Spring注解事件源码分析
Spring注解事件源码分析
@EventListener 解析处理器 EventListenerMethodProcessor
@EventListener事件监听器ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter
事件发布器ApplicationEventMulticaster
事件对象
事件源
@EventListener 通知业务逻辑方法限制
注解事件处理阶段
@EventListener
AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
先定位到代码:
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
//① 容器中创建bean
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Boolean>)
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
//② bean已近完全处理完了
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
//主角
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}
概要:
-
容器中创建bean
- 主要是创建bean
- 工厂方法@Bean FactoryMethod
- 接口生成代理 FactoryBean
- 反射 newInstance
- xxxx
- 主要是创建bean
-
bean已近完全处理完后置处理
-
主要执行bean的方法
-
(类似于FactoryMethod)只是执行方法不在是创建bean,而是执行业务逻辑
-
bean需要是SmartInitializingSingleton类型
-
@Component public class MyInitializingBean implements SmartInitializingSingleton { @Override public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() { System.out.println(this.getClass().getName()+"#afterSingletonsInstantiated invoked"); } }
-
-
SmartInitializingSingleton声明
SmartInitializingSingleton#afterSingletonsInstantiated的整个类的声明
/**
* Callback interface triggered at the end of the singleton pre-instantiation phase
* during {@link BeanFactory} bootstrap. This interface can be implemented by
* singleton beans in order to perform some initialization after the regular
* singleton instantiation algorithm, avoiding side effects with accidental early
* initialization (e.g. from {@link ListableBeanFactory#getBeansOfType} calls).
* In that sense, it is an alternative to {@link InitializingBean} which gets
* triggered right at the end of a bean's local construction phase.
*
* This callback variant is somewhat similar to
* {@link org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent} but doesn't
* require an implementation of {@link org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener},
* with no need to filter context references across a context hierarchy etc.
* It also implies a more minimal dependency on just the {@code beans} package
* and is being honored by standalone {@link ListableBeanFactory} implementations,
* not just in an {@link org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext} environment.
*
*
NOTE: If you intend to start/manage asynchronous tasks, preferably
* implement {@link org.springframework.context.Lifecycle} instead which offers
* a richer model for runtime management and allows for phased startup/shutdown.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 4.1
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons()
*/
public interface SmartInitializingSingleton {
/**
* Invoked right at the end of the singleton pre-instantiation phase,
* with a guarantee that all regular singleton beans have been created
* already. {@link ListableBeanFactory#getBeansOfType} calls within
* this method won't trigger accidental side effects during bootstrap.
* NOTE: This callback won't be triggered for singleton beans
* lazily initialized on demand after {@link BeanFactory} bootstrap,
* and not for any other bean scope either. Carefully use it for beans
* with the intended bootstrap semantics only.
*/
void afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
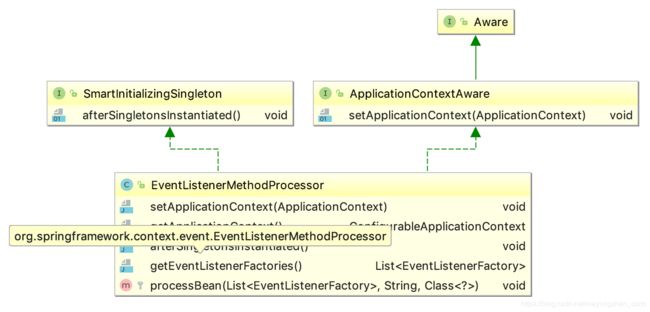
EventListenerMethodProcessor
事件方法处理器就是前面讲过的SmartInitializingSingleton,看它是如何初始化会后执行bean方法的
public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {
List<EventListenerFactory> factories = getEventListenerFactories();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = getApplicationContext();
String[] beanNames = context.getBeanNamesForType(Object.class);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
//省略部分代码
try {
processBean(factories, beanName, type);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Failed to process @EventListener " +
"annotation on bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
}
两个逻辑:
-
从BeanFactory中获取EventListenerFactory的bean
-
默认情况下的两个实现
-
DefaultEventListenerFactory --- springContext自己注入的 TransactionalEventListenerFactory -- 使用配置进去的
-
-
对所有的bean进行处理
注册事件到context
EventListenerMethodProcessor#processBean
protected void processBean(
final List<EventListenerFactory> factories, final String beanName, final Class<?> targetType) {
if (!this.nonAnnotatedClasses.contains(targetType)) {
Map<Method, EventListener> annotatedMethods = null;
try {
annotatedMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(targetType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<EventListener>) method ->
AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, EventListener.class));
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable type in a method signature, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve methods for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(annotatedMethods)) {
this.nonAnnotatedClasses.add(targetType);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No @EventListener annotations found on bean class: " + targetType.getName());
