IdentityHashMap源码详解
1. IdentityHashMap概述
IdentityHashMap是一致性哈希表,使用引用相等,而不是equals方法来比较两个对象的相等性。因此,IdentityHashMap中,如果存在两个键key1和key2,当且仅当key1==key2时,两个键相等,而其他大部分的哈希表,当且仅当k1 == null ? k2 == null : k1.equals(k2)时,两个键才认为是相等的。
IdentityHashMap使用System.identityHashCode来确定对象的哈希码,该方法返回对象的地址。
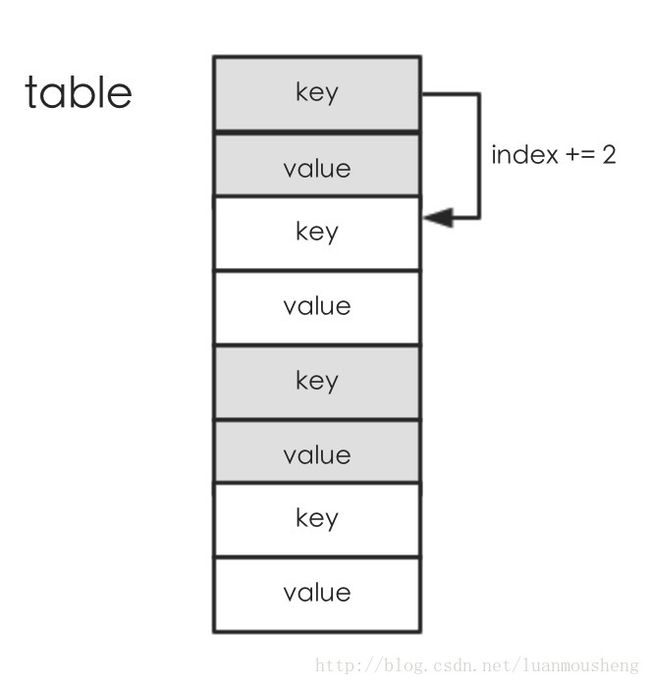
看下IdentityHashMap的存储原理图,和HashMap不同,HashMap是通过数组+拉链法存储元素并解决哈希冲突的。IdentityHashMap将所有的key和value都存储到Object[]数组table中,并且key和value相邻存储,当出现哈希冲突时,会往下遍历数组,直到找到一个空闲的位置。注意,数组第一个位置存储的是key,第二个位置存储的是value。因此奇数位置处存储的是key,偶数位置处存储的是value。
2. 私有变量
//哈希表的默认容量
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 32;
//哈希表的最小容量
private static final int MINIMUM_CAPACITY = 4;
//哈希表的最大容量,其中包括了一个键为null的键值对
private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 29;
//哈希表内部存储的数组
transient Object[] table;
//哈希表存储的键值对数量
int size;
//哈希表的修改次数
transient int modCount;
//存储键为null的key,如果键为null,实际用NULL_KEY存储
static final Object NULL_KEY = new Object();注意,IdentityHashMap的加载因子为2/3。
3. 构造函数
//默认构造函数,容量为32,加载因子为2/3,最多可存储32*2/3=21个键值对
public IdentityHashMap() {
init(DEFAULT_CAPACITY);
}
//根据指定容量构造
public IdentityHashMap(int expectedMaxSize) {
if (expectedMaxSize < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("expectedMaxSize is negative: "
+ expectedMaxSize);
init(capacity(expectedMaxSize));
}
//返回一个介于MINIMUM_CAPACITY和MAXIMUM_CAPACITY,且大于3*expectedMaxSize/2的值
//如果该值不存在,返回MAXIMUM_CAPACITY
private static int capacity(int expectedMaxSize) {
// assert expectedMaxSize >= 0;
return
(expectedMaxSize > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY / 3) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
(expectedMaxSize <= 2 * MINIMUM_CAPACITY / 3) ? MINIMUM_CAPACITY :
Integer.highestOneBit(expectedMaxSize + (expectedMaxSize << 1));
}
//初始化内部存储数组table,table数组大小为参数initCapacity的两倍
//为何是两倍?因为这是包括了键和值,刚好两倍
private void init(int initCapacity) {
table = new Object[2 * initCapacity];
}
//通过指定map初始化
public IdentityHashMap(Map m) {
this((int) ((1 + m.size()) * 1.1));
putAll(m);
}4. get方法
该方法返回键对应的值。
public V get(Object key) {
//如果key为null,取null键对应的key
Object k = maskNull(key);
Object[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
//取键k在table的索引
int i = hash(k, len);
while (true) {
Object item = tab[i];
//如果索引i处存储的值就是键k,那么下一个存储位置就是键对应的值
if (item == k)
return (V) tab[i + 1];
//如果索引i处存储的值为null,返回null
if (item == null)
return null;
//轮询遍历下一个键
i = nextKeyIndex(i, len);
}
}通过该方法可以发现IdentityHashMap的存储原理,将键值对存储到内部的Object[]数组中,相邻两个位置处分别是key和value。查找过程中,如果发现当前位置存储的不是要查找的键,则轮询下一个(i+2)位置,这也是IdentityHashMap解决冲突的方法。看下hash方法的实现原理:
//返回对象x在数组table中的位置
private static int hash(Object x, int length) {
int h = System.identityHashCode(x);
