Spring Boot 电商系统之秒杀实战 -- 1.基础环境搭建
记录学习总结
目标:
1.掌握Spring Boot环境搭建
2.掌握Lombok的集成使用
2.掌握Thymeleaf集成,Result结果封装
3.掌握Mybatis+Druid集成
4.掌握Jedis集成+通用缓存Key封装
文章总体目录
文章目录
- Spring Boot项目搭建
- Spring Boot环境搭建
- 集成Lombok
- 集成Mybatis+Druid
- 集成Thymeleaf
- 集成Jedis
- Result结果封装
- 通用缓存Key封装
- 测试验证
Spring Boot项目搭建
Spring Boot环境搭建
这里使用 IDEA 来进行项目开发,提供了很方便了模板。
集成Lombok
1.菜单栏File > Settings > Plugins > Browse repositories
2.搜索 Lombok Plugin 安装后,重启IDEA即可生效

3.添加lombok依赖
org.projectlombok
lombok
1.18.2
true
4.编写一个实体类 User,使用@Data注解(包含了set和get方法)
@Data
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
}
其他的Lombok用法这里不多说,大家可以自行查阅
集成Mybatis+Druid
1.在 pom.xml 添加依赖
mysql
mysql-connector-java
com.alibaba
druid
1.1.10
2.在 application.properties 中添加相关配置
# mybatis
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.chandler.seckill.domain
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
mybatis.configuration.default-fetch-size=100
mybatis.configuration.default-statement-timeout=3000
mybatis.mapperLocations = classpath:com/chandler/seckill/dao/*.xml
# druid
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/seckill?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&allowMultiQueries=true&useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.datasource.filters=stat
spring.datasource.maxActive=2
spring.datasource.initialSize=1
spring.datasource.maxWait=60000
spring.datasource.minIdle=1
spring.datasource.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis=60000
spring.datasource.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis=300000
spring.datasource.validationQuery=select 'x'
spring.datasource.testWhileIdle=true
spring.datasource.testOnBorrow=false
spring.datasource.testOnReturn=false
spring.datasource.poolPreparedStatements=true
spring.datasource.maxOpenPreparedStatements=20
3.在DAO中添加相关注解
@Mapper
public interface UserDao {
@Select("select * from user where id = #{id}")
public User getById(@Param("id")int id);
@Insert("insert into user(id,name) values(#{id},#{name})")
public int insert(User user);
}
集成Thymeleaf
1.在 pom.xml 添加依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
2.在 application.properties 中添加相关配置
# thymeleaf
spring.thymeleaf.prefix=classpath:/templates/
spring.thymeleaf.suffix=.html
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
spring.thymeleaf.servlet.content-type=text/html
spring.thymeleaf.enabled=true
spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8
spring.thymeleaf.mode=HTML5
集成Jedis
1.在 pom.xml 添加依赖
redis.clients
jedis
2.在 application.properties 中添加相关配置
#redis
redis.host=192.168.25.128
redis.port=6379
redis.timeout=3
redis.password=123456
redis.poolMaxTotal=10
redis.poolMaxIdle=10
redis.poolMaxWait=3
Result结果封装
很多时候都是需要返回JSON对象,根据需求事先先封装好一个结果对象,方便复用。
因为希望的返回结果形式为:
{
code:0,
msg:success,
name:chandler
}
所有最终设计的Result结果类为:
@Data
public class Result {
private int code;
private String msg;
private T data;
/**
* 成功时的调用
* @param data
* @param
* @return
*/
public static Result success(T data){
return new Result(data);
}
/**
* 失败时候的调用
* @param cm
* @param
* @return
*/
public static Result error(CodeMsg cm){
return new Result(cm);
}
public Result(T data) {
