scala(二)
文章目录
- 1.类
- class基本用法
- 占位符
- 2.构造器
- 主构造器
- 附属构造器
- 3.继承
- 执行顺序
- 子类重写
- toSting()
- 继承中val和var
- 4.抽象类
- 5.class object
- 6. apply
- class apply1
- object apply 类名()==>object apply
- class apply2
- 总结
- 其他
- 看源码
- 全局变量
1.类
class基本用法
package com.ruozedata.bigdata.scala.scala02
object SimpleClassApp {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val people = new People //实例化一个class对象
people.name = "xingxing"
people.age = 30
println(people.name + ":" + people.age)
people.playBasketball("wrrior")
println(people.drink())
}
}
class People {
var name = ""
var age = 3
def playBasketball(team: String): Unit = {
println(name + " is playing in " + team)
}
def drink() = {
name + " is drinking"
}
占位符
//_ 占位符 前提是明确一定要知道是什么数据类型
var name = _ //会报错
var name:String = _
- 默认占位的值
scala> var name:String=_
name: String = null
scala> var b:Boolean=_
b: Boolean = false
2.构造器
主构造器
- 类名(…)
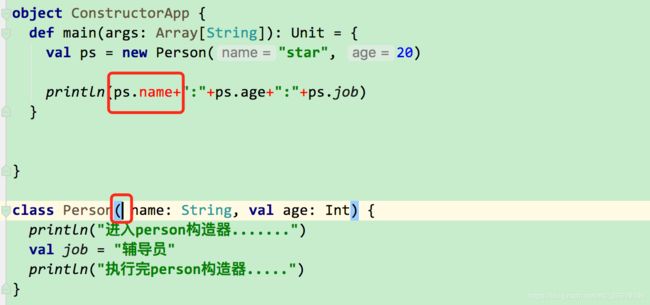
class Person(val name:String, val age:Int)
object ConstructorApp {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val ps = new Person("star", 20)
println(ps.name+":"+ps.age+":"+ps.job)
}
}
class Person(val name: String, val age: Int) {
println("进入person构造器.......")
val job = "辅导员"
println("执行完person构造器.....")
}
- 注意点:
附属构造器
- 1)附属构造器的名称 this
2)每个附属构造器的第一行必须调用主构造器或者其他附属构造器
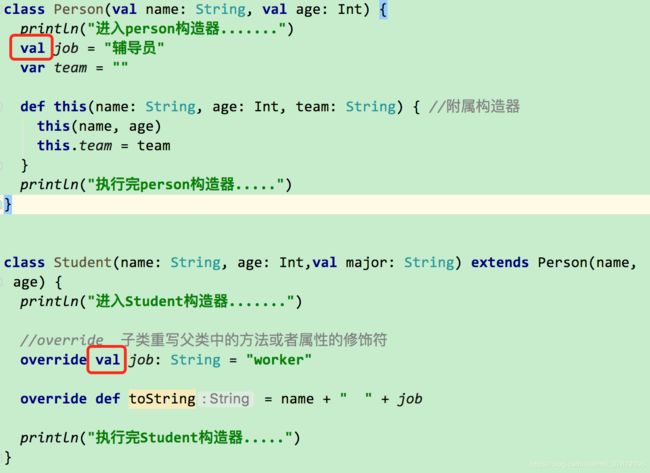
class Person(val name: String, val age: Int) {
println("进入person构造器.......")
val job = "辅导员"
var team = ""
def this(name: String, age: Int, team: String) { //附属构造器
this(name, age)
this.team = team
}
3.继承
执行顺序
package com.ruozedata.bigdata.scala.scala02
object ConstructorApp {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val student = new Student("star", 20, "cs")
println(student.major)
}
}
class Person(val name: String, val age: Int) {
println("进入person构造器.......")
val job = "辅导员"
var team = ""
def this(name: String, age: Int, team: String) { //附属构造器
this(name, age)
this.team = team
}
println("执行完person构造器.....")
}
class Student(name: String, age: Int,val major: String) extends Person(name, age) {
println("进入Student构造器.......")
println("执行完Student构造器.....")
}
- 输出结果
进入person构造器.......
执行完person构造器.....
进入Student构造器.......
执行完Student构造器.....
cs
调用子类的构造方法前,必须先调用父类的构造方法
对于父类没有的字段,要使用var/val修饰,否则访问不到.
子类重写
class Student(name: String, age: Int,val major: String) extends Person(name, age) {
println("进入Student构造器.......")
