tensorflow随笔——C++工程化
本文主要描述如何基于Tensroflow从线下训练到线上预测的整个流程。主要包括以下几步:
- 使用Python接口搭建模型训练参数并固化成pb文件
- 使用Bazel编译Tensorflow源码得到tensorflow_cc.so的动态库
- 调用Tensorflow C++ API编写预测代码
使用Python搭建模型训练mnist手写字符
简单搭建2层CNN+2层FC的神经网络,保存网络图结构和参数文件。
# coding=UTF-8
'''
当神经网络比较复杂,训练数据比较多,模型训练耗时很长,训练过程中会出现某些不可预计的错误而导致训练意外终止,
为了避免以上问题,可以通过模型持久化,保存为CKPT格式来暂存训练过程中的临时数据
保存ckpt格式的模型流程:
1.定义运算过程
2.声明并得到一个Saver
3.通过Saver.save保存模型
'''
import os
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=False)
def build_network(x):
def weight_variable(shape, name="weights"):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, dtype=tf.float32, stddev=0.1) * 0.001
return tf.Variable(initial, name=name)
def bias_variable(shape, name="biases"):
initial = tf.constant(0.1, dtype=tf.float32, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial, name=name)
def conv2d(input, w):
return tf.nn.conv2d(input, w, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
def pool_max(input):
return tf.nn.max_pool(input, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME', name='pool1')
def fc(input, w, b):
return tf.matmul(input, w) + b
# conv1
with tf.name_scope('conv1_1') as scope:
kernel = weight_variable([3, 3, 1, 32])
biases = bias_variable([32])
output_conv1_1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x, kernel) + biases, name=scope)
pool1 = pool_max(output_conv1_1) # [n,14,14,32]
# conv2
with tf.name_scope('conv1_2') as scope:
kernel = weight_variable([3, 3, 32, 64])
biases = bias_variable([64])
output_conv1_2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(pool1, kernel) + biases, name=scope)
pool2 = pool_max(output_conv1_2) # [n,7,7,64]
# fc1
with tf.name_scope('fc1') as scope:
shape = int(np.prod(pool2.get_shape()[1:]))
kernel = weight_variable([shape, 512])
biases = bias_variable([512])
pool2_flat = tf.reshape(pool2, [-1, shape])
output_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(fc(pool2_flat, kernel, biases), name=scope)
# fc2
with tf.name_scope('fc2') as scope:
kernel = weight_variable([512, 10])
biases = bias_variable([10])
output_fc2 = fc(output_fc1, kernel, biases)
output = tf.nn.softmax(output_fc2, name='softmax')
return output
def train_network(batch_size, num_epochs, checkpoint_dir, model):
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 28, 28, 1], name='input')
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.int64, shape=[None,], name='y_')
# 创建目录
if not tf.gfile.Exists(checkpoint_dir):
tf.gfile.MakeDirs(checkpoint_dir)
logits = build_network(x)
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=y_))
optimize = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(cost)
prediction_labels = tf.argmax(logits, axis=1, name="output")
correct_prediction = tf.equal(prediction_labels, y_)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
# 初始化参数
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 声明saver保存模型
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
# 验证之前是否已经保存了检查点文件
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(checkpoint_dir)
if ckpt and ckpt.model_checkpoint_path:
saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for i in range(1000):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
op, acc, costt = sess.run([optimize, accuracy, cost], feed_dict={
x: np.reshape(batch_xs, (-1, 28, 28, 1)),
y_: batch_ys})
if i % 100 == 0:
print('step', i, 'acc', acc, 'loss', costt)
saver.save(sess, os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, model), global_step=i)
# 打印模型节点信息
#for op in tf.get_default_graph().get_operations():
# print(op.name, op.values())
if __name__ == '__main__':