}
}
else {
// Non-empty set of methods
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = getApplicationContext();
for (Method method : annotatedMethods.keySet()) {
for (EventListenerFactory factory : factories) {
if (factory.supportsMethod(method)) {
Method methodToUse = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, context.getType(beanName));
//①创建事件监听器
ApplicationListener<?> applicationListener =
factory.createApplicationListener(beanName, targetType, methodToUse);
if (applicationListener instanceof ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) {
((ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) applicationListener).init(context, this.evaluator);
}
//②注册事件到Context中
context.addApplicationListener(applicationListener);
break;
}
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(annotatedMethods.size() + " @EventListener methods processed on bean '" +
beanName + "': " + annotatedMethods);
}
}
}
}
两个逻辑:
-
查找当前bean标注了@EventListener的方法
-
创建事件监听器
-
标有@EventListener方法用EventListenerFactory工厂创建相应的ApplicationListener
-
默认EventListenerFactory–>DefaultEventListenerFactory创建的ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter
-
public ApplicationListener<?> createApplicationListener(String beanName, Class<?> type, Method method) { return new ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter(beanName, type, method); }
-
-
注册事件到ApplicationContext中
-
context.addApplicationListener(applicationListener);
-
事件方法约束
在通过DefaultEventListenerFactory将@EventListener标注的方法 创建出事件对象的时候需要注解
@EventListener标注的方法的约束
public ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter(String beanName, Class<?> targetClass, Method method) {
this.beanName = beanName;
this.method = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
this.targetMethod = (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass) ?
AopUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass) : this.method);
this.methodKey = new AnnotatedElementKey(this.targetMethod, targetClass);
EventListener ann = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(this.targetMethod, EventListener.class);
this.declaredEventTypes = resolveDeclaredEventTypes(method, ann);
this.condition = (ann != null ? ann.condition() : null);
this.order = resolveOrder(method);
}
限制:
private List<ResolvableType> resolveDeclaredEventTypes(Method method, @Nullable EventListener ann) {
int count = method.getParameterCount();
if (count > 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Maximum one parameter is allowed for event listener method: " + method);
}
if (ann != null) {
Class<?>[] classes = ann.classes();
if (classes.length > 0) {
List<ResolvableType> types = new ArrayList<>(classes.length);
for (Class<?> eventType : classes) {
types.add(ResolvableType.forClass(eventType));
}
return types;
}
}
if (count == 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Event parameter is mandatory for event listener method: " + method);
}
return Collections.singletonList(ResolvableType.forMethodParameter(method, 0));
}
总结:
方法的参数不能多于一个
注解上有classes 就是用注解上的事件对象(可以为多个)
注解上没有classes 那么必须要有且只有一个方法参数事件对象
执行注册
ApplicationContext#addApplicationListener
public void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener) {
Assert.notNull(listener, "ApplicationListener must not be null");
if (this.applicationEventMulticaster != null) {
this.applicationEventMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
else {
this.applicationListeners.add(listener);
}
}
这个applicationEventMulticaster的构建
AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()#initApplicationEventMulticaster
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) {
this.applicationEventMulticaster =
beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
else {
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Unable to locate ApplicationEventMulticaster with name '" +
APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME +
"': using default [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
}
如果bean中没有名字为applicationEventMulticaster的使用默认的SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster
事件广播器
public interface ApplicationEventMulticaster {
void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener);
void addApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName);
void removeApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener);
void removeApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName);
void removeAllListeners();
void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event);
void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType);
}
跟观察者类似就是对事件的增、删、广播操作!!!

最终listener是注册到了SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster中的成员
public void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener) {
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
// Explicitly remove target for a proxy, if registered already,
// in order to avoid double invocations of the same listener.
