单源加权图最短路径问题(权值非负)-Dijkstra算法
解决单源最短路径的一个常用算法叫做:Dijkstra算法,这是一个非常经典的贪心算法例子。
注意:这个算法只对权值非负情况有效。
在每个阶段,Dijkstra算法选择一个顶点v,它在所有unknown顶点中具有最小的distance,同时算法将起点s到v的最短路径声明为known。
这个算法的本质就是 给定起点,然后假设你有一个点集(known点集),对这个点集中的点,我们已经求出起点到其的最短距离。然后慢慢扩张这个集合。直到某一时刻它包括目标点。
具体概念详细介绍见书吧,下面结合一个例子,阐述一下该算法遍历顶点的过程。
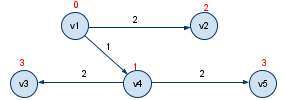
假设开始顶点s为v1。
则,第一个选择的顶点是v1,路径长是0,该顶点标记为known,
1: known(v1) unknown(v2,v3,v4,v5,v6,v7); 这时由known点集扩充,v4 为下一个最短路径顶点,路径长为1,标记v4为known
2: known(v1,v4) unknown(v2,v3,v5,v6,v7); 这时由known点集扩充,v2 为下一个最短路径顶点,路径长为2,标记v2为known
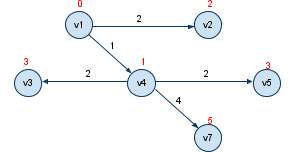
3: known(v1,v4,v2) unknown(v3,v5,v6,v7); 这时由known点集扩充,v3,v5 为下一个最短路径顶点,路径长为3, 标记v3,v5为known
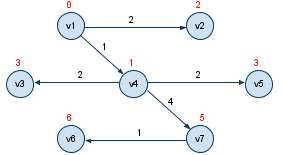
4: known(v1,v4,v2,v3,v5) unknown(v6,v7); 这时由known点集扩充,v7 为下一个最短路径顶点,路径长为5, 标记v7为known
5: known(v1,v4,v2,v3,v5,v7) unknown(v6); 这时由known点集扩充,v6 为下一个最短路径顶点,路径长为6, 标记v6为known
伪代码:
struct VertexNode
{
char data[2];
int distance;
bool known;
VertexNode* path;
adjVertexNode* list;
};
void
Dijkstra(Graph& g, VertexNode& s)
{
for each vertex v in g
{
{
v.distance = INFINITY;
v.known = false;
v.path = NULL;
}
s.distance = 0;
for (int i=0; i
{
vertex v = smallest unknown distance vertex;
if (v==NULL)
break;
else
v.known = true;
for each w adjacent to v
{
if (!w.known)
{
if (v.distance + weight(v,w) < w.distance)
{
w.distance = v.distance + weight(v,w);
w.path = v;
}
}
}
}
}
void PrintPath(
Graph& g, VertexNode* target)
{// print the shortest path from s to target
if(target.path!=NULL)
{
PrintPath(g, target.path);
cout << " " ;
}
cout << target ;
}
代码实现:
#include
using namespace std;
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20
#define INFINITY 2147483647
struct adjVertexNode
{
int adjVertexPosition;
int weight;
adjVertexNode * next;
};
struct VertexNode
{
char data [ 2 ];
int distance;
bool known;
VertexNode * path;
adjVertexNode * list;
};
struct Graph
{
VertexNode VertexNode [ MAX_VERTEX_NUM ];
int vertexNum;
int edgeNum;
};
void CreateGraph ( Graph & g)
{
int i , j , edgeStart , edgeEnd , edgeWeight;
adjVertexNode * adjNode;
cout << "Please input vertex and edge num (vnum enum):" << endl;
cin >> g . vertexNum >> g . edgeNum;
cout << "Please input vertex information (v1) /n note: every vertex info end with Enter" << endl;
for ( i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
cin >> g . VertexNode [ i ]. data; // vertex data info.
