Ansible自动部署(基础篇)
Ansible自动部署(基础篇)
一、ansible简介
1、ansible介
Ansible这个名字来源于科幻小说,是一种超光速通讯设备。在Linux中,ansible是新出现的自动化运维工具,基于Python开发,集合了众多运维工具(puppet、cfengine、chef、func、fabric)的优点,实现了批量系统配置、批量程序部署、批量运行命令等功能。支持linux、BSD、MacOS、等,支持openstack 、docker等结合使用。

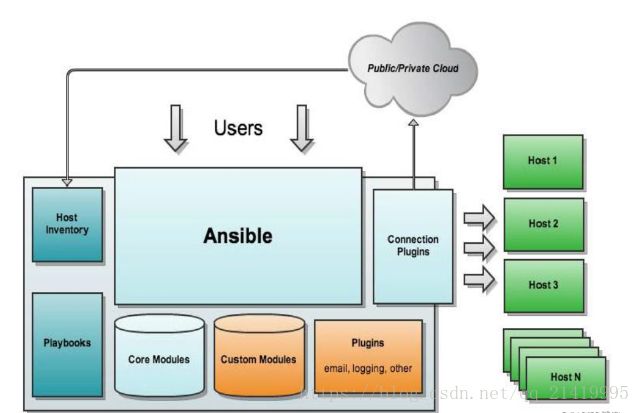
2、ansible架构
2.1 Ansible核心组件说明:
- Ansible:Ansible的核心程序
- Host Inventory:记录了每一个由Ansible管理的主机信息,信息包括ssh端口,root帐号密码,ip地址等等。可以通过file来加载,可以通过CMDB加载
- Playbooks:YAML格式文件,多个任务定义在一个文件中,使用时可以统一调用,“剧本”用来定义那些主机需要调用那些模块来完成的功能.
- Core Modules:Ansible执行任何管理任务都不是由Ansible自己完成,而是由核心模块完成;Ansible管理主机之前,先调用core Modules中的模块,然后指明管理Host Lnventory中的主机,就可以完成管理主机。
- Custom Modules:自定义模块,完成Ansible核心模块无法完成的功能,此模块支持任何语言编写。
- Connection Plugins:连接插件,Ansible和Host通信使用
2.2 Ansible工作流程:
Ansile----->host(主机资源定义)------>模块(核心模块/自定义模块)------>插件(ssh)
2.3 Ansible 特性
- no agent 不需要安装客户端(支持ssh)
- no server 不需要启动服务(ansible)
- 基于模块工作,可以使用任意语言开发模块
- 基于ssh工作( 基于密钥认证)
- YAML格式,编排任务,支持丰富的数据结构(剧本playbook)
- 使用python编写,维护简单
二、Ansible安装部署
1、ansible安装
- 升级ssh
[root@ansible ~]# yum update openssh
...
Updated:
openssh.x86_64 0:5.3p1-123.el6_9
Dependency Updated:
openssh-clients.x86_64 0:5.3p1-123.el6_9
openssh-server.x86_64 0:5.3p1-123.el6_9
Complete!
//升级完成- 安装ansible
[root@ansible ~]# yum install -y ansible
......
Installed:
ansible.noarch 0:2.5.5-1.el6
Dependency Installed:
PyYAML.x86_64 0:3.10-3.1.el6
libyaml.x86_64 0:0.1.3-4.el6_6
python-babel.noarch 0:0.9.4-5.1.el6
python-crypto.x86_64 0:2.0.1-22.el6
python-crypto2.6.x86_64 0:2.6.1-2.el6
python-httplib2.noarch 0:0.7.7-1.el6
python-jinja2-26.noarch 0:2.6-3.el6
python-keyczar.noarch 0:0.71c-1.el6
python-markupsafe.x86_64 0:0.9.2-4.el6
python-paramiko.noarch 0:1.7.5-4.el6_9
python-pyasn1.noarch 0:0.0.12a-1.el6
python-setuptools.noarch 0:0.6.10-4.el6_9
python-simplejson.x86_64 0:2.0.9-3.1.el6
python-six.noarch 0:1.9.0-2.el6
sshpass.x86_64 0:1.06-1.el6
Complete!