this.code = 0;
this.msg = "success";
this.data = data;
}
public Result(CodeMsg cm) {
if (cm == null) {
return;
}
this.code = cm.getCode();
this.msg = cm.getMsg();
}
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class CodeMsg {
private int code;
private String msg;
//通用异常
public static CodeMsg SUCCESS = new CodeMsg(0,"success");
public static CodeMsg SERVER_ERROR = new CodeMsg(500100,"服务端异常");
//TODO其他异常
}
通用缓存Key封装
我们还需要创建一个 Redis 服务方便进行缓存操作
先定义一个读取application.properties文件中 redis 配置的类
@Component
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "redis")
public class RedisConfig {
private String host;
private int port;
private int timeout;//秒
private String password;
private int poolMaxTotal;
private int poolMaxIdle;
private int poolMaxWait;//秒
}
有了配置文件中的信息我们在来创建一个工厂类,方便初始化 redis 连接池
@Service
public class RedisPoolFactory {
@Autowired
RedisConfig redisConfig;
//注册bean对象
@Bean
public JedisPool jedisPoolFactory(){
JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig = new JedisPoolConfig();
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxIdle(redisConfig.getPoolMaxIdle());
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxTotal(redisConfig.getPoolMaxTotal());
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(redisConfig.getPoolMaxWait());
JedisPool jp = new JedisPool(jedisPoolConfig,redisConfig.getHost(),redisConfig.getPort(),redisConfig.getTimeout() * 1000,redisConfig.getPassword(),0);
return jp;
}
}
为了方便我们在读取 key 值的时候能够显示的读取相关值且存入的key值 在不同模块间不同名重复和后期拓展,我们这里稍微对读取和存储 key 值进行一点加工设计,实现了 KeyPrefix 接口和 BasePrefix 基础抽象类,这样其他模块的添加只需要继承基础抽象类即可。
- 接口扩展类
public interface KeyPrefix {
public int expireSeconds();
public String getPrefix();
}
- 基础抽象类
@AllArgsConstructor
public abstract class BasePrefix implements KeyPrefix{
private int expireSeconds;
private String prefix;
public BasePrefix(String prefix) {
//0代表永不过期
this(0,prefix);
}
@Override
public int expireSeconds(){
return expireSeconds;
}
@Override
public String getPrefix() {
String className = getClass().getSimpleName();
return className+":"+prefix;
}
}
- 业务相关类
public class OrderKey extends BasePrefix {
public OrderKey(int expireSeconds, String prefix) {
super(expireSeconds, prefix);
}
}
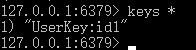
public class UserKey extends BasePrefix {
public UserKey(String prefix) {
super(prefix);
}
public static UserKey getById = new UserKey("id");
public static UserKey getByName = new UserKey("name");
}
- 最后是比较关键的RedisService 服务类,缓存相关操作都封装在这个类中
@Service
public class RedisService {
@Autowired
JedisPool jedisPool;
/**
* 获取单个对象
*
* @param prefix
* @param key
* @param clazz
* @param
* @return
*/
public T get(KeyPrefix prefix, String key, Class clazz) {
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
String realKey = prefix.getPrefix() + key;
String str = jedis.get(realKey);
T t = stringToBean(str, clazz);
return t;
} finally {
returnToPool(jedis);
}
}
/**
* 设置对象
* @param prefix
* @param key
* @param value
* @param
* @return
*/
public boolean set(KeyPrefix prefix,String key,T value){
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
String str = beanToString(value);
if (str == null || str.length() <= 0) {