Object singletonTarget = AopProxyUtils.getSingletonTarget(listener);
if (singletonTarget instanceof ApplicationListener) {
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.remove(singletonTarget);
}
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.add(listener);
this.retrieverCache.clear();
}
}
注册的监听器的最终存储位置是:
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster的父类AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster的内部类的成员
abstract class AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster{
private final ListenerRetriever defaultRetriever = new ListenerRetriever(false);
final Map<ListenerCacheKey, ListenerRetriever> retrieverCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);
}
默认所有的Listenner全部都装入到这个类的默认的成员defaultRetriever.applicationListeners
private class ListenerRetriever {
public final Set<ApplicationListener<?>> applicationListeners;
public final Set<String> applicationListenerBeans;
}
retrieverCache每次装入都会clear掉 ,其实后边会根据事件类型+事件源 作为key重新对defaultRetriever进行重新分组
事件广播
AbstractApplicationContext可以广播事件,
根据上面的分析它肯定会调用ApplicationEventListener#multicastEvent
protected void publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Publishing event in " + getDisplayName() + ": " + event);
}
// Decorate event as an ApplicationEvent if necessary
ApplicationEvent applicationEvent;
if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) {
applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event;
}
else {
applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<>(this, event);
if (eventType == null) {
eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent) applicationEvent).getResolvableType();
}
}
// Multicast right now if possible - or lazily once the multicaster is initialized
if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) {
this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);
}
else {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);
}
// Publish event via parent context as well...
if (this.parent != null) {
if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);
}
else {
this.parent.publishEvent(event);
}
}
}
- 将事件对象包装成ApplicationEvent
- 获取事件对象和事件类型
- 广播
事件源
这里是AbstractApplicationContext自己
通常都是调用者自己哈
事件对象
前面没有提过事件对象有什么要求
Object不是ApplicationEvent类型的包装成了PayloadApplicationEvent 实际它也是ApplicationEvent
最终都会变成是ApplicationEvent
广播
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
for (final ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
筛选通知Listener
AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster
protected Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> getApplicationListeners(
ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
Object source = event.getSource();
Class<?> sourceType = (source != null ? source.getClass() : null);
ListenerCacheKey cacheKey = new ListenerCacheKey(eventType, sourceType);
// Quick check for existing entry on ConcurrentHashMap...
ListenerRetriever retriever = this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey);
if (retriever != null) {
return retriever.getApplicationListeners();
}
if (this.beanClassLoader == null ||
(ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(event.getClass(), this.beanClassLoader) &&
(sourceType == null || ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(sourceType, this.beanClassLoader)))) {
// Fully synchronized building and caching of a ListenerRetriever
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
retriever = this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey);
if (retriever != null) {
return retriever.getApplicationListeners();
}
retriever = new ListenerRetriever(true);
//通过eventType,sourceType 去匹配了
Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners =
retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, retriever);
this.retrieverCache.put(cacheKey, retriever);
return listeners;
}
}
else {
// No ListenerRetriever caching -> no synchronization necessary
return retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, null);
}
}
- 从retrieverCache查询根据(source+eventType)查询事件
- 没有的话则从defaultRetriever中获取,并放入到retrieverCache中
还记得这个retrieverCache是什么吗
public abstract class AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster
implements ApplicationEventMulticaster, BeanClassLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware {
private final ListenerRetriever defaultRetriever = new ListenerRetriever(false);
final Map<ListenerCacheKey, ListenerRetriever> retrieverCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);
集合一下前面提过的 defaultRetriever.applicationListeners是所有的事件,每次添加事件到这里边都会retrieverCache#clear
添加完了之后发布事件publishEvent的时候,会重新根据事件源+事件类型重新分组 defaultRetriever.applicationListeners
private Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> retrieveApplicationListeners(
ResolvableType eventType, @Nullable Class<?> sourceType, @Nullable ListenerRetriever retriever) {
LinkedList<ApplicationListener<?>> allListeners = new LinkedList<>();
Set<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners;
Set<String> listenerBeans;
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
listeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners);
listenerBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans);
}
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : listeners) {
if (supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)) {
if (retriever != null) {
retriever.applicationListeners.add(listener);
}
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
if (!listenerBeans.isEmpty()) {
BeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeans) {
try {
Class<?> listenerType = beanFactory.getType(listenerBeanName);
if (listenerType == null || supportsEvent(listenerType, eventType)) {
ApplicationListener<?> listener =
beanFactory.getBean(listenerBeanName, ApplicationListener.class);
if (!allListeners.contains(listener) && supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)) {
if (retriever != null) {
retriever.applicationListenerBeans.add(listenerBeanName);
}
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Singleton listener instance (without backing bean definition) disappeared -
// probably in the middle of the destruction phase
}
}
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(allListeners);
return allListeners;
}
总结:
@EventListener标注的方法被DefaultEventListenerFactory包装成ApplicationListenerMethodApdapter
@EventListener中的classes就是事件对象
ApplicationListenerMethodApdapter注册到ApplicationContext中。
等待是事件源发布通知
通知后执行的逻辑就是标注@EventListener的方法的逻辑
同一进程
可以做代码解耦
可以做异步和错误处理
需要自己创建一个名字为applicationEventMulticaster
设置两个成员
private Executor taskExecutor; private ErrorHandler errorHandler;