//安装完成2、ansible配置使用
2.1 ansible配置文件
[root@ansible ~]# rpm -qc ansible //查看有哪些配置文件
/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
/etc/ansible/hosts //主机配置文件2.2 ansible免密连接认证
- 方法一:配置ssh密钥
//如果主机数量较少,可以直接复制
[root@ansible ~]# ssh-keygen -t rsa
[root@ansible ~]# ssh-copy-id -i 192.168.137.133
//如果主机较多,可以使用批量复制的方式
1、解决连接新主机时,进行公钥确认问题
方法一:在配置文件中修改 (当前用户家目录.ssh/config,没有则自行创建)
StrictHostKeyChecking=no
方法二:在复制密钥时增加参数
ssh-copy-id -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@IP
2、解决验证时,非交互式输入密码问题
sshpass命令(若系统没有,需要自行安装)
sshpass -p 'YOUR_PASSWORD' ssh-copy-id root@IP
3、设置完成后用脚本批量传递秘钥
1 #!/bin/bash
2
3 for host in $(cat remote-hosts)
4 do
5 /usr/bin/sshpass -p '123456' ssh-copy-id root@${host}
6 done
//创建一个文件remote-hosts ,将主机ip放入文件中
//如果密码每台都不同,需要将密码用正则取出,传递给变量注意: 如果已经将StrictHostKeyChecking=no 写入配置文件/root/.ssh/config 中,就不要在命令行中再写一次,可能会报错,错误如下:
command-line: line 0: Bad configuration option: exec
command-line: line 0: Bad configuration option: exec- 方法二:在ansible的hosts中设定
[web]
server01-137-14.yu.net ansible_ssh_host=192.168.137.14 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=123456
//指定域名对应的IP,用户和密码,这样就不用做ssh免密了
//注意StrictHostKeyChecking=no这项也要配置,才能通过,这项在/etc/ssh/ssh_config中也有
# StrictHostKeyChecking ask 改为
StrictHostKeyChecking no
//测试
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m ping
server01-137-14.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}2.3 ansible 免密认证可能出现的问题
- 初次使用ansible出现的问题
[root@ansible ~]# ansible mysql -m ping
paramiko: The authenticity of host 'mysql02.yu.net' can't be established.
The ssh-rsa key fingerprint is 4a6aab0478058f324688426c732c660e.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?
yes
paramiko: The authenticity of host 'mysql03.yu.net' can't be established.
The ssh-rsa key fingerprint is 0134343743600531ff38afc7b4851e0f.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?
yes
paramiko: The authenticity of host 'mysql01.yu.net' can't be established.
The ssh-rsa key fingerprint is 930535c64203f5681b0c5826175fbb74.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?
mysql02.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
mysql03.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
mysql01.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
出现问题原因:
虽然配置了ssh免密,且ssh免密没有问题,但是初次使用ansible还是需要确认主机,也就是说缺少
/root/.ssh/known_hosts这个文件。所以在第一次部署时必须确认一次。如果不想手动确认,可以用expect编写脚本来确认。解决方案
1 #!/usr/bin/bash
2 # copy the ssh-key to all hosts
3 #$1=host_name $2=password_server
4 #v3
5
6 for host in `grep "$1" /etc/hosts |awk '{print $1}'`
7 do
8 /usr/bin/sshpass -p "$2" ssh-copy-id root@${host}
9
10 done
11
12 /usr/bin/expect <<-EOF
13 spawn /usr/bin/ansible $1 -m ping
14 expect {
15 "yes/no" { send "yes\r"; exp_continue }
16 }
17 expect eof
18 EOF
1. 在执行完分发秘钥的任务后,再执行一次ansible的ping模块,同时使用expect来自动答复,经过这个过程后,主机间就会完成认证。
2. expect 需要自行安装。
3. 注意命令使用绝对路径。2.4 ansible配置
- 配置ansible hosts文件(不是/etc/hosts文件)
1 # This is the default ansible 'hosts' file .
2 #
3 # It should live in /etc/ansible/hosts
4 #
......
