《深入理解Mysql》之SQL优化利器-explain
SQL的书写和执行顺序完全不同,今天我们就探究一下存储引擎是怎么执行SQL来查找数据的
explain语法
explain + QueryStatement ,如下
 标题
标题
分别有 id、select_type、table、partitions、type、possible_keys、key、ref、rows、filtered、Extra这12列
1、id 表示执行顺序,用一个整数表示,当id都相同时从上往下执行、当id不同时id大的先执行、当有一部分相同、有一部分不同时、最大的先执行,相同的部分从上往下执行
2、type表示使用索引的情况,有如下取值
system > const > eq_ref > ref > fulltext > ref_or_null > index_merge > unique_subquery > index_subquery > range > index > ALL
2.1 system:基本可以忽略,实际开发中几乎不会出现
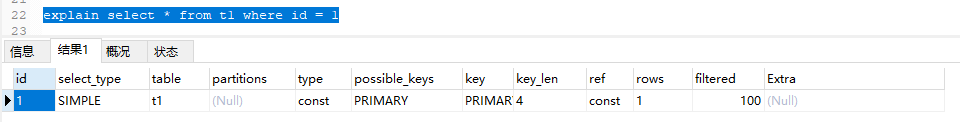
2.2 const:常量,表示一个sql查询时只需要通过常量次的查找就可以找到某一条数据,一般是通过主键/唯一索引找到某一条数据
create table t1(id int not null auto_increment,
username varchar(32),
age smallint,
remark varchar(128),
PRIMARY KEY(id))
insert into t1(username,age,remark)
values
('aaa',22,'燃烧我的卡路里'),
('bbb',33,'燃烧我的卡路里1'),
('ccc',34,'燃烧我的卡路里2'),
('ddd',35,'燃烧我的卡路里3'),
('eee',36,'燃烧我的卡路里4')
-- 添加如上数据后执行以下sql
explain select * from t1 where id = 12.3 eq_ref :表示通过主键或者唯一索引(该字段必须是not null)做连接
create table t2 (id int,user1 varchar(32),passwd varchar(32),
rid int not null,PRIMARY KEY(id))
create unique index rid_unique_index on t2(rid)
insert into t2(id,user1,passwd,rid)
values
(1,'aaa','a_password1',1),
(2,'aaa','a_password2',2),
(3,'aaa','a_password3',3),
(4,'aaa','a_password4',4),
(5,'aaa','a_password5',5),
(6,'aaa','a_password6',6),
(7,'aaa','a_password7',7)
--eq_ref 下面2条sql一样的效果
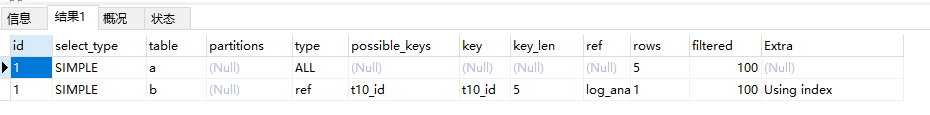
explain select t1.*,t2.* from t1,t2 where t1.id = t2.id
explain select a.*,b.* from t1 a left join t2 b on a.id = b.id
-- 在on后面的条件t1.id = t2.id中,t2.id在t2表中一定只有一条,t1.id 最多只能匹配到一条t2.id的
--记录满足 t1.id = t2.id这个等式,按照这个逻辑,t1.id = t2.rid也是满足2.4 ref:也是索引扫描,除了主键关联之外的其他索引扫描(唯一索引/普通索引)
create table t10 (id int)
create index t10_id on t10(id)
explain select * from t1 a left join t10 b on a.id = b.id2.5 rang:表示通过有的索引字段的范围查找
-- range
explain select * from t1 WHERE id in (1,23)2.6 index:只扫描索引树并获取数据
explain select id from t2执行上面的这条sql语句,直接通过索引树就可以获取所有的数据,不用扫描实际的数据文件即可以获取
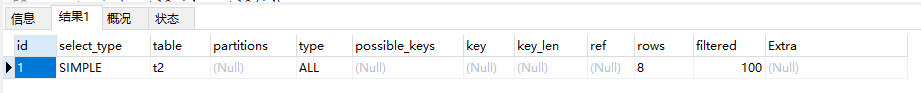
2.7 ALL:权标扫描,在实际开发中最好不要出现
explain select user1 from t2
3、table表示操作的目标即对那一张表做操作
4、possible_keys 表示可能用到的索引
5、key 表示实际使用到的索引
6、rows 根据表统计信息及索引选用情况,大致估算出找到所需的记录所需要读取的行数
7、key_len 表示索引所用到的长度,这是一个计算出来的理论值,单位是字节
具体的计算规则是
某个字段所占用的字节长度 + 是否为null
eg:在utf8mb4编码下一个字符占4个字节
create table t4 (id int not null auto_increment,tag1 varchar(8) not null,
tag2 varchar(8) not null ,tag3 varchar(8) not null,PRIMARY key(id))
create index unionIndexTag1Tag2Tag3 on t4(tag1,tag2,tag3)
insert into t4(tag1,tag2,tag3)
values
('tag_1','tag_2','tag_3'),
('tag_11','tag_21','tag_31'),
('tag_12','tag_22','tag_32')
EXPLAIN select * from t4 where t4.tag1 = ''
也可看到,key_len=35 即使用到了tag1(varchar(8)) 8*4 + 2 + 1 = 35 表示tag1的8个字符每个占用4个字节 + 边长varchar中有2个字节用来存储这个边长字符数组的实际长度 最后的1代表可以为null,如果不可以为null则不用+1
8、ref 显示索引的那一列被使用了,如果可能,是一个常量const。
同样是上面的例子中可以看到,ref是一个常数,这表示 where 后面的tag1匹配的是''空字符串
运行如下代码