return false;
}
String realKey = prefix.getPrefix() + key;
int seconds = prefix.expireSeconds();
if (seconds <= 0){
jedis.set(realKey,str);
} else {
jedis.setex(realKey,seconds,str);
}
return true;
} finally {
returnToPool(jedis);
}
}
/**
* 判断 key 是否存在
* @param prefix
* @param key
* @param
* @return
*/
public boolean exists(KeyPrefix prefix,String key){
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
String realKey = prefix.getPrefix() + key;
return jedis.exists(realKey);
} finally {
returnToPool(jedis);
}
}
/**
* 执行原子增加 key 值
* @param prefix
* @param key
* @param
* @return
*/
public Long incr(KeyPrefix prefix,String key){
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
String realKey = prefix.getPrefix() + key;
return jedis.incr(realKey);
} finally {
returnToPool(jedis);
}
}
/**
* 减少 key 值
* @param prefix
* @param key
* @param
* @return
*/
public Long decr(KeyPrefix prefix,String key){
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
String realKey = prefix.getPrefix() + key;
return jedis.decr(realKey);
} finally {
returnToPool(jedis);
}
}
private String beanToString(T value) {
if (value == null) {
return null;
}
Class clazz = value.getClass();
if (clazz == int.class || clazz == Integer.class){
return ""+value;
} else if (clazz == Long.class || clazz == long.class){
return "" + value;
} else if (clazz == String.class){
return (String) value;
} else {
return JSON.toJSONString(value);
}
}
private T stringToBean(String str, Class clazz) {
if (str == null || str.length() <= 0 || clazz == null) {
return null;
}
if (clazz == int.class || clazz == Integer.class) {
return (T) Integer.valueOf(str);
} else if (clazz == String.class) {
return (T) str;
} else if (clazz == Long.class || clazz == long.class) {
return (T) Long.valueOf(str);
} else {
return JSON.toJavaObject(JSON.parseObject(str), clazz);
}
}
private void returnToPool(Jedis jedis) {
if (jedis != null) {
jedis.close();
}
}
}
测试验证
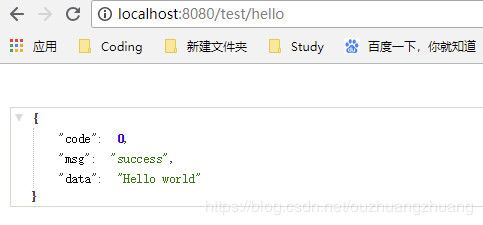
环境都搭建配置之后测试是必不可少的环节,开始动手搞起来。
1.创建测试 TestController 类
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
@Autowired
RedisService redisService;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@ResponseBody
public Result home(){
return Result.success("Hello world");
}
@RequestMapping("/error")
@ResponseBody
public Result error(){
return Result.error(CodeMsg.SERVER_ERROR);
}
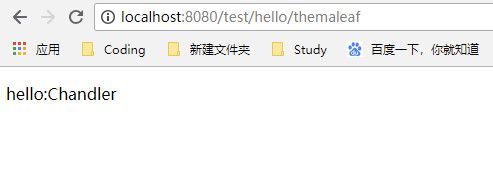
@RequestMapping("/hello/themaleaf")
public String themaleaf(Model model){
model.addAttribute("name","Chandler");
return "hello";
}
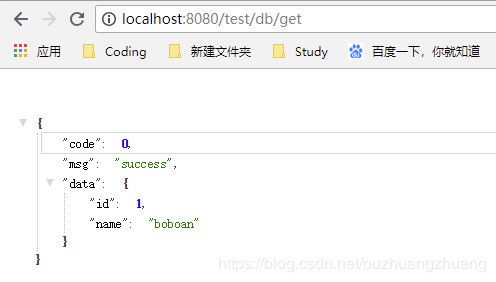
@RequestMapping("/db/get")
@ResponseBody
public Result dbGet(){
User user = userService.getById(1);
return Result.success(user);
}
@RequestMapping("/redis/get")
@ResponseBody
public Result redisGet(){
User user = redisService.get(UserKey.getById,""+1,User.class);
return Result.success(user);
}
@RequestMapping("/redis/set")
@ResponseBody
public Result redisSet(){
User user =new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("Chandler");
redisService.set(UserKey.getById,""+1,user);
return Result.success(true);
}
}
这样大概的环境流程验证OK,接下来就可以开始实现功能开发了~~