//override 子类重写父类中的方法或者属性的修饰符
override val job: String = "worker"
println("执行完Student构造器.....")
}
toSting()
- 类中有默认的tostring方法
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val student = new Student("star", 20, "")
print(student)
}
//输出结果--全路径的包名+类名
//com.ruozedata.bigdata.scala.scala02.Student@548a9f61
- 子类中重写toString方法 override修饰
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val student = new Student("star", 20, "")
print(student)
}
class Student(name: String, age: Int,val major: String) extends Person(name, age) {
println("进入Student构造器.......")
//override 子类重写父类中的方法或者属性的修饰符
override val job: String = "worker"
override def toString = name + " " + job
println("执行完Student构造器.....")
}
输出结果:
star worker
继承中val和var
4.抽象类
- 类中只有一个或者多个方法或属性的定义,没有实现
- 抽象类不能直接使用(new)
- 使用时要有完全实现了抽象方法/属性子类才行
- 子类重写父类方法或者属性时一定需要overwrite么?
object AbstractClassApp {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val student1 = new Student2
student1.speak
println(student1.name)
}
}
abstract class Person2{
def speak
val name:String
}
class Student2 extends Person2 {
override def speak: Unit = {
println("speaking....")
}
val name: String = "huhu" //没有override修饰
}
//结果输出正常,没报错
5.class object
- object里面的方法直接通过object.方法名调用,不需要new
- new的一定是class,不是object
val test = new ApplyTest //new的一定是class
println(test)
6. apply
- 一般情况下object的apply方法的作用是完成new class
class apply1
object ApplyApp {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//对于object里的方法,可以直接调用,不需要new
//ApplyTest.static
val test = new ApplyTest //new的一定是class
println(test)
}
}
//class ApplyTest是object ApplyTest的伴生类
//object ApplyTest是class ApplyTest的伴生对象
class ApplyTest{
println("进入class ApplyTest...")
def apply()={
println("Class apply.......")
}
println("执行完class ApplyTest...")
}
/*
输出结果:
进入class ApplyTest...
执行完class ApplyTest...
com.ruozedata.bigdata.scala.scala02.ApplyTest@548a9f61
*/
object apply 类名()==>object apply
- debug时,val test = ApplyTest()这一步会直接进入def apply(), 然后new一个对象出来 .表象没有new,实际object new了出来
package com.ruozedata.bigdata.scala.scala02
object ApplyApp {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val test = ApplyTest() //类名()==>object apply
println(test)
}
}
//class ApplyTest是object ApplyTest的伴生类
//object ApplyTest是class ApplyTest的伴生对象
class ApplyTest{
println("进入class ApplyTest...")
def apply()={
println("Class apply.......")
}
println("执行完class ApplyTest...")
}
object ApplyTest{
println("进入object ApplyTest...")
def static: Unit ={
println("我是一个static方法")
}
def apply() ={
println("Object apply.......")
new ApplyTest
}
println("执行完object ApplyTest...")
}
/*
输出结果:
进入object ApplyTest...
执行完object ApplyTest...
Object apply.......
进入class ApplyTest...
执行完class ApplyTest...
com.ruozedata.bigdata.scala.scala02.ApplyTest@548a9f61
*/
class apply2
package com.ruozedata.bigdata.scala.scala02
object ApplyApp {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val test = new ApplyTest
test() //对象() ==> Class apply
}
}
//class ApplyTest是object ApplyTest的伴生类
//object ApplyTest是class ApplyTest的伴生对象
class ApplyTest{
println("进入class ApplyTest...")
def apply()={
println("Class apply.......")
}
println("执行完class ApplyTest...")
}
object ApplyTest{
println("进入object ApplyTest...")
def static: Unit ={
println("我是一个static方法")
}
def apply() ={
println("Object apply.......")
new ApplyTest
}
println("执行完object ApplyTest...")
}
/*
进入class ApplyTest...
执行完class ApplyTest...
Class apply.......
*/
总结
类名() ==> Object apply
new出来的对象() ==>Class apply
其他
看源码
类的定义及构造:SparkContext
继承:MemoryManager
全局变量
- 放入object中
scala> object Timer {
| var count = 0
| def incr()={
| count+=1
| count
| }
| }
defined object Timer
scala> Timer.incr()
res0: Int = 1
scala> Timer.incr()
res1: Int = 2
scala> Timer.incr()
res2: Int = 3
scala> Timer.incr()
res3: Int = 4