数据挖掘学习日记7·k-means算法JAVA代码实现
算法回顾
聚类概念
聚类是一种无监督学习方法,使类内元素距离尽量相近,类间元素距离尽量远。
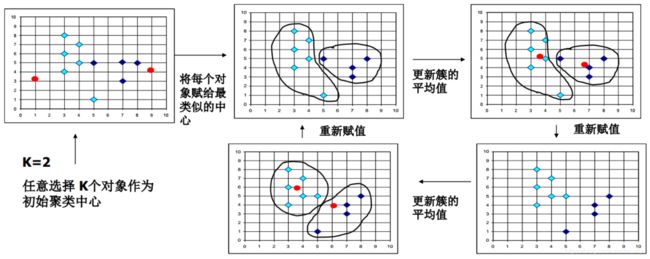
k-means算法流程
- 在数据集D中随机地选择k个对象,每个对象代表一个簇的初始均值或中心。其余每个对象根据与簇中心的欧氏距离,分配到最近的簇中。
- 迭代地改编簇内变差:对每个簇,根据上次迭代分配到的簇对象,重新计算均值(将对象的x值和y值分别取平均得到新的簇中心)。
- 将更新后的均值作为新的簇中心,重新分配所有对象。
- 迭代继续,直到分配稳定——本轮形成的簇与前一轮形成的簇相同(所有对象所属的类标签或所有簇中心不再改变)。
算法实现
基本思路与设计
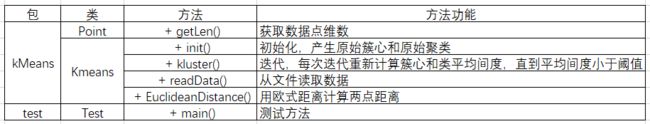
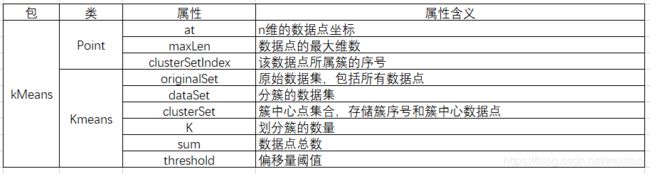
编写三个类来实现算法:使用Point类来记录数据点,Kmeans类执行算法,Test类进行测试。
类图及类和属性含义如下所示(省略属性的getter和setter方法):
Point类
public class Point {
/*n维的坐标*/
private ArrayList at = new ArrayList<>();
/*所在簇编号*/
private int clusterSetIndex;
/*最大维数*/
public static int maxLen = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public Point() {
}
/**
*
*@desc:返回数据点的维数
*@return:int
*@trhows
*/
public int getLen() {
return at.size();
}
public ArrayList getAt() {
return at;
}
public void setAt(ArrayList at) {
this.at = at;
}
public int getClusterSetIndex() {
return clusterSetIndex;
}
public void setClusterSetIndex(int clusterSetIndex) {
this.clusterSetIndex = clusterSetIndex;
}
} KMeans类
原始簇中心的选择
本实现代码中,采用随机产生的数据点编号作为原始簇中心,并在初始化后做第一次调整。
迭代终止条件
最小簇中心偏移量小于等于阈值时,迭代终止。
偏移量由原簇中心和对应新簇中心的欧氏距离得出。
public class KMeans {
//簇包含数据点point-->数组
//数据集包含若干簇cluster-->数组的集合
/*原始数据集*/
private ArrayList originalSet = new ArrayList<>();
/*数据集*/
private ArrayList> dataSet = new ArrayList<>();
/*簇中心<原始数据集序号,数据点>*/
private Map clusterSet = new HashMap<>();
/*k*/
private static final int K = 2;
/*数据总量*/
private static int sum = 0;
private double threshold = 0.01;
public KMeans() {
}
public double getThreshold() {
return threshold;
}
public void setThreshold(double threshold) {
this.threshold = threshold;
}
public ArrayList> getDataSet() {
return dataSet;
}
/**
*
*@desc:初始化,随机地选择簇中心,并将其余点归入最近的簇
*@return:void
*@trhows
*/
public void init() {
Random rand = new Random();
Set tSet = new HashSet<>();
//随机取k个数据点作为簇中心,记入簇中心集合中
for(int i = 0;i clusterList = new ArrayList<>();
dataSet.add(clusterList);
}
