数据结构篇:校园最短路径导航(三:地图图像显示以及完整程序)
首先是地图的显示,因为控制台限制,只能通过外部程序来显示图片
如果你使用的是VC6.0或者Dev C++将准备好的图片放在工程根目录,命名为SchoolMap.png
如果有小伙伴和我一样使用的是CLion的话,就把图片放到cmake-build-debug下面
在main函数里调用以下语句即可显示图片
system("mspaint SchoolMap.png");可是问题来了,如果调用这一个语句,程序会暂停,不把图片关闭程序就不会继续运行,还好控制台会缓存我们的输入。也就有了挽救的可能。
while(1){
cout<<"请按照图片选择你想去的地方,输入起始点和目的地的序号,以空格间隔。"<>originPos>>endPos;
adjacencyList.ShowShortestResult(originPos,endPos);
} 真的有点麻烦,我哭了,你们呢。
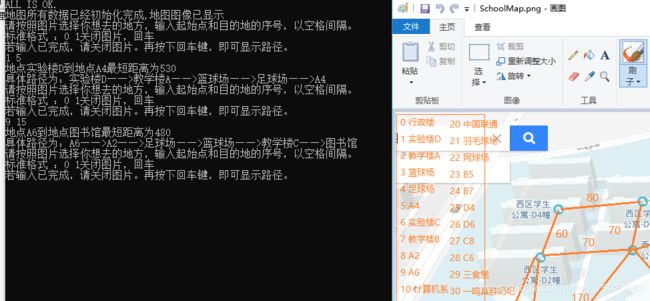
运行截图
Gif版
完整程序
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
//存储最短路径值
int ShortestPathvalue[32][32] = {0};
//存储具体路径
int ShortestPathmatrix[32][32] = {0};
//地点信息
char _mapName[32][50] = {"行政楼", "实验楼D", "教学楼A", "篮球场", "足球场", "A4", "实验楼C", "教学楼B", "A2", "A6", "计算机系", "苏果超市",
"果曼优品", "实验楼A", "教学楼C", "图书馆", "一食堂", "D2", "D8", "C4", "中国联通", "羽毛球场", "网球场",
"B5", "B7", "D4", "D6", "C8", "C6", "三食堂", "一鸣真鲜奶吧", "B11"};
//距离信息,_distance[0][1] = 50;代表从下标为0到下表为1地点距离为50
int _distance[32][32] = {0};
//边表结点
typedef struct EdgeNode {
//顶点对应的下标
int adjvex;
//权值
int weight;
//指向下一个邻接点
struct EdgeNode *next;
} edgeNode;
//顶点表结点
typedef struct VertexNode {
//顶点数据
char data[50];
//边表头指针
edgeNode *firstedge;
} VertexNode, AdjList[100];
//集合
typedef struct {
AdjList adjList;
//顶点数和边数
int numVertexes, numEdges;
} GraphAdjList;
class AdjacencyList {
public:
void ShowALGraph(GraphAdjList *G);
void Test();
//初始化地图
void InitMap(GraphAdjList *G);
//创建地图
void CreateALGraph(GraphAdjList *G);
//计算各个顶点之间最短路径
void ShortestPath_Floyd(GraphAdjList *G, int P[32][32], int D[32][32]);
//输出路径长度和具体路径
void ShowShortestResult(int originPos,int endPos);
};
//创建地图
void AdjacencyList::CreateALGraph(GraphAdjList *G) {
edgeNode *e;
//读入顶点信息,建立顶点表
for (int i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)
{
//读入顶点信息
strcpy(G->adjList[i].data, _mapName[i]);
//将边表置为空表
G->adjList[i].firstedge = NULL;
}
//建立边表(头插法)
for (int i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
int temp;
if (_distance[i][j] != 0 || _distance[j][i] != 0)
{
if (_distance[i][j] != 0)
{
temp = _distance[i][j];
_distance[j][i] = _distance[i][j];
}
else
{
temp = _distance[j][i];
_distance[i][j] = _distance[j][i];
}
e = new EdgeNode;
e->adjvex = j;
e->next = G->adjList[i].firstedge;
e->weight = temp;
G->adjList[i].firstedge = e;
e = new EdgeNode;
e->adjvex = i;
e->next = G->adjList[j].firstedge;
e->weight = temp;
G->adjList[j].firstedge = e;
}
}
}
}
void AdjacencyList::Test() {
cout << "ALL IS OK." << endl;
}
void AdjacencyList::ShowALGraph(GraphAdjList *G) {
for (int i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)
{
cout << "顶点" << i << ": " << G->adjList[i].data << "--firstedge--";
edgeNode *p = new edgeNode;