return ((h << 1) - (h << 8)) & (length - 1);
}接着看下nextKeyIndex的实现原理:
//返回当前键索引的下一个索引,如果越过数组大小,返回数组位置0
private static int nextKeyIndex(int i, int len) {
return (i + 2 < len ? i + 2 : 0);
}IdentityHashMap的containsKey方法实现和get实现基本相同,不再说明。
IdentityHashMap的containsMapping方法实现和get实现也基本相同,不再说明。
5. containsValue方法
该方法判断是否存在指定的值。
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
Object[] tab = table;
for (int i = 1; i < tab.length; i += 2)
if (tab[i] == value && tab[i - 1] != null)
return true;
return false;
}该方法实现很简单,table中第一个存储value的位置是1,因此从1开始查找,步长为2。引用相等并且该value对应的的key不为null的情况下,返回true。
6. put方法
该方法将指定的key-value对添加到table数组中,如果对应key已经存在,则更新对应的value。该方法返回该key之前对应的value。
public V put(K key, V value) {
final Object k = maskNull(key);
retryAfterResize: for (;;) {
final Object[] tab = table;
final int len = tab.length;
int i = hash(k, len);
for (Object item; (item = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextKeyIndex(i, len)) {
if (item == k) {
//键已经存在,替换并返回老的value
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
V oldValue = (V) tab[i + 1];
tab[i + 1] = value;
return oldValue;
}
}
//键值对数量加1
final int s = size + 1;
//如果3*s大于数组的大小,需要重新分配table
if (s + (s << 1) > len && resize(len))
continue retryAfterResize;
//修改次数+1
modCount++;
tab[i] = k;
tab[i + 1] = value;
size = s;
return null;
}
}该方法查找key对应的键值对,如果已经存在,替换并返回老的value。添加键值对之前先判断是否需要重新分配数组的大小。如果需要,则重新分配。
IdentityHashMap的putAll方法其实是循环调用了put方法,不再说明。
继续看下resize方法
7. resize方法
private boolean resize(int newCapacity) {
//新数组的大小为参数的两倍
int newLength = newCapacity * 2;
Object[] oldTable = table;
int oldLength = oldTable.length;
if (oldLength == 2 * MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
if (size == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY - 1)
throw new IllegalStateException("Capacity exhausted.");
return false;
}
if (oldLength >= newLength)
return false;
Object[] newTable = new Object[newLength];
//将老数组的元素复制到新的数组
for (int j = 0; j < oldLength; j += 2) {
Object key = oldTable[j];
if (key != null) {
Object value = oldTable[j+1];
//let gc
oldTable[j] = null;
oldTable[j+1] = null;
//找到key在新数组的索引
int i = hash(key, newLength);
//找到不为空的索引位置
while (newTable[i] != null)
i = nextKeyIndex(i, newLength);
//存储到新数组的位置
newTable[i] = key;
newTable[i + 1] = value;
}
}
table = newTable;
return true;
}resize方法首先确定新数组的大小,然后将老数组的元素复制到新的数组。
8. remove方法
该方法删除指定键对应的键值对,返回键对应的老的值。
public V remove(Object key) {
Object k = maskNull(key);
Object[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = hash(k, len);
while (true) {
Object item = tab[i];
//如果找到了该键
if (item == k) {
modCount++;
size--;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