//计算剩余点与簇中心的距离,将数据点归入最邻近的簇
for(int i=0;i cluster : dataSet) {
//获取簇编号
int index = dataSet.indexOf(cluster);
Point centerPoint = new Point();
centerPoint.setClusterSetIndex(dataSet.indexOf(cluster));
/*n维计数器*/
double counter[] = new double[cluster.get(0).getLen()];
for(Point p : cluster) {
for(int i=0;ithreshold;times++) {
//清空工作数据集并初始化
dataSet.clear();
for(int i = 0;i clusterList = new ArrayList<>();
dataSet.add(clusterList);
}
bias = Double.MAX_VALUE;
//1.计算簇中心外的点与簇中心的距离,将数据点归入距离最近的簇
for(int i=0;i cluster : dataSet) {
//获取簇编号
int index = dataSet.indexOf(cluster);
Point centerPoint = new Point();
centerPoint.setClusterSetIndex(dataSet.indexOf(cluster));
/*n维计数器*/
double counter[] = new double[Point.maxLen];
for(Point p : cluster) {
for(int i=0;iPoint.maxLen)
Point.maxLen = tempStrs.length;
Point p = new Point();
p.setClusterSetIndex(0);
for(String s : tempStrs) {
p.getAt().add(Double.valueOf(s));
}
originalSet.add(p);
sum++;
}
}
/**
*
*@desc:计算两个数据点的欧氏距离
*@param a
*@param b
*@return:double
*@trhows
*/
public double EuclideanDistance(Point a,Point b) {
double sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i Test类
在Test类的main方法中,调用KMeans类对象执行整个算法流程:
- 从文件中读取数据集;
- 算法初始化,生成原始簇和簇中心点;
- 开始迭代,不断更新簇和簇中心点,直到聚类各簇区域稳定;
- 算法终止,输出聚类结果
public class Test {
/**
*@desc:一句话描述
*@param args
*@return:void
* @throws IOException
*@trhows
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
KMeans kMeans = new KMeans();
kMeans.readData("\\k-means\\in.txt");
kMeans.init();
kMeans.kluster();
for(ArrayList cluster: kMeans.getDataSet()) {
System.out.println("第"+(kMeans.getDataSet().indexOf(cluster)+1)+"个簇"+"共包含"+cluster.size()+"个结点");
for(Point p :cluster) {
System.out.println("结点"+(cluster.indexOf(p)+1)+":"
+p.getAt().toString());
}
}
}
}
数据集、参数与测试结果
数据集
使用了网上找到的一组纯数值型效性数据集作为测试集。数据集如下:
1 1
2 1
1 2
2 2
3 3
8 8
8 9
9 8
9 9>> 数据来源
参数
k = 4
threshold = 0.01
测试结果
第1个簇共包含2个结点
结点1:[8.0, 9.0]
结点2:[9.0, 9.0]
第2个簇共包含1个结点
结点1:[3.0, 3.0]
第3个簇共包含2个结点
结点1:[8.0, 8.0]
结点2:[9.0, 8.0]
第4个簇共包含4个结点
