下面对测试图像进行预测,predictedLabel是预测标签结果
int predictedLabel = model->predict(testSample);
int predictedLabel1 = model1->predict(testSample);
int predictedLabel2 = model2->predict(testSample);
// 还有一种调用方式,可以获取结果同时得到阈值:
// int predictedLabel = -1;
// double confidence = 0.0;
// model->predict(testSample, predictedLabel, confidence);
string result_message = format("Predicted class = %d / Actual class = %d.", predictedLabel, testLabel);
string result_message1 = format("Predicted class = %d / Actual class = %d.", predictedLabel1, testLabel);
string result_message2 = format("Predicted class = %d / Actual class = %d.", predictedLabel2, testLabel);
cout << result_message << endl;
cout << result_message1 << endl;
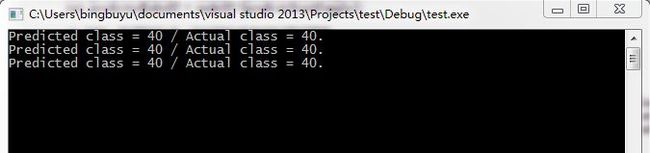
cout << result_message2 << endl; 由于本来的数据集中是40个人,加上自己的人脸集就是41个。标签是从0开始标的,所以在这里我是第40个人。也即是说Actual class应该40。Predicted class也应该是40才说明预测准确。这里我们可以看到结果:
模型训练的全部代码:
//#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
static Mat norm_0_255(InputArray _src) {
Mat src = _src.getMat();
// 创建和返回一个归一化后的图像矩阵:
Mat dst;
switch (src.channels()) {
case1:
cv::normalize(_src, dst, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_8UC1);
break;
case3:
cv::normalize(_src, dst, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_8UC3);
break;
default:
src.copyTo(dst);
break;
}
return dst;
}
//使用CSV文件去读图像和标签,主要使用stringstream和getline方法
static void read_csv(const string& filename, vector model = createEigenFaceRecognizer();
model->train(images, labels);
model->save("MyFacePCAModel.xml");
Ptr model1 = createFisherFaceRecognizer();
model1->train(images, labels);
model1->save("MyFaceFisherModel.xml");
Ptr model2 = createLBPHFaceRecognizer();
model2->train(images, labels);
model2->save("MyFaceLBPHModel.xml");
// 下面对测试图像进行预测,predictedLabel是预测标签结果
int predictedLabel = model->predict(testSample);
int predictedLabel1 = model1->predict(testSample);
int predictedLabel2 = model2->predict(testSample);
// 还有一种调用方式,可以获取结果同时得到阈值:
// int predictedLabel = -1;
// double confidence = 0.0;
// model->predict(testSample, predictedLabel, confidence);
string result_message = format("Predicted class = %d / Actual class = %d.", predictedLabel, testLabel);
string result_message1 = format("Predicted class = %d / Actual class = %d.", predictedLabel1, testLabel);
string result_message2 = format("Predicted class = %d / Actual class = %d.", predictedLabel2, testLabel);
cout << result_message << endl;
cout << result_message1 << endl;
cout << result_message2 << endl;
waitKey(0);
return 0;
} 本文由@星沉阁冰不语出品,转载请注明作者和出处。
文章链接:http://blog.csdn.net/xingchenbingbuyu/article/details/51407336
学习有益,进而不止。