Shaders for Game Programmers and Artists(6) - 反射与折射
反射
反射在上一篇的HDR中就已经用到了。简单说一下
反射发生的原理就是光线打到一个物体的面上之后,一部分光被弹回去的现象,
原理如下图
只要知道入射光线和发现,出射光线的方向就可以求出。通过这个方向对天空盒进行采样,就可以得到天空盒上的颜色了。
在vs中计算出射光线的方向
float4x4 view_proj_matrix;
float4 view_position;
struct VS_OUTPUT
{
float4 Pos: POSITION;
float2 TexCoord: TEXCOORD0;
float3 Reflect: TEXCOORD1;
};
VS_OUTPUT vs_main(float4 inPos: POSITION, float3 inNormal: NORMAL,
float2 inTxr: TEXCOORD0)
{
VS_OUTPUT Out;
// Compute the projected position and send out the texture coordinates
Out.Pos = mul(view_proj_matrix, inPos);
Out.TexCoord = inTxr;
// Compute the reflection vector
Out.Reflect = -reflect(view_position-inPos,inNormal);
return Out;
}
在ps中对天空盒进行采样,同时和采自身贴图的结果相加。
sampler Wood;
sampler EnvMap;
float4 ps_main(float2 inTxr: TEXCOORD0,float3 inReflect: TEXCOORD1) : COLOR
{
// Output texture color with reflection map
return 0.2*tex2D(Wood,inTxr)+0.8*texCUBE(EnvMap,inReflect);
}
折射
折射是光线穿过折射率不同的两种介质所产生的现象,其中入射角和出射角遵循斯涅尔定律(snell’s low)
![]()
下面列出了一些常用物质的折射率
当然,这个折射率是对某个特定波长的光来说的,对于波长不同的光,介质的折射率也是不一样的。
所以折射的实现最终就是求折射光线的问题了,这是一道三角函数题。
直接看vs吧,注释里面有计算的步骤
float4x4 view_proj_matrix;
float4 view_position;
float refractingPower;
struct VS_OUTPUT
{
float4 Pos: POSITION;
float2 TexCoord: TEXCOORD0;
float3 Refract: TEXCOORD1;
};
VS_OUTPUT vs_main(float4 inPos: POSITION, float3 inNormal: NORMAL,
float2 inTxr: TEXCOORD0)
{
VS_OUTPUT Out;
// Compute the projected position and send out the texture coordinates
//mvp矩阵变换
Out.Pos = mul(view_proj_matrix, inPos);
Out.TexCoord = inTxr;
float3 viewVec = normalize(view_position - inPos);
//根据斯涅尔法则计算反射角
// n_i * sin(theta_i) = n_r * sin(theta_r)
// sin(theta_i)
//首先用向量点乘计算出cos,然后用勾股定理计算sin值
float cosine = dot(viewVec, inNormal);
float sine = sqrt(1 - cosine * cosine);
// sin(theta_r)
//根据斯涅尔法则计算出射角的sin,saturate到0,1,所以当入射角足够大的时候,然后用勾股定理计算cos值
float sine2 = saturate(refractingPower * sine);
float cosine2 = sqrt(1 - sine2 * sine2);
//首先构建一对正交基x,y 然后变换到标准的坐标轴上,cross是向量叉乘,a × b为一个新生成的向量,这个向量垂直于a 和 b展成的平面
float3 x = -inNormal;
float3 y = normalize(cross(cross(viewVec, inNormal), inNormal));
Out.Refract = x * cosine2 + y * sine2;
return Out;
}
折射率是1.14时候的结果
折射率是1.66时候的结果
反射+折射
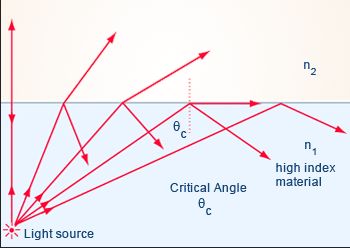
光线和物质表面相交的时候,一部分光线发生了反射,一部分发生了折射。根据斯涅尔定律,当入射角大到一定程度的时候,折射现象就不会发生了,这个角就是临界角,任何超过这个角的入射光线都会被完全反射,称为全反射(total internal reflection)现象,示意图如下
当我们斜着看水面的时候,到一定角度就看不到水下的东西,而水面看起来就像一面镜子,原理就是这样。
Shader中vs需要同时计算反射光线和折射光线的向量,
float4x4 view_proj_matrix;
float4 view_position;
struct VS_OUTPUT
{
float4 Pos: POSITION;
float2 TexCoord: TEXCOORD0;
float3 Refract: TEXCOORD1;
float3 Reflect: TEXCOORD2;
float2 Factors: TEXCOORD3;
};
VS_OUTPUT vs_main(float4 inPos: POSITION, float3 inNormal: NORMAL,
float2 inTxr: TEXCOORD0)
{
VS_OUTPUT Out;
// Compute the projected position and send out the texture coordinates
Out.Pos = mul(view_proj_matrix, inPos);
Out.TexCoord = inTxr;
float3 viewVec = normalize(view_position - inPos);
// Compute reflection
Out.Reflect = reflect(-viewVec,inNormal);
// Compute the reflection vector using Snell's law
// the refract HLSL function does not always work properly
// n_i * sin(theta_i) = n_r * sin(theta_r)
// sin(theta_i)
float cosine = dot(viewVec, inNormal);
float sine = sqrt(1 - cosine * cosine);
// sin(theta_r)
float sine2 = saturate(1.14 * sine);
float cosine2 = sqrt(1 - sine2 * sine2);
// Determine the refraction vector be using the normal and tangent
// vectors as basis to determine the refraction direction
float3 x = -inNormal;
float3 y = normalize(cross(cross(viewVec, inNormal), inNormal));
Out.Refract = x * cosine2 + y * sine2;
// Determine proper reflection and refraction factors through
// a Fresnel approximation. (x = reflect, y = refract)
Out.Factors.x = sine;
Out.Factors.y = (1 - sine2);
return Out;
}
同时根据近似的Fresnel,算出两者叠加的比例。
最后在Ps中叠加
sampler Wood;
sampler EnvMap;
float4 ps_main(float2 inTxr: TEXCOORD0,float3 inRefract: TEXCOORD1,
float3 inReflect: TEXCOORD2,float2 inFct: TEXCOORD3) : COLOR
{
// Output texture color with reflection map
return inFct.x * texCUBE(EnvMap,inReflect) +
(inFct.y * texCUBE(EnvMap,inRefract) + 0.4)
* tex2D(Wood,inTxr);
}
0.4是为了模拟ambient color