结点1:[1.0, 1.0]
结点2:[2.0, 1.0]
结点3:[1.0, 2.0]
结点4:[2.0, 2.0]其中,迭代过程如下:
原始簇中心编号
rand:6
rand:1
rand:5
rand:4
原始簇中心
[8.0, 9.0]
[2.0, 1.0]
[8.0, 8.0]
[3.0, 3.0]
点[1.0, 1.0]与点[8.0, 9.0]的距离:10.63014581273465
点[1.0, 1.0]与点[2.0, 1.0]的距离:1.0
点[1.0, 1.0]与点[8.0, 8.0]的距离:9.899494936611665
点[1.0, 1.0]与点[3.0, 3.0]的距离:2.8284271247461903
结点0属于簇1
点[2.0, 1.0]与点[8.0, 9.0]的距离:10.0
点[2.0, 1.0]与点[2.0, 1.0]的距离:0.0
点[2.0, 1.0]与点[8.0, 8.0]的距离:9.219544457292887
点[2.0, 1.0]与点[3.0, 3.0]的距离:2.23606797749979
结点1属于簇1
点[1.0, 2.0]与点[8.0, 9.0]的距离:9.899494936611665
点[1.0, 2.0]与点[2.0, 1.0]的距离:1.4142135623730951
点[1.0, 2.0]与点[8.0, 8.0]的距离:9.219544457292887
点[1.0, 2.0]与点[3.0, 3.0]的距离:2.23606797749979
结点2属于簇1
点[2.0, 2.0]与点[8.0, 9.0]的距离:9.219544457292887
点[2.0, 2.0]与点[2.0, 1.0]的距离:1.0
点[2.0, 2.0]与点[8.0, 8.0]的距离:8.48528137423857
点[2.0, 2.0]与点[3.0, 3.0]的距离:1.4142135623730951
结点3属于簇1
点[3.0, 3.0]与点[8.0, 9.0]的距离:7.810249675906654
点[3.0, 3.0]与点[2.0, 1.0]的距离:2.23606797749979
点[3.0, 3.0]与点[8.0, 8.0]的距离:7.0710678118654755
点[3.0, 3.0]与点[3.0, 3.0]的距离:0.0
结点4属于簇3
点[8.0, 8.0]与点[8.0, 9.0]的距离:1.0
点[8.0, 8.0]与点[2.0, 1.0]的距离:9.219544457292887
点[8.0, 8.0]与点[8.0, 8.0]的距离:0.0
点[8.0, 8.0]与点[3.0, 3.0]的距离:7.0710678118654755
结点5属于簇2
点[8.0, 9.0]与点[8.0, 9.0]的距离:0.0
点[8.0, 9.0]与点[2.0, 1.0]的距离:10.0
点[8.0, 9.0]与点[8.0, 8.0]的距离:1.0
点[8.0, 9.0]与点[3.0, 3.0]的距离:7.810249675906654
结点6属于簇0
点[9.0, 8.0]与点[8.0, 9.0]的距离:1.4142135623730951
点[9.0, 8.0]与点[2.0, 1.0]的距离:9.899494936611665
点[9.0, 8.0]与点[8.0, 8.0]的距离:1.0
点[9.0, 8.0]与点[3.0, 3.0]的距离:7.810249675906654
结点7属于簇2
点[9.0, 9.0]与点[8.0, 9.0]的距离:1.0
点[9.0, 9.0]与点[2.0, 1.0]的距离:10.63014581273465
点[9.0, 9.0]与点[8.0, 8.0]的距离:1.4142135623730951
点[9.0, 9.0]与点[3.0, 3.0]的距离:8.48528137423857
结点8属于簇0
初始簇中心
[8.5, 9.0]
[3.0, 3.0]
[8.5, 8.0]
[1.5, 1.5]
---------------------------------------------------------
第1次迭代
原始簇中心
[8.5, 9.0]
[3.0, 3.0]
[8.5, 8.0]
[1.5, 1.5]
点[1.0, 1.0]与点[8.5, 9.0]的距离:10.965856099730654
点[1.0, 1.0]与点[3.0, 3.0]的距离:2.8284271247461903
点[1.0, 1.0]与点[8.5, 8.0]的距离:10.259142264341596
