tensorflow实现FCN完成训练自己标注的数据
一、先复现FCN
环境:Ubuntu18.04+tensorflow(我的)
1.下载代码:
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1605.06211v1.pdf
论文视频地址:http://techtalks.tv/talks/fully-convolutional-networks-for-semantic-segmentation/61606/
GitHub资源:https://github.com/shekkizh/FCN.tensorflow
代码的实现有四个python文件,分别是FCN.py、BatchDatasetReader.py、TensorFlowUtils.py、read_MITSceneParsingData.py,将这四个文件放在一个当前目录下。
2.然后下载VGG网络的权重参数,下载好后的文件路径为./Model_zoo/imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat.
网址:http://www.vlfeat.org/matconvnet/models/beta16/imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat
3.然后下载训练会用到的数据集,并解压到路径: ./Data_zoo/MIT_SceneParsing/ADEChallengeData2016。
网址:http://data.csail.mit.edu/places/ADEchallenge/ADEChallengeData2016.zip
4.训练时把FCN.py中的全局变量mode该为“train”,运行该文件。测试时改为“visualize”运行即可。
这个很简单的。
下面解析一下部分FCN.py为主文件代码,
加载vgg参数:
def vgg_net(weights, image):
layers = (
'conv1_1', 'relu1_1', 'conv1_2', 'relu1_2', 'pool1',
'conv2_1', 'relu2_1', 'conv2_2', 'relu2_2', 'pool2',
'conv3_1', 'relu3_1', 'conv3_2', 'relu3_2', 'conv3_3',
'relu3_3', 'conv3_4', 'relu3_4', 'pool3',
'conv4_1', 'relu4_1', 'conv4_2', 'relu4_2', 'conv4_3',
'relu4_3', 'conv4_4', 'relu4_4', 'pool4',
'conv5_1', 'relu5_1', 'conv5_2', 'relu5_2', 'conv5_3',
'relu5_3', 'conv5_4', 'relu5_4'
)
net = {}
current = image
for i, name in enumerate(layers):
kind = name[:4]
if kind == 'conv':
kernels, bias = weights[i][0][0][0][0]
# matconvnet: weights are [width, height, in_channels, out_channels]
# tensorflow: weights are [height, width, in_channels, out_channels]
kernels = utils.get_variable(np.transpose(kernels, (1, 0, 2, 3)), name=name + "_w")
bias = utils.get_variable(bias.reshape(-1), name=name + "_b")
current = utils.conv2d_basic(current, kernels, bias)
elif kind == 'relu':
current = tf.nn.relu(current, name=name)
if FLAGS.debug:
utils.add_activation_summary(current)
elif kind == 'pool':
current = utils.avg_pool_2x2(current)
net[name] = current
return net
主要是获取VGG模型预先训练好的模型系数文件。该文件为Mat格式,我们可以使用Python的scipy.io进行数据读取。
读取这块在TensorFlowUtils.py中有。该数据包含很多信息,而我们需要的信息是每层神经网络的kernels和bias。
kernels的获取方式是data['layers'][0][第i层][0][0][0][0][0],形状为[width, height, in_channels, out_channels],bias的获取方式是data['layers'][0][第i层][0][0][0][0][0],形状为[1,out_channels]。
对于VGG-19的卷积,全部采用了3X3的filters,所以width为3,height为3。
注意,这里面的层数i,指的是包括conv、relu、pool、fc各种操作。因此,i=0为卷积核,i=1为relu,i=2为卷积核,i=3为relu,i=4为pool,i=5为卷积核,……,i=37为全连接层,以此类推。VGG-19的pooling采用了长宽为2X2的max-pooling。
生成FCN网络:
def inference(image, keep_prob):
"""
Semantic segmentation network definition
:param image: input image. Should have values in range 0-255
:param keep_prob:
:return:
"""
# 加载模型数据
print("setting up vgg initialized conv layers ...")
model_data = utils.get_model_data(FLAGS.model_dir, MODEL_URL)
mean = model_data['normalization'][0][0][0]
mean_pixel = np.mean(mean, axis=(0, 1))
weights = np.squeeze(model_data['layers']) #把形状中为1的维度去掉
# 图像预处理
processed_image = utils.process_image(image, mean_pixel)
with tf.variable_scope("inference"):
image_net = vgg_net(weights, processed_image)
conv_final_layer = image_net["conv5_3"]
pool5 = utils.max_pool_2x2(conv_final_layer)
W6 = utils.weight_variable([7, 7, 512, 4096], name="W6")
b6 = utils.bias_variable([4096], name="b6")
conv6 = utils.conv2d_basic(pool5, W6, b6)
relu6 = tf.nn.relu(conv6, name="relu6")
if FLAGS.debug:
utils.add_activation_summary(relu6)
relu_dropout6 = tf.nn.dropout(relu6, keep_prob=keep_prob)
W7 = utils.weight_variable([1, 1, 4096, 4096], name="W7")
b7 = utils.bias_variable([4096], name="b7")
conv7 = utils.conv2d_basic(relu_dropout6, W7, b7)
relu7 = tf.nn.relu(conv7, name="relu7")
if FLAGS.debug:
utils.add_activation_summary(relu7)
relu_dropout7 = tf.nn.dropout(relu7, keep_prob=keep_prob)
W8 = utils.weight_variable([1, 1, 4096, NUM_OF_CLASSESS], name="W8")
b8 = utils.bias_variable([NUM_OF_CLASSESS], name="b8")
conv8 = utils.conv2d_basic(relu_dropout7, W8, b8)
# annotation_pred1 = tf.argmax(conv8, dimension=3, name="prediction1")
# now to upscale to actual image size
deconv_shape1 = image_net["pool4"].get_shape()
W_t1 = utils.weight_variable([4, 4, deconv_shape1[3].value, NUM_OF_CLASSESS], name="W_t1")
b_t1 = utils.bias_variable([deconv_shape1[3].value], name="b_t1")
conv_t1 = utils.conv2d_transpose_strided(conv8, W_t1, b_t1, output_shape=tf.shape(image_net["pool4"]))
fuse_1 = tf.add(conv_t1, image_net["pool4"], name="fuse_1")
deconv_shape2 = image_net["pool3"].get_shape()
W_t2 = utils.weight_variable([4, 4, deconv_shape2[3].value, deconv_shape1[3].value], name="W_t2")
b_t2 = utils.bias_variable([deconv_shape2[3].value], name="b_t2")
conv_t2 = utils.conv2d_transpose_strided(fuse_1, W_t2, b_t2, output_shape=tf.shape(image_net["pool3"]))
fuse_2 = tf.add(conv_t2, image_net["pool3"], name="fuse_2")
shape = tf.shape(image)
deconv_shape3 = tf.stack([shape[0], shape[1], shape[2], NUM_OF_CLASSESS])
W_t3 = utils.weight_variable([16, 16, NUM_OF_CLASSESS, deconv_shape2[3].value], name="W_t3")
b_t3 = utils.bias_variable([NUM_OF_CLASSESS], name="b_t3")
conv_t3 = utils.conv2d_transpose_strided(fuse_2, W_t3, b_t3, output_shape=deconv_shape3, stride=8)
annotation_pred = tf.argmax(conv_t3, dimension=3, name="prediction")
return tf.expand_dims(annotation_pred, dim=3), conv_t3VGG-19需要对输入图片进行一步预处理,把每个像素点的取值减去训练集算出来的RGB均值。
VGG-19的RGB均值可以通过np.mean(data['normalization'][0][0][0], axis=(0, 1)获得,其取值为[ 123.68 116.779 103.939],不细解释了。
TensorFlowUtils.py主要定义了一些工具函数,如变量初始化、卷积反卷积操作、池化操作、批量归一化、图像预处理等,read_MITSceneParsingData.py主要是用于读取数据集的数据,BatchDatasetReader.py主要用于制作数据集batch块。
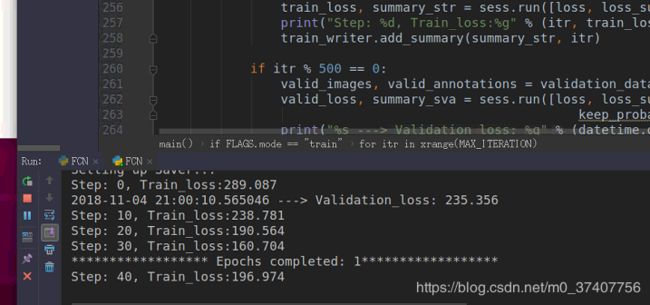
执行FCN.py这样就开始训练了。
二、制作自己的训练数据
1. 做标签安装
下载网址:https://github.com/wkentaro/labelme#ubuntu
我的环境ubuntu18+py36.