g . VertexNode [ i ]. list = NULL;
}
cout << "input edge information(start end weight):" << endl;
for ( j = 0; j < g . edgeNum; j ++)
{
cin >> edgeStart >> edgeEnd >> edgeWeight;
adjNode = new adjVertexNode;
adjNode -> weight = edgeWeight;
adjNode -> adjVertexPosition = edgeEnd - 1; // because array begin from 0, so it is j-1
// 将邻接点信息插入到顶点Vi的边表头部,注意是头部!!!不是尾部。
adjNode -> next = g . VertexNode [ edgeStart - 1 ]. list;
g . VertexNode [ edgeStart - 1 ]. list = adjNode;
}
}
void PrintAdjList( const Graph & g)
{
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
cout << g . VertexNode [ i ]. data << "->";
adjVertexNode * head = g . VertexNode [ i ]. list;
if ( head == NULL)
cout << "NULL";
while ( head != NULL)
{
cout << head -> adjVertexPosition + 1 << " ";
head = head -> next;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
void DeleteGraph( Graph & g)
{
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
adjVertexNode * tmp = NULL;
while( g . VertexNode [ i ]. list != NULL)
{
tmp = g . VertexNode [ i ]. list;
g . VertexNode [ i ]. list = g . VertexNode [ i ]. list -> next;
delete tmp;
tmp = NULL;
}
}
}
VertexNode * FindSmallestVertex( Graph & g)
{
int smallest = INFINITY;
VertexNode * sp = NULL;
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
if ( ! g . VertexNode [ i ]. known && g . VertexNode [ i ]. distance < smallest)
{
smallest = g . VertexNode [ i ]. distance;
sp = &( g . VertexNode [ i ]);
}
}
return sp;
}
void Dijkstra( Graph & g , VertexNode & s)
{
int i;
for ( i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
g . VertexNode [ i ]. known = false;
g . VertexNode [ i ]. distance = INFINITY;
g . VertexNode [ i ]. path = NULL;
}
s . distance = 0;
for( i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
VertexNode * v = FindSmallestVertex( g);
if( v == NULL)
break;
v -> known = true;
adjVertexNode * head = v -> list;
while ( head != NULL)
{
VertexNode * w = & g . VertexNode [ head -> adjVertexPosition ];
if( !( w -> known) )
{
if( v -> distance + head -> weight < w -> distance)
{
w -> distance = v -> distance + head -> weight;
w -> path = v;
}
}
head = head -> next;
}
}
void PrintPath( Graph & g , VertexNode * source , VertexNode * target)
{
if ( source != target && target -> path == NULL)
{
cout << "There is no shortest path from " << source -> data << " to " << target -> data << endl;
}
else
{
if ( target -> path != NULL)
{
PrintPath( g , source , target -> path);
cout << " ";
}
cout << target -> data ;
}
}
int main( int argc , const char ** argv)
{
Graph g;
CreateGraph( g);
PrintAdjList( g);
VertexNode & start = g . VertexNode [ 0 ];
VertexNode & end = g . VertexNode [ 6 ];
Dijkstra( g , start);
cout << "print the shortest path from v1 to v7" << endl;
PrintPath( g , & start , & end);
using namespace std;
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20
#define INFINITY 2147483647
struct adjVertexNode
{
int adjVertexPosition;
int weight;
adjVertexNode * next;
};
struct VertexNode
{
char data [ 2 ];
int distance;
bool known;
VertexNode * path;
adjVertexNode * list;
};
struct Graph
{
VertexNode VertexNode [ MAX_VERTEX_NUM ];
int vertexNum;
int edgeNum;
};
void CreateGraph ( Graph & g)
{
int i , j , edgeStart , edgeEnd , edgeWeight;
adjVertexNode * adjNode;
cout << "Please input vertex and edge num (vnum enum):" << endl;
cin >> g . vertexNum >> g . edgeNum;
cout << "Please input vertex information (v1) /n note: every vertex info end with Enter" << endl;
for ( i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
cin >> g . VertexNode [ i ]. data; // vertex data info.
