在之前的深度学习笔记(一):logistic分类 中,已经描述了普通logistic回归以及如何将logistic回归用于多类分类。在这一节,我们再进一步,往其中加入隐藏层,构建出最简单的神经网络
2.简单神经网络及后向传播算法
2.1 大概描述和公式表达
神经网络的大概结构如图所示,

从左往右,分别是输入层,隐藏层,输出层,分别记为
x ,
h ,
y . 从输入层到隐藏层的矩阵记为
Whx , 偏置向量
bh ; 从隐藏层到输出层的矩阵记为
Wyh , 偏置向量为
by . 那么根据之前logistic分类的公式稍作扩展,不难得到
hz=Whxx+bhha=σ(hz)yz=Wyhha+byya=σ(yz)
其实就是两层logistic分类的堆叠,将前一个分类器的输出作为后一个的输入。得到输出
ya 以后的判断方法也比较类似,哪项最高就判定属于哪一类。真正值得写一下的是神经网络中的后向算法。按照传统的logistic分类,只能做到根据误差来更新
Wyh 和
by 那么如何来更新从输入层到隐藏层的参数
Whx 和
bh 呢?这就要用到后向算法了。所谓后向算法,就是指误差由输出层逐层往前传递,进而逐层更新参数矩阵和偏执向量。后向算法的核心其实就4个字:链式法则。首先来看
Wyh 和
by 的更新
C=12(ya−y)2∂C∂yz=C′σ′(yz)=(ya−y).×a.×(1−a)∂C∂Wyh=∂C∂yz∂yz∂Wyh=C′σ′(yz)hTa∂C∂by=∂C∂yz∂yz∂by=C′σ′(yz)
其实在上面的公式中,已经用到了链式法则。 类似的,可以得到
∂C∂ha=∂C∂yz∂yz∂ha=WTyh[C′σ′(yz)]∂C∂Whx=∂C∂ha∂ha∂W=[∂C∂haσ′(hz)]xT∂C∂bh=∂C∂ha∂ha∂bh=[∂C∂haσ′(hz)]
可以看到,在
Whx 和
bh 的计算中都用到了
∂C∂ha 这可以看成由输出层传递到中间层的误差。那么在获得了各参数的偏导数以后,就可以对参数进行修正了
Wyh:=Wyh−η∂C∂Wyhby:=by−η∂C∂byWhx:=Whx−η∂C∂Whxbh:=bh−η∂C∂bh
2.2 神经网络的简单实现
为了加深印象,我自己实现了一个神经网络分类器,分类效果如下图所示
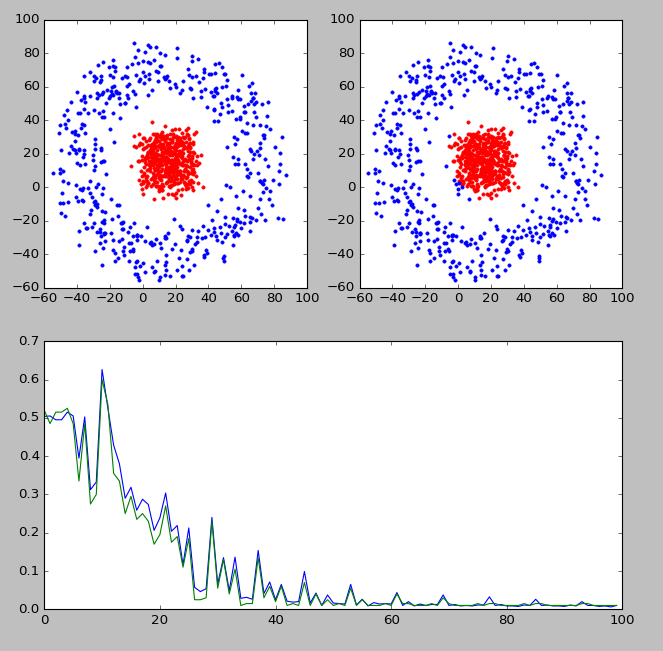
上图中,左上角显示的是实际的分类,右上角显示的是分类器判断出的各点分类。靠下的图显示的是分类器的判断准确率随迭代次数的变化情况。可以看到,经过训练以后,分类器的判断准确率还是可以的。
下面是代码部分
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
import math
def gen_sample():
data = []
radius = [0,50]
for i in range(1000):
catg = random.randint(0,1)
r = random.random()*10
arg = random.random()*360
len = r + radius[catg]
x_c = math.cos(math.radians(arg))*len
y_c = math.sin(math.radians(arg))*len
x = random.random()*30 + x_c
y = random.random()*30 + y_c
data.append((x,y,catg))
return data
def plot_dots(data):
data_asclass = [[] for i in range(2)]
for d in data:
data_asclass[int(d[2])].append((d[0],d[1]))
colors = ['r.','b.','r.','b.']
for i,d in enumerate(data_asclass):
nd = np.array(d)
plt.plot(nd[:,0],nd[:,1],colors[i])
plt.draw()
def train(input, output, Whx, Wyh, bh, by):
"""
完成神经网络的训练过程
:param input: 输入列向量, 例如 [x,y].T
:param output: 输出列向量, 例如[0,1,0,0].T
:param Whx: x->h 的参数矩阵
:param Wyh: h->y 的参数矩阵
:param bh: x->h 的偏置向量
:param by: h->y 的偏置向量
:return:
"""
h_z = np.dot(Whx, input) + bh
h_a = 1/(1+np.exp(-1*h_z))
y_z = np.dot(Wyh, h_a) + by
y_a = 1/(1+np.exp(-1*y_z))
c_y = (y_a-output)*y_a*(1-y_a)
dWyh = np.dot(c_y, h_a.T)
dby = c_y
c_h = np.dot(Wyh.T, c_y)*h_a*(1-h_a)
dWhx = np.dot(c_h,input.T)
dbh = c_h
return dWhx,dWyh,dbh,dby,c_y
def test(train_set, test_set, Whx, Wyh, bh, by):
train_tag = [int(x) for x in train_set[:,2]]
test_tag = [int(x) for x in test_set[:,2]]
train_pred = []
test_pred = []
for i,d in enumerate(train_set):
input = train_set[i:i+1,0:2].T
tag = predict(input,Whx,Wyh,bh,by)
train_pred.append(tag)
for i,d in enumerate(test_set):
input = test_set[i:i+1,0:2].T
tag = predict(input,Whx,Wyh,bh,by)
test_pred.append(tag)
train_err = 0
test_err = 0
for i in range(train_pred.__len__()):
if train_pred[i]!=int(train_tag[i]):
train_err += 1
for i in range(test_pred.__len__()):
if test_pred[i]!=int(test_tag[i]):
test_err += 1
train_ratio = train_err / train_pred.__len__()
test_ratio = test_err / test_pred.__len__()
return train_err,train_ratio,test_err,test_ratio
def predict(input,Whx,Wyh,bh,by):
h_z = np.dot(Whx, input) + bh
h_a = 1/(1+np.exp(-1*h_z))
y_z = np.dot(Wyh, h_a) + by
y_a = 1/(1+np.exp(-1*y_z))
tag = np.argmax(y_a)
return tag
if __name__=='__main__':
input_dim = 2
output_dim = 2
hidden_size = 200
Whx = np.random.randn(hidden_size, input_dim)*0.01
Wyh = np.random.randn(output_dim, hidden_size)*0.01
bh = np.zeros((hidden_size, 1))
by = np.zeros((output_dim, 1))
data = gen_sample()
plt.subplot(221)
plot_dots(data)
ndata = np.array(data)
train_set = ndata[0:800,:]
test_set = ndata[800:1000,:]
train_ratio_list = []
test_ratio_list = []
for times in range(10000):
i = times%train_set.__len__()
input = train_set[i:i+1,0:2].T
tag = int(train_set[i,2])
output = np.zeros((2,1))
output[tag,0] = 1
dWhx,dWyh,dbh,dby,c_y = train(input,output,Whx,Wyh,bh,by)
if times%100==0:
train_err,train_ratio,test_err,test_ratio = test(train_set,test_set,Whx,Wyh,bh,by)
print('times:{t}\t train ratio:{tar}\t test ratio: {ter}'.format(tar=train_ratio,ter=test_ratio,t=times))
train_ratio_list.append(train_ratio)
test_ratio_list.append(test_ratio)
for param, dparam in zip([Whx, Wyh, bh, by],
[dWhx,dWyh,dbh,dby]):
param -= 0.01*dparam
for i,d in enumerate(ndata):
input = ndata[i:i+1,0:2].T
tag = predict(input,Whx,Wyh,bh,by)
ndata[i,2] = tag
plt.subplot(222)
plot_dots(ndata)
plt.subplot(212)
plt.plot(train_ratio_list)
plt.plot(test_ratio_list)
plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144