ckpt_dir = '/home/positec/CW/tf_dispose/frozen_model/ckpt'
model = 'model.ckpt'
train_network(128, 2, ckpt_dir, model)程序运行后会在ckpt目录下生成4个文件
checkpoint:检查点文件,文件保存了目录下所有的模型文件列表
model.ckpt.meta:保存Tensorflow计算图的结构
model.ckpt-data:保存模型中每个变量的取值
model.ckpt.index:保存参数索引文件
将ckpt固化成pb文件
code snippet widget
通过freeze_graph函数将ckpt格式的模型文件固化成pb格式,用于后续预测时的前向传播调用。
源码编译Tensorflow
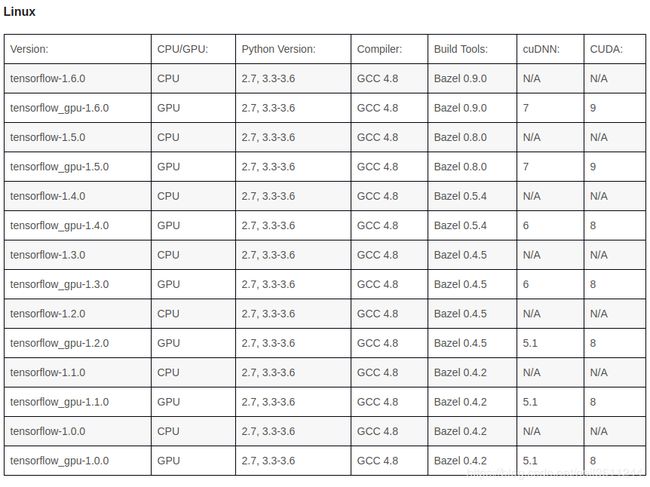
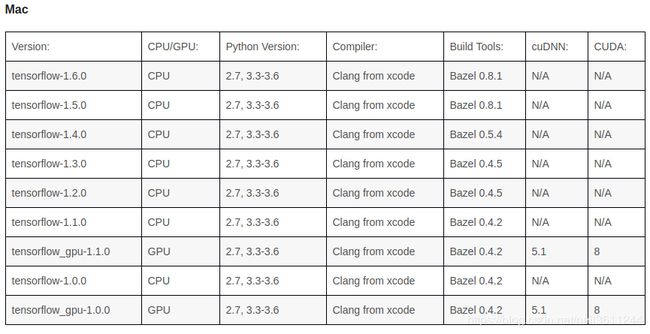
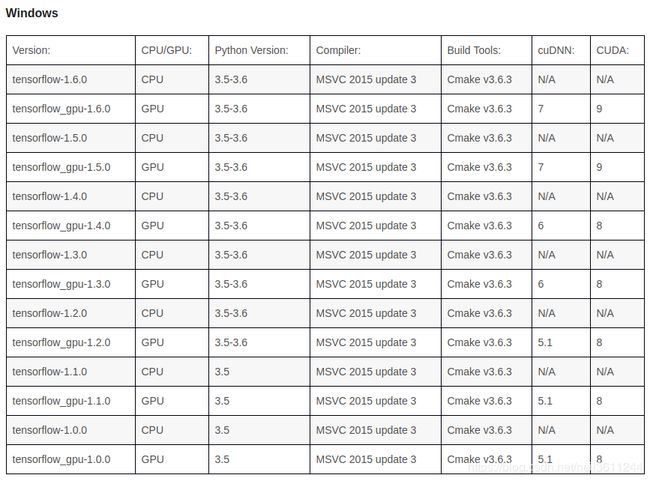
先贴一份不同平台上Tensorflow与cudnn、cuda、bazel的版本配套关系表:
我采用的Tensorflow版本是1.4,
1.下载源码:git clone https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow.git
2. cd到tensorflow目录,更新到1.4版本:git checkout r1.4
3. 执行./configure进行项目配置
4. 使用bazel工具进行编译:bazel build --config=opt //tensorflow:libtensorflow_cc.so
编译完成后,在tensorflow根目录下出现 bazel-bin, bazel-genfiles 等文件夹, 按顺序执行以下命令将对应的libtensorflow_cc.so文件和其他文件拷贝进入 /usr/local/lib/ 目录
mkdir /usr/local/include/tf
cp -r bazel-genfiles/ /usr/local/include/tf/
cp -r tensorflow /usr/local/include/tf/
cp -r third_party /usr/local/include/tf/
cp -r bazel-bin/tensorflow/libtensorflow_cc.so /usr/local/lib/
完成后我们就准备好了tensorflow_cc.so文件,后面在自己的C++编译环境和代码目录下编译时链接这些库即可。
使用Tensorflow C++ API编写预测代码
预测代码主要包括以下几个步骤:
- 创建Session
- 导入之前生成的模型
- 将模型设置到创建的Session里
- 设置模型输入输出,调用Session的Run做预测
- 关闭Session
第一步,创建Session
//创建新会话Session
Session* session;
Status status = NewSession(SessionOptions(), &session);
if (!status.ok()){
std::cout << status.ToString() << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Session created successful" << std::endl;
}第二步,导入模型
string model_path = "/home/positec/CW/tf_dispose/frozen_model/pb/model.pb";
GraphDef graphdef;
//从pb文件中读取图模型
Status status_load = ReadBinaryProto(Env::Default(), model_path, &graphdef);
if (!status_load.ok()){
std::cout << "ERROR: Loading model failed..." << model_path << std::endl;
std:cout << status_load.ToString() << "\n";
return -1;
}第三步,将模型设置到创建的Session里
Status status_create = session->Create(graphdef);
if (!status_create.ok()){
std::cout << "ERROR: Creating graph in session failed..." << status_create.ToString() << std::endl;
return -1;
}
cout << "Session successfully created." << endl;第四步,设置模型输入
string image_path = "/home/positec/CW/tf_dispose/frozen_model/test/test.jpg";
int input_height = 28;
int input_width = 28;
// 从csv文件中读取数据
std::vector resized_tensors;
Status read_tensor_status = ReadTensorFromImageFile(image_path, input_height, input_width, &resized_tensors);
if (!read_tensor_status.ok()){
LOG(ERROR) << read_tensor_status;
cout << "resing error" << endl;
return -1;
}
const Tensor& resized_tensor = resized_tensors[0];
std::cout << resized_tensor.DebugString()< 在ReadTensorFromImageFile()函数,建立一个会话session,在会话中对读取到的tensor进行预处理,例如,对tensor进行解码( DecodeJpeg),resize,归一化等
第五步,预测结果
vector outputs;
string output_node = "softmax";
Status status_run = session->Run({{"input_x", resized_tensor}}, {output_node}, {}, &outputs);
if (!status_run.ok()) {
std::cout << "ERROR: RUN failed..." << std::endl;
std::cout << status_run.ToString() << "\n";
return -1;
}
//Fetch output value
std::cout << "Output tensor size:" << outputs.size() << std::endl;
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < outputs.size(); i++) {
std::cout << outputs[i].DebugString()< 模型预测时使用的函数为session->Run({{"inputs_x", resized_tensor}}, {output_node}, {}, &outputs)。"inputs_x"是图模型输入tensor的名字(name),变量output_node保存的是图模型输出tensor的名字(name)。这两个名字(name)一定要与保存的图模型(.pb)文件中的名字一致,否则会报错。最后得到的输出tensor保存在容器outputs中。
第六步,关闭Session