V oldValue = (V) tab[i + 1];
//let gc
tab[i + 1] = null;
tab[i] = null;
closeDeletion(i);
return oldValue;
}
if (item == null)
return null;
i = nextKeyIndex(i, len);
}
}IdentityHashMap的removeMapping方法和该方法的实现类似,不再说明。这里主要看下closeDeletion方法的用处。closeDeletion方法在删除某个键值对后调用,比如位置i处的元素删除了,调用closeDeletion方法更新该位置之后的元素,减少地址冲突。
8. clear方法
clear方法很简单,遍历table数组并将数组元素值设置为null。
public void clear() {
modCount++;
Object[] tab = table;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; i++)
tab[i] = null;
size = 0;
}9. 迭代器-IdentityHashMapIterator
IdentityHashMap的迭代器是由抽象内部类IdentityHashMapIterator实现的,看下该抽象类的源码:
private abstract class IdentityHashMapIterator<T> implements Iterator<T> {
//当前位置
int index = (size != 0 ? 0 : table.length);
//迭代器的快速失败机制
int expectedModCount = modCount;
//最后一个返回的位置,删除的时候也是删除该位置的值
int lastReturnedIndex = -1;
//这个参数是为了避免无效计算
boolean indexValid;
Object[] traversalTable = table;
//哈希表是否还有下一个元素
public boolean hasNext() {
Object[] tab = traversalTable;
for (int i = index; i < tab.length; i+=2) {
Object key = tab[i];
if (key != null) {
//更新当前位置并返回true
index = i;
return indexValid = true;
}
}
//到这,说明已经没有更多元素了
index = tab.length;
return false;
}
//返回下一个索引
protected int nextIndex() {
//迭代器的快速失败机制,说明有其他线程并发修改了该哈希表
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
if (!indexValid && !hasNext())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
//调用nextIndex方法后,设置indexValid为不可用,也就是说,不能连续调用nextIndex方法
indexValid = false;
lastReturnedIndex = index;
index += 2;
return lastReturnedIndex;
}
//删除当前位置的键值对后,重新调整后面的元素,减少冲突
public void remove() {
if (lastReturnedIndex == -1)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
expectedModCount = ++modCount;
int deletedSlot = lastReturnedIndex;
lastReturnedIndex = -1;
index = deletedSlot;
indexValid = false;
Object[] tab = traversalTable;
int len = tab.length;
int d = deletedSlot;
Object key = tab[d];
tab[d] = null;
tab[d + 1] = null;
if (tab != IdentityHashMap.this.table) {
IdentityHashMap.this.remove(key);
expectedModCount = modCount;
return;
}
size--;
Object item;
for (int i = nextKeyIndex(d, len); (item = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextKeyIndex(i, len)) {
int r = hash(item, len);
if ((i < r && (r <= d || d <= i)) ||
(r <= d && d <= i)) {
if (i < deletedSlot && d >= deletedSlot &&
traversalTable == IdentityHashMap.this.table) {
int remaining = len - deletedSlot;
Object[] newTable = new Object[remaining];
System.arraycopy(tab, deletedSlot,
newTable, 0, remaining);
traversalTable = newTable;
index = 0;
}
tab[d] = item;
tab[d + 1] = tab[i + 1];
tab[i] = null;
tab[i + 1] = null;
d = i;
}
}
}
}IdentityHashMap的剩余代码都是对该抽象迭代器的扩展,不再说明。