# Python3
sudo apt-get install python3-pyqt5 # PyQt5
sudo pip3 install labelme2.标注:
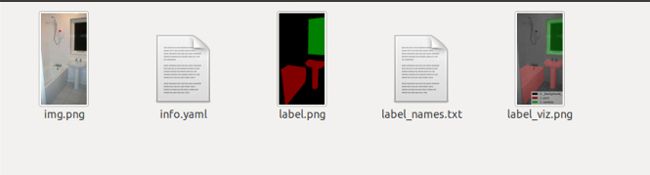
运行labelme打开取名标注即可,点击Save后会生成改图片对应的json文件。
单张pnglabel图片生成:labelme_json_to_dataset 《文件名》.json
如:
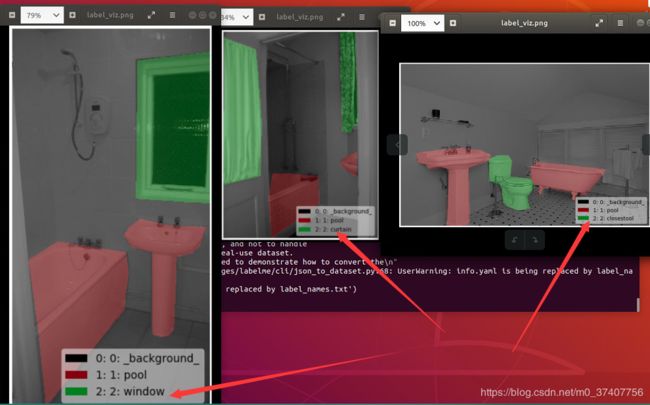
有的 看起来是全黑的,然而读到像素中,是可以看到对相同类别的文件进行标注了。
而实际中我们希望能对文件夹下多个json文件进行批量处理。
代码:参考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41831559/article/details/80835913
import argparse
import json
import os
import os.path as osp
import warnings
import numpy as np
import PIL.Image
import yaml
from labelme import utils
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('json_file')
parser.add_argument('-o', '--out', default=None)
args = parser.parse_args()
json_file = args.json_file
list = os.listdir(json_file)
for i in range(0, len(list)):
path = os.path.join(json_file, list[i])
if os.path.isfile(path):
data = json.load(open(path))
img = utils.img_b64_to_arr(data['imageData'])
lbl, lbl_names = utils.labelme_shapes_to_label(img.shape, data['shapes'])
captions = ['%d: %s' % (l, name) for l, name in enumerate(lbl_names)]
lbl_viz = utils.draw_label(lbl, img, captions)
out_dir = osp.basename(list[i]).replace('.', '_')
out_dir = osp.join(osp.dirname(list[i]), out_dir)
if not osp.exists(out_dir):
os.mkdir(out_dir)
PIL.Image.fromarray(img).save(osp.join(out_dir, 'img.png'))
PIL.Image.fromarray(lbl).save(osp.join(out_dir, 'label.png'))
PIL.Image.fromarray(lbl_viz).save(osp.join(out_dir, 'label_viz.png'))
with open(osp.join(out_dir, 'label_names.txt'), 'w') as f:
for lbl_name in lbl_names:
f.write(lbl_name + '\n')
warnings.warn('info.yaml is being replaced by label_names.txt')
info = dict(label_names=lbl_names)
with open(osp.join(out_dir, 'info.yaml'), 'w') as f:
yaml.safe_dump(info, f, default_flow_style=False)
print('Saved to: %s' % out_dir)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()使用时:python3 此文件名 文件夹(你的json)
代码可以将json文件中的label存储为png图像文件。但是存在一个问题:对于多类分割任务,任意一张图可能不包含所有分类。因此整个文件夹下生成的所有label图像中,不同图像中的相同类别的目标在label.png中可能对应不同的灰度值,使标注的label不具备统一性,因而出错。即假如我总共有10个类别,但分割一张图片时,只有其中的3个类别,这样的话,我生成标签就是[0,1,2],当我分割另外一张图像时,有其中的2个类别,那么对应的标签是[0,1],而且这两张图中的1,并不是相同的类别。
例如:
针对一此情况,对代码进行了改进,使用时:
python3 batch_json_to_dataset.py json《json文件夹》 labels《转换的png图》
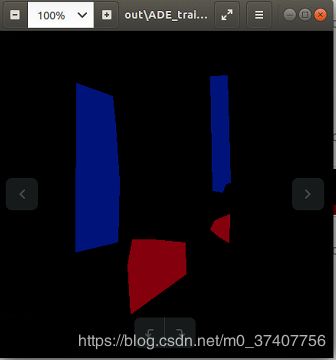
此时会在label文件下就会生成label图片,都是黑乎乎的,你如果要可视化的话,可以python3 batch_color_map.py labels out 5, 最后的5表示类别,我这个地方是四种类别(如下图的蓝色:curtain,红色:pool,绿色:closestool,黄色:window),加背景也作为一种像素,所以为5,生成的图象如下图所示。
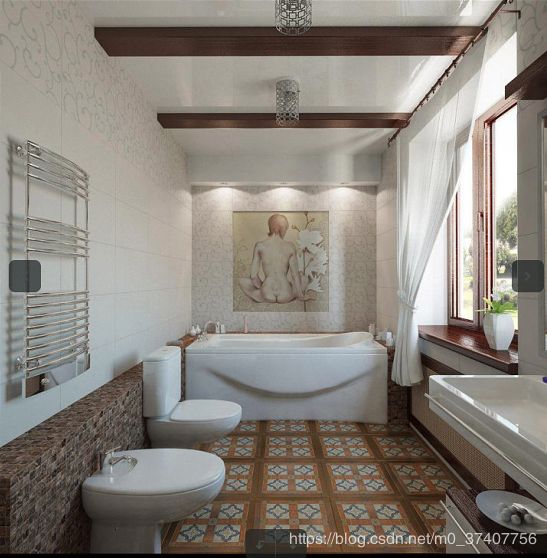
上图最后一张图的原图:标注的太粗糙了~~
代码依赖包好几个,我压缩打包下载网址:
https://download.csdn.net/download/m0_37407756/10764018
好了数据集准备好了,就可以修改代码开始训练了。
我的类别是4类,加上背景则就是五类,所以NUM_OF_CLASSESS = 5 # 类的个数
我自己做的数据比较小,不到100张,迭代1000次,此博客仅入手篇。
当测试时,按照作者的代码,将train改为visualize即可。
后期有需要再补充,如有错误欢迎指出。