session->Close()完整代码如下:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "tensorflow/cc/ops/const_op.h"
#include "tensorflow/cc/ops/image_ops.h"
#include "tensorflow/cc/ops/standard_ops.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/framework/graph.pb.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/framework/tensor.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/graph/default_device.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/graph/graph_def_builder.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/lib/core/errors.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/lib/core/stringpiece.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/lib/core/threadpool.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/lib/io/path.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/lib/strings/stringprintf.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/platform/env.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/platform/init_main.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/platform/logging.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/platform/types.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/public/session.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/util/command_line_flags.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace tensorflow;
using namespace tensorflow::ops;
using tensorflow::Flag;
using tensorflow::Tensor;
using tensorflow::Status;
using tensorflow::string;
using tensorflow::int32;
static Status ReadEntireFile(tensorflow::Env* env, const string& filename,
Tensor* output) {
tensorflow::uint64 file_size = 0;
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(env->GetFileSize(filename, &file_size));
string contents;
contents.resize(file_size);
std::unique_ptr file;
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(env->NewRandomAccessFile(filename, &file));
tensorflow::StringPiece data;
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(file->Read(0, file_size, &data, &(contents)[0]));
if (data.size() != file_size) {
return tensorflow::errors::DataLoss("Truncated read of '", filename,
"' expected ", file_size, " got ",
data.size());
}
output->scalar()() = data.ToString();
return Status::OK();
}
Status ReadTensorFromImageFile(const string& file_name, const int input_height, const int input_width, std::vector* out_tensors){
auto root = tensorflow::Scope::NewRootScope();
using namespace ::tensorflow::ops;
// read file_name into a tensor named input
Tensor input(tensorflow::DT_STRING, tensorflow::TensorShape());
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(ReadEntireFile(tensorflow::Env::Default(), file_name, &input));
// use a placeholder to read input data
auto file_reader =
Placeholder(root.WithOpName("input_x"), tensorflow::DataType::DT_STRING);
std::vector> inputs = {
{"input_x", input},
};
// Now try to figure out what kind of file it is and decode it.
const int wanted_channels = 1;
tensorflow::Output image_reader;
if (tensorflow::StringPiece(file_name).ends_with(".png")) {
image_reader = DecodePng(root.WithOpName("png_reader"), file_reader,
DecodePng::Channels(wanted_channels));
} else if (tensorflow::StringPiece(file_name).ends_with(".gif")) {
// gif decoder returns 4-D tensor, remove the first dim
image_reader =
Squeeze(root.WithOpName("squeeze_first_dim"),
DecodeGif(root.WithOpName("gif_reader"), file_reader));
} else if (tensorflow::StringPiece(file_name).ends_with(".bmp")) {
image_reader = DecodeBmp(root.WithOpName("bmp_reader"), file_reader);
} else {
// Assume if it's neither a PNG nor a GIF then it must be a JPEG.
