Java NIO Buffer核心源码解读与分析
关于Java NIO Buffer中的3个重要状态属性:position,limit,capacity。
Buffer基本简介
抽象类Buffer源码中关于Buffer的介绍如下:
A container for data of a specific primitive type.
A buffer is a linear, finite sequence of elements of a specific
primitive type.
Buffer是一个关于基本数据类型线性的,有限序列的容器。
the essential properties of a buffer are its capacity, limit, and position:
一个Buffer的最基本属性是capacity、limit 和 position。
Capacity解读
A buffer's capacity is the number of elements it contains.The
capacity of a buffer is never negative and never changes.
capacity是一个buffer所能容纳的元素的个数,也就是Buffer的最大容量。Buffer的capacity不能是负的也是不可变的。
limit 解读
A buffer's limit is the index of the first element that should not
be read or written. A buffer's limit is never negative and is never
greater than its capacity.
limit是缓冲区中第一个不可读写的元素的下标,也即limit后的数据不可进行读写。limit不能为负,也不能大于capacity。
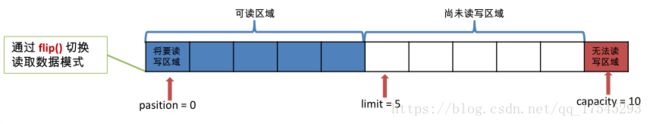
如上图所示,声明了一个包含10个元素大小的Buffer。调用flip()方法切换到读取模式后,从position= 0 到limit =5(不包含5)这之间表示数据可读写区域,上图的Buffer中,第一个不可读写的下标为5,也即limit所指的位置。
position 解读
A buffer's position is the index of the next element to be read or written.
A buffer's position is never negative and is never greater than its limit.
缓冲区的position 表示下一个元素即将读或者写的下标。position 不能为负也不能大于limit。
好了, 介绍完了一些基本属性,我们再来看一些核心方法。
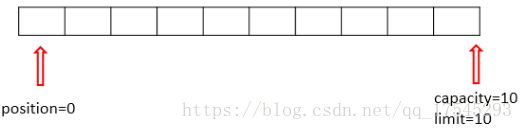
allocate()
allocate()是初始化缓冲区的一个方法。如下代码所示:
IntBuffer buffer = IntBuffer.allocate(10);
初始化了一个能容纳10个int类型元素的缓冲区。进入这个方法的源码一探究竟:
public static IntBuffer allocate(int capacity) {
if (capacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
return new HeapIntBuffer(capacity, capacity);
}
可以看到,在方法内部又调用了HeapIntBuffer(capacity, capacity)的构造方法进行初始化操作,这一步操作把limit设置为跟capacity一样的值,即 limit = capacity = 10。再进入HeapIntBuffer()里面看一下:
HeapIntBuffer(int cap, int lim) { // package-private
super(-1, 0, lim, cap, new int[cap], 0);
/*
hb = new int[cap];
offset = 0;
*/
}
在这里调用了父类构造,mark默认值为-1,postition默认值为0,通过new int[cap] 可以发现缓存区底层是利用数组进行实现。
进入父类的构造方法:
Buffer(int mark, int pos, int lim, int cap) { // package-private
if (cap < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative capacity: " + cap);
this.capacity = cap;
limit(lim);
position(pos);
if (mark >= 0) {
if (mark > pos)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("mark > position: ("
+ mark + " > " + pos + ")");
this.mark = mark;
}
}
在父类的构造方法里,我们看到capacity是不允许小于0的,并且会把我们声明的cap大小赋值给全局capacity。然后又调用了limit()、position()这两个方法,分别进入两个方法看一下:
- limit(lim)
public final Buffer limit(int newLimit) {
if ((newLimit > capacity) || (newLimit < 0))
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
limit = newLimit;
if (position > limit) position = limit;
if (mark > limit) mark = -1;
return this;
}
在if判断条件里,可以知道limit不允许大于capacity或者小于0,同时给全局limit赋值。根据if (position > limit) position = limit;,可以说明position<=limit。
- position(pos)
public final Buffer position(int newPosition) {
if ((newPosition > limit) || (newPosition < 0))
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
position = newPosition;
if (mark > position) mark = -1;
return this;
}
这里主要是对position的一些界值判断,然后赋值操作。
切换读写的flip()方法
一般是通过buffer.flip(); 实现状态的反转,读写的切换。
然后进入方法分如下:
public final Buffer flip() {
limit = position;
position = 0;
mark = -1;
return this;
}
可以看到,执行flip读写切换时,将limit设置在了当前position的下标位置;然后position置为缓冲区第一个元素的下标位置;清空mark。
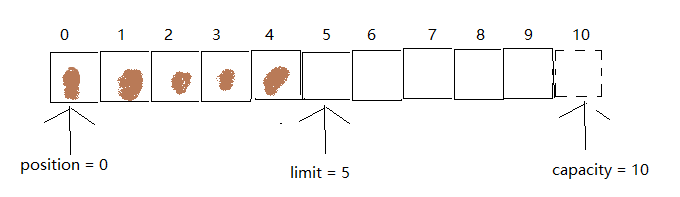
代码示例解读 flip 操作:
- 通过put()向缓冲区写入五个数据
for(int i = 0;i < 5; ++i){
int randomNumber = new SecureRandom().nextInt(20);
buffer.put(randomNumber);
}