点[1.0, 1.0]与点[1.5, 1.5]的距离:0.7071067811865476
结点0属于簇3
点[2.0, 1.0]与点[8.5, 9.0]的距离:10.307764064044152
点[2.0, 1.0]与点[3.0, 3.0]的距离:2.23606797749979
点[2.0, 1.0]与点[8.5, 8.0]的距离:9.5524865872714
点[2.0, 1.0]与点[1.5, 1.5]的距离:0.7071067811865476
结点1属于簇3
点[1.0, 2.0]与点[8.5, 9.0]的距离:10.259142264341596
点[1.0, 2.0]与点[3.0, 3.0]的距离:2.23606797749979
点[1.0, 2.0]与点[8.5, 8.0]的距离:9.604686356149273
点[1.0, 2.0]与点[1.5, 1.5]的距离:0.7071067811865476
结点2属于簇3
点[2.0, 2.0]与点[8.5, 9.0]的距离:9.5524865872714
点[2.0, 2.0]与点[3.0, 3.0]的距离:1.4142135623730951
点[2.0, 2.0]与点[8.5, 8.0]的距离:8.845903006477066
点[2.0, 2.0]与点[1.5, 1.5]的距离:0.7071067811865476
结点3属于簇3
点[3.0, 3.0]与点[8.5, 9.0]的距离:8.139410298049853
点[3.0, 3.0]与点[3.0, 3.0]的距离:0.0
点[3.0, 3.0]与点[8.5, 8.0]的距离:7.433034373659253
点[3.0, 3.0]与点[1.5, 1.5]的距离:2.1213203435596424
结点4属于簇1
点[8.0, 8.0]与点[8.5, 9.0]的距离:1.118033988749895
点[8.0, 8.0]与点[3.0, 3.0]的距离:7.0710678118654755
点[8.0, 8.0]与点[8.5, 8.0]的距离:0.5
点[8.0, 8.0]与点[1.5, 1.5]的距离:9.192388155425117
结点5属于簇2
点[8.0, 9.0]与点[8.5, 9.0]的距离:0.5
点[8.0, 9.0]与点[3.0, 3.0]的距离:7.810249675906654
点[8.0, 9.0]与点[8.5, 8.0]的距离:1.118033988749895
点[8.0, 9.0]与点[1.5, 1.5]的距离:9.924716620639604
结点6属于簇0
点[9.0, 8.0]与点[8.5, 9.0]的距离:1.118033988749895
点[9.0, 8.0]与点[3.0, 3.0]的距离:7.810249675906654
点[9.0, 8.0]与点[8.5, 8.0]的距离:0.5
点[9.0, 8.0]与点[1.5, 1.5]的距离:9.924716620639604
结点7属于簇2
点[9.0, 9.0]与点[8.5, 9.0]的距离:0.5
点[9.0, 9.0]与点[3.0, 3.0]的距离:8.48528137423857
点[9.0, 9.0]与点[8.5, 8.0]的距离:1.118033988749895
点[9.0, 9.0]与点[1.5, 1.5]的距离:10.606601717798213
结点8属于簇0
点[8.5, 9.0]与点[8.5, 9.0]的距离:0.0
点[3.0, 3.0]与点[1.5, 1.5]的距离:2.1213203435596424
点[8.5, 8.0]与点[8.5, 8.0]的距离:0.0
点[1.5, 1.5]与点[3.0, 3.0]的距离:2.1213203435596424
新的簇中心:
[8.5, 9.0]
[1.5, 1.5]
[8.5, 8.0]
[3.0, 3.0]
偏移量为:0.0遗留问题和缺陷
代码缺陷
k-means算法的重点在于K值与阈值的选择。根据数据的分布,被分为某些数量的簇是无法实现的,这时候会出现某一或某几簇元素为零的情况。合适的做法是,先将数据进行可视化,分析合适的K值取值。
另外好像还有一种叫做“肘部法则”的K值选择方法,我去学习一下。
遗留问题
在每轮迭代中,都要重新计算新的簇中心,并与原来的簇中心比较,得出偏移量,以衡量整个聚类划分是否趋于稳定。
如何在具体代码中得出合理的偏移量,是一个亟待解决的问题。
最初,我使用的是计算各新的簇中心坐标和对应原簇中心之间距离的均值,但在测试特殊数据时成了死循环。
后又改用距离的最小值代表偏差距离,似乎有缺少鲁棒性之嫌。