g . VertexNode [ i ]. list = NULL;
}
cout << "input edge information(start end weight):" << endl;
for ( j = 0; j < g . edgeNum; j ++)
{
cin >> edgeStart >> edgeEnd >> edgeWeight;
adjNode = new adjVertexNode;
adjNode -> weight = edgeWeight;
adjNode -> adjVertexPosition = edgeEnd - 1; // because array begin from 0, so it is j-1
// 将邻接点信息插入到顶点Vi的边表头部,注意是头部!!!不是尾部。
adjNode -> next = g . VertexNode [ edgeStart - 1 ]. list;
g . VertexNode [ edgeStart - 1 ]. list = adjNode;
}
}
void PrintAdjList( const Graph & g)
{
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
cout << g . VertexNode [ i ]. data << "->";
adjVertexNode * head = g . VertexNode [ i ]. list;
if ( head == NULL)
cout << "NULL";
while ( head != NULL)
{
cout << head -> adjVertexPosition + 1 << " ";
head = head -> next;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
void DeleteGraph( Graph & g)
{
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
adjVertexNode * tmp = NULL;
while( g . VertexNode [ i ]. list != NULL)
{
tmp = g . VertexNode [ i ]. list;
g . VertexNode [ i ]. list = g . VertexNode [ i ]. list -> next;
delete tmp;
tmp = NULL;
}
}
}
VertexNode * FindSmallestVertex( Graph & g)
{
int smallest = INFINITY;
VertexNode * sp = NULL;
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
if ( ! g . VertexNode [ i ]. known && g . VertexNode [ i ]. distance < smallest)
{
smallest = g . VertexNode [ i ]. distance;
sp = &( g . VertexNode [ i ]);
}
}
return sp;
}
void Dijkstra( Graph & g , VertexNode & s)
{
int i;
for ( i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
g . VertexNode [ i ]. known = false;
g . VertexNode [ i ]. distance = INFINITY;
g . VertexNode [ i ]. path = NULL;
}
s . distance = 0;
for( i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
VertexNode * v = FindSmallestVertex( g);
if( v == NULL)
break;
v -> known = true;
adjVertexNode * head = v -> list;
while ( head != NULL)
{
VertexNode * w = & g . VertexNode [ head -> adjVertexPosition ];
if( !( w -> known) )
{
if( v -> distance + head -> weight < w -> distance)
{
w -> distance = v -> distance + head -> weight;
w -> path = v;
}
}
head = head -> next;
}
}
void PrintPath( Graph & g , VertexNode * source , VertexNode * target)
{
if ( source != target && target -> path == NULL)
{
cout << "There is no shortest path from " << source -> data << " to " << target -> data << endl;
}
else
{
if ( target -> path != NULL)
{
PrintPath( g , source , target -> path);
cout << " ";
}
cout << target -> data ;
}
}
int main( int argc , const char ** argv)
{
Graph g;
CreateGraph( g);
PrintAdjList( g);
VertexNode & start = g . VertexNode [ 0 ];
VertexNode & end = g . VertexNode [ 6 ];
Dijkstra( g , start);
cout << "print the shortest path from v1 to v7" << endl;
PrintPath( g , & start , & end);
cout << endl;
DeleteGraph( g);
return 0;
}
DeleteGraph( g);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
对于这个算法,vertex v = smallest unknown distance vertex;如果用最简单的扫描数组方式实现,则该部操作时间复杂度为O(|V|), 所以该算法将花费O(|V|2)查找最小距离顶点,同时,注意到最内层循环,最终对每条边会执行一次,所以该算法时间复杂度为O(|V|2+|E|)
对于无向图,可以认为是双向的有向图,所以只要更改边的输入信息即可。
仍以上例看,有向图输入的边信息为12条边:
1 2 2
3 1 4
1 4 1
2 4 3
2 5 10
4 3 2
4 5 2
3 6 5
4 6 8
4 7 4
5 7 6
7 6 1
3 1 4
1 4 1
2 4 3
2 5 10
4 3 2
4 5 2
3 6 5
4 6 8
4 7 4
5 7 6
7 6 1
如果是无相图,即双向的有向图,则应该输入24条边信息,12组对称的边信息即可:
1 2 2
2 1 2
3 1 4
3 1 4
1 3 4
1 4 1
1 4 1
4 1 1
2 4 3
2 4 3
4 2 3
2 5 10
2 5 10
5 2 10
4 3 2
4 3 2
3 4 2
4 5 2
4 5 2
5 4 2
3 6 5
3 6 5
6 3 5
4 6 8
4 6 8
6 4 8
4 7 4
4 7 4
7 4 4
5 7 6
5 7 6
7 5 6
7 6 1
7 6 1
6 7 1
运行结果:
即:Dijkstra算法既可以求无向图也可以求有向图最短路径。