image_reader = DecodeJpeg(root.WithOpName("jpeg_reader"), file_reader,
DecodeJpeg::Channels(wanted_channels));
}
// Now cast the image data to float so we can do normal math on it.
auto float_caster =
Cast(root.WithOpName("float_caster"), image_reader, tensorflow::DT_FLOAT);
// The convention for image ops in TensorFlow is that all images are expected
// to be in batches, so that they're four-dimensional arrays with indices of
// [batch, height, width, channel]. Because we only have a single image, we
// have to add a batch dimension of 1 to the start with ExpandDims().
auto dims_expander = ExpandDims(root.WithOpName("expand"), float_caster, 0);
// Bilinearly resize the image to fit the required dimensions.
// auto resized = ResizeBilinear(
//root, dims_expander,
//Const(root.WithOpName("size"), {input_height, input_width}));
// Subtract the mean and divide by the scale.
//Div(root.WithOpName(output_name), Sub(root, resized, {input_mean}),
//{input_std});
float input_max = 255;
Div(root.WithOpName("div"),dims_expander,input_max);
// This runs the GraphDef network definition that we've just constructed, and
// returns the results in the output tensor.
tensorflow::GraphDef graph;
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(root.ToGraphDef(&graph));
std::unique_ptr session(
tensorflow::NewSession(tensorflow::SessionOptions()));
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(session->Create(graph));
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(session->Run({inputs}, {"div"}, {}, out_tensors));
return Status::OK();
}
int main(int argc, char** argv )
{
//*******************step1: 加载模型************************//
//创建新会话Session
Session* session;
Status status = NewSession(SessionOptions(), &session);
if (!status.ok()){
std::cout << status.ToString() << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Session created successful" << std::endl;
}
string model_path = "/home/positec/CW/tf_dispose/frozen_model/pb/model.pb";
// Graph Definition for current model
GraphDef graphdef;
//从pb文件中读取图模型
Status status_load = ReadBinaryProto(Env::Default(), model_path, &graphdef);
if (!status_load.ok()){
std::cout << "ERROR: Loading model failed..." << model_path << std::endl;
std:cout << status_load.ToString() << "\n";
return -1;
}
//将模型导入会话Session中
Status status_create = session->Create(graphdef);
if (!status_create.ok()){
std::cout << "ERROR: Creating graph in session failed..." << status_create.ToString() << std::endl;
return -1;
}
cout << "Session successfully created." << endl;
//*******************step2: 读取图片************************//
string image_path = "/home/positec/CW/tf_dispose/frozen_model/test/test.jpg";
int input_height = 28;
int input_width = 28;
// 从csv文件中读取数据
std::vector resized_tensors;
Status read_tensor_status = ReadTensorFromImageFile(image_path, input_height, input_width, &resized_tensors);
if (!read_tensor_status.ok()){
LOG(ERROR) << read_tensor_status;
cout << "resing error" << endl;
return -1;
}
const Tensor& resized_tensor = resized_tensors[0];
std::cout << resized_tensor.DebugString()< outputs;
string output_node = "softmax";
Status status_run = session->Run({{"input_x", resized_tensor}}, {output_node}, {}, &outputs);
if (!status_run.ok()) {
std::cout << "ERROR: RUN failed..." << std::endl;
std::cout << status_run.ToString() << "\n";
return -1;
}
//Fetch output value
std::cout << "Output tensor size:" << outputs.size() << std::endl;
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < outputs.size(); i++) {
std::cout << outputs[i].DebugString()<(); // Tensor Shape: [batch_size, target_class_num]
int output_dim = t.shape().dim_size(1); // Get the target_class_num from 1st dimension
std::vector tout;
// Argmax: Get Final Prediction Label and Probability
int output_class_id = -1;
double output_prob = 0.0;
for (int j = 0; j < output_dim; j++)
{
std::cout << "Class " << j << " prob:" << tmap(0, j) << "," << std::endl;
if (tmap(0, j) >= output_prob) {
output_class_id = j;
output_prob = tmap(0, j);
}
}
// Log
std::cout << "Final class id: " << output_class_id << std::endl;
std::cout << "Final class prob: " << output_prob << std::endl;
// 关闭会话
session-> Close();
return 0;
} 最后进入build文件夹,对工程进行编译:
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
sudo make install