p = G->adjList[i].firstedge;
while (p)
{
cout << p->adjvex << "--Weight: " << p->weight << "--Next--";
p = p->next;
}
cout << "--NULL" << endl;
}
}
//初始化地图基本数据
void AdjacencyList::InitMap(GraphAdjList *G) {
//输入顶点数和边数
G->numVertexes = 32;
G->numEdges = 59;
_distance[0][2] = 60;
_distance[1][2] = 190;
_distance[1][7] = 210;
_distance[1][6] = 70;
_distance[2][7] = 80;
_distance[2][16] = 320;
_distance[2][3] = 120;
_distance[3][7] = 100;
_distance[3][14] = 170;
_distance[3][4] = 80;
_distance[4][11] = 180;
_distance[4][8] = 90;
_distance[4][5] = 140;
_distance[5][9] = 70;
_distance[6][7] = 220;
_distance[6][10] = 50;
_distance[7][10] = 210;
_distance[7][14] = 90;
_distance[7][16] = 260;
_distance[8][11] = 110;
_distance[8][9] = 60;
_distance[9][11] = 110;
_distance[10][17] = 190;
_distance[10][13] = 50;
_distance[11][16] = 80;
_distance[11][12] = 90;
_distance[12][16] = 100;
_distance[13][17] = 160;
_distance[13][18] = 170;
_distance[13][15] = 120;
_distance[13][14] = 190;
_distance[14][15] = 80;
_distance[14][16] = 210;
_distance[15][18] = 140;
_distance[15][20] = 200;
_distance[15][21] = 170;
_distance[16][21] = 200;
_distance[16][23] = 80;
_distance[17][25] = 60;
_distance[17][18] = 70;
_distance[18][26] = 70;
_distance[18][19] = 120;
_distance[19][20] = 60;
_distance[20][21] = 100;
_distance[20][22] = 110;
_distance[20][27] = 130;
_distance[20][28] = 120;
_distance[21][22] = 90;
_distance[22][29] = 120;
_distance[22][30] = 110;
_distance[22][24] = 110;
_distance[23][24] = 80;
_distance[24][30] = 40;
_distance[25][26] = 80;
_distance[26][27] = 80;
_distance[28][29] = 80;
_distance[29][31] = 180;
_distance[29][30] = 100;
_distance[30][31] = 100;
}
void AdjacencyList::ShortestPath_Floyd(GraphAdjList *G, int P[32][32], int D[32][32]) {
//初始化D与P
for (int v = 0; v < G->numVertexes; ++v)
{
for (int w = 0; w < G->numVertexes; ++w)
{
if(_distance[v][w]==0&&v!=w){
_distance[v][w] = 10000;
}
D[v][w] = _distance[v][w];
P[v][w] = w;
}
}
for (int k = 0; k < G->numVertexes; ++k)
{
for (int v = 0; v < G->numVertexes; ++v)
{
for (int w = 0; w < G->numVertexes; ++w)
{
if (D[v][w] > D[v][k] + D[k][w])
{
D[v][w] = D[v][k] + D[k][w];
P[v][w] = P[v][k];
}
}
}
}
}
void AdjacencyList::ShowShortestResult(int originPos,int endPos) {
int temp;
cout << "地点" << _mapName[originPos] << "到地点" << _mapName[endPos] << "最短距离为" << ShortestPathvalue[originPos][endPos] << endl;
temp = ShortestPathmatrix[originPos][endPos];
cout<<"具体路径为:"<<_mapName[originPos]<<"——>";
while (temp!=endPos){
cout<<_mapName[temp]<<"——>";
temp = ShortestPathmatrix[temp][endPos];
}
cout<<_mapName[endPos]<>originPos>>endPos;
adjacencyList.ShowShortestResult(originPos,endPos);
}
return 0;
}