45 [web]
46 server01-137-14.yu.net ansible_ssh_host=192.168.137.14 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=123456
//web是hosts文件中主机标签,可以是IP,也可以是主机名,后面可以加各个配置项- 测试连接(通过模块)
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m ping
server01-137-14.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
注意:
1、 测试时使用的ping是指ansible的ping模块,而不是ping命令。
2、这里测试的只是远程主机是否存在。
三、ansible实践
1、实验环境
| 主机名 | IP | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| ansible.yu.net | 192.168.137.133 | |
| mysql01.yu.net | 192.168.137.139 | |
| mysql02.yu.net | 192.168.137.140 | |
| mysql03.yu.net | 192.168.137.137 | |
| web01.yu.net | 192.168.137.135 | |
| web02.yu.net | 192.168.137.136 |
注: 系统版本是CentOS release 6.5 (Final)
2、ansible的命令行使用方式
2.1 命令格式
# ansible <PATTERN> -m <module_name> -a <arguments>2.2 PATTERN 写法
- 某一个主机组 如:mysql
[root@ansible ~]# ansible mysql -m ping
mysql03.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
mysql01.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
mysql02.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}- 所有主机 all
[root@ansible scripts]# ansible all -m ping
web01.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
web02.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
mysql02.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
mysql01.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
mysql03.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
- 多个主机或IP用“:”隔开
[root@ansible scripts]# ansible mysql03.yu.net:mysql02.yu.net -m ping
mysql03.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
mysql02.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}- 用通配符匹配
[root@ansible scripts]# ansible mysql*.yu.net -m ping
mysql03.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
mysql01.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
mysql02.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}注:
1、这些匹配到的主机一定是/etc/ansible/hosts 文件里有的才能匹配到。
2、推荐用组的形式管理主机,更加方便。
2.3 模块使用方法
2.3.1 查看支持的模块
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc -l
a10_server
a10_server_axapi3
a10_service_group
a10_virtual_server
accelerate
...2.3.2 查看模块使用方法
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc a10_server
> A10_SERVER (/usr/lib/python2.6/site-packages/an
Manage SLB (Server Load Balancer) server obj
Networks devices via aXAPIv2.
OPTIONS (= is mandatory):
- client_cert
PEM formatted certificate chain file to be u
authentication. This file can also include t
and if the key is included, `client_key' is
[Default: (null)]
...2.3.3 ping 模块
- 作用:测试管理端与被管理端连接状况(并不等于ping命令)
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m ping
web01.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
web02.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}2.3.4 user模块
- 作用:管理远程主机上用户的账号
- 参数:
- name:指定要管理的账号名称
- state:present(创建)|absent(删除)
- system:yes|no 是否为系统账号
- uid:指明用户UID
- group:指明用户的基本组
- groups:指明用户附加组
- shell: 指明默认shell
- home:指明用户家目录
- move_home:yes|no 当home设定了家目录,如果创建的家目录已存在,是否将家目录移动
- password:指明用户密码
- comment:指明用户注释信息
- remove:删除用户时,是否要删除用户家目录
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m user -a 'name=Tom uid=666 shell=/bin/bash state=present comment="user Tom"'
web01.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"comment": "user Tom",
"create_home": true,
"group": 666,
"home": "/home/Tom",
"name": "Tom",
"shell": "/bin/bash",
"state": "present",
"system": false,
"uid": 666
}
web02.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"comment": "user Tom",
"create_home": true,
"group": 666,
"home": "/home/Tom",
"name": "Tom",
"shell": "/bin/bash",
"state": "present",
"system": false,
"uid": 666
}
//创建成功
//检查
[root@web01 ~]# tail -3 /etc/passwd
postfix:x:89:89::/var/spool/postfix:/sbin/nologin
sshd:x:74:74:Privilege-separated SSH:/var/empty/sshd:/sbin/nologin
Tom:x:666:666:user Tom:/home/Tom:/bin/bash
[root@web02 ~]# tail -3 /etc/passwd
postfix:x:89:89::/var/spool/postfix:/sbin/nologin
sshd:x:74:74:Privilege-separated SSH:/var/empty/sshd:/sbin/nologin
Tom:x:666:666:user Tom:/home/Tom:/bin/bash2.3.5 group 模块
- 作用: 用来添加或删除远端主机的用户组
- 参数:
- name: 被管理的组名
- state: present(添加)|absent (删除) 不指名,默认为添加
- gid: 指明组ID
- system: yes|no 是否为系统组
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m group -a 'name=animal gid=555 state=present'
web01.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"gid": 555,
"name": "animal",
"state": "present",
"system": false
}
web02.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"gid": 555,
"name": "animal",
"state": "present",
"system": false
}
[root@web01 ~]# tail -3 /etc/group
sshd:x:74:
Tom:x:666:
animal:x:555:Tom
[root@web02 ~]# tail -3 /etc/group
sshd:x:74:
Tom:x:666:
animal:x:555:Tom
2.3.6 file模块
- 作用:用于设定远程主机上的文件属性(不能创建文件,但是可以创建文件夹和软链接)
- 参数:
- path:指明哪个文件
- src: 用于path指明的文件是软链接文件,其对应的源文件是谁,必须要在state=link时才有用
- state:directory|link|absent|file 指出创建的文件是目录还是软连接
- owner:属主
- group: 属组
- mode:文件权限
需求:在/tmp目录中创建/root/file_source的软连接文件file_dest,并修改其文件属性为755
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web01.yu.net -m file -a 'path=/tmp/file_dest state=link src=/root/file_source mode=755'
web01.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"dest": "/tmp/file_dest",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0777",
"owner": "root",
"size": 17,
"src": "/root/file_source",
"state": "link",
"uid": 0
}
//web01上检查
[root@web01 ~]# cd /tmp/
[root@web01 tmp]# ll
total 0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 17 Aug 23 11:54 file_dest -> /root/file_source // 测试成功
-rw-------. 1 root root 0 Jul 14 14:15 yum.log
2.3.7 copy模块
- 作用:拷贝ansible管理端文件到远程主机指定位置
- 参数:
- dest: 目标目录位置,使用绝对路径,如果源是目录,目标也要是目录,如果文件已经存在,会覆盖原有内容
- src: 指源路径(管理端)如果源路径是目录,目标也要是目录
- mode: 指明文件权限
- owner: 指明属主
- group: 指明属组
- content: 指明复制到目标主机上的内容,不能与src一起使用,相当于复制content指明的数据,到目标文件中。
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m copy -a 'src=/root/ansible_test.txt dest=/tmp/ mode=755 owner=Tom'
web01.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "fb59b25b7fe6b4ca0c6a48acd125b4052deab7e9",
"dest": "/tmp/ansible_test.txt",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "6031be4ce171ac11dd7fd9df985ee4f3",
"mode": "0755",
"owner": "Tom",
"size": 21,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1535008709.0-164426125312085/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 666
}
web02.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "fb59b25b7fe6b4ca0c6a48acd125b4052deab7e9",
"dest": "/tmp/ansible_test.txt",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "6031be4ce171ac11dd7fd9df985ee4f3",
"mode": "0755",
"owner": "Tom",
"size": 21,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1535008709.0-206707679338359/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 666
}
//测试
[root@web01 tmp]# ll
total 4
-rwxr-xr-x 1 Tom root 21 Aug 23 15:18 ansible_test.txt
[root@web02 tmp]# ll
total 4
-rwxr-xr-x 1 Tom root 21 Aug 23 15:18 ansible_test.txt
//直接写入内容
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m copy -a 'content="hello ansible" dest=/tmp/file1 mode=755 owner=Tom'
web02.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "7b320b1dc0c867516cf00728df488daa3532bc1f",
"dest": "/tmp/file1",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "37bc018071eae9a0e879c31b2f9aa554",
"mode": "0755",
"owner": "Tom",
"size": 13,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1535010466.83-147620108230697/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 666
}
web01.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "7b320b1dc0c867516cf00728df488daa3532bc1f",
"dest": "/tmp/file1",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "37bc018071eae9a0e879c31b2f9aa554",
"mode": "0755",
"owner": "Tom",
"size": 13,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1535010466.82-92220590094473/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 666
}
[root@web01 tmp]# ls
ansible_test.txt file1 file_dest yum.log
[root@web02 tmp]# ls
ansible_test.txt file1 yum.log
[root@web02 tmp]# cat file1
hello ansible[root@web02 tmp]# 2.3.8 shell 模块
- 作用:在被管理端执行shell命令,支持重定向,管道符
- 参数:
- chdir:执行命令前切换到指定目录
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m shell -a "ps -ef |grep httpd"
web01.yu.net | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
root 2249 2248 0 16:01 pts/1 00:00:00 /bin/sh -c ps -ef |grep httpd
root 2251 2249 0 16:01 pts/1 00:00:00 grep httpd
web02.yu.net | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
root 1903 1902 0 16:01 pts/1 00:00:00 /bin/sh -c ps -ef |grep httpd
root 1905 1903 0 16:01 pts/1 00:00:00 grep httpd注: 可以与下面的command对比记忆
2.3.9 command 模块
- 作用:在被管理端执行命令(不支持管道符和重定向)
- 参数:
- chdir:执行命令前切换到指定目录
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web01.yu.net -m command -a "ls chdir=/root"
web01.yu.net | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
anaconda-ks.cfg
file_source
install.log
install.log.syslog2.3.10 yum模块
- 作用:基于yum机制,对远程主机管理程序包
- 参数:
- name:包名,可以指定版本,默认为最新版
- state:present(安装)|lastest(最新版本)|absent(卸载)
- disablerepo: 在用yum安装时,临时禁用某个仓库,仓库ID(可以用yum repolist查看)
- enablerepo: 在用yum安装时,临时启用某个仓库
- disable_gpg_check: yes|no 是否启用gpgcheck
[root@ansible yum.repos.d]# ansible web -m yum -a 'name=nginx state=present '
web02.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
...
web01.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
...
//检查
[root@ansible yum.repos.d]# ansible web -m shell -a 'rpm -q nginx '
[WARNING]: Consider using the yum, dnf or zypper module rather than running rpm. If you need to use
command because yum, dnf or zypper is insufficient you can add warn=False to this command task or set
command_warnings=False in ansible.cfg to get rid of this message.
web02.yu.net | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
nginx-1.10.2-1.el6.x86_64
web01.yu.net | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
nginx-1.10.2-1.el6.x86_64
//安装成功2.3.11 service 模块
- 作用:远程管理主机上的服务模块
- 参数:
- name :服务名
- state:started|stopped|restarted
- enabled:yes|no 是否开机启动
- runlevel : 开机启动运行在哪些级别下
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m service -a 'name=nginx state=started enabled=yes runlevel=35'
web01.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"enabled": true,
"name": "nginx",
"state": "started"
}
web02.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"enabled": true,
"name": "nginx",
"state": "started"
}
//检查
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m shell -a 'ps -ef |grep 80'
web01.yu.net | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
root 803 2 0 10:05 ? 00:00:00 [ipoib]
root 2718 2717 0 17:36 pts/1 00:00:00 /bin/sh -c ps -ef |grep 80
root 2720 2718 0 17:36 pts/1 00:00:00 grep 80
web02.yu.net | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
root 2280 2279 0 17:36 pts/1 00:00:00 /bin/sh -c ps -ef |grep 80
root 2281 2280 0 17:36 pts/1 00:00:00 ps -ef
root 2282 2280 0 17:36 pts/1 00:00:00 grep 80
2.3.12 Uri模块
- 作用:用于直接请求web服务器某个网页
- 参数:
- url :指明请求的url路径
- user: 请求的url如果需要认证,认证的用户名是什么
- password: 请求的url如果需要认证,认证的密码是什么
- method: 指明请求方式,如GET, POST, PUT, HEAD, DELETE, OPTIONS, PATCH, TRACE, CONNECT, REFRESH(必须大写)
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m uri -a 'url=http://192.168.137.135 method=GET'
web02.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"accept_ranges": "bytes",
"changed": false,
"connection": "close",
"content_length": "3698",
"content_type": "text/html",
"cookies": {},
"cookies_string": "",
"date": "Fri, 24 Aug 2018 00:49:49 GMT",
"etag": "\"58173b0b-e72\"",
"last_modified": "Mon, 31 Oct 2016 12:37:31 GMT",
"msg": "OK (3698 bytes)",
"redirected": false,
"server": "nginx/1.10.2",
"status": 200,
"url": "http://192.168.137.135"
}
web01.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"accept_ranges": "bytes",
"changed": false,
"connection": "close",
"content_length": "3698",
"content_type": "text/html",
"cookies": {},
"cookies_string": "",
"date": "Fri, 24 Aug 2018 00:49:49 GMT",
"etag": "\"58173b0b-e72\"",
"last_modified": "Mon, 31 Oct 2016 12:37:31 GMT",
"msg": "OK (3698 bytes)",
"redirected": false,
"server": "nginx/1.10.2",
"status": 200,
"url": "http://192.168.137.135"
}
2.3.13 cron模块
- 作用:设置计划任务
- 参数:
- minute,hour,day,mouth,weekday: 分别对应计划任务的分,时,日,月,周(要分开写,不能写一行)
- reboot : 指明计划任务的执行时间为每次重启后
- name:为计划任务起名,每个任务名称不能一样
- job: 执行的任务是什么,当state=present时才有意义
- state:present|absent 表示任务是创建还是删除,present表示创建,absent是删除,默认是present
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m cron -a 'minute=*/5 state=present name=date job="/usr/sbin/ntpdate 120.25.108.11 &>/dev/null"'
web02.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": [
"date"
]
}
web01.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": [
"date"
]
}
//检测
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m shell -a "crontab -l"
web01.yu.net | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
#Ansible: date
*/5 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate 120.25.108.11 &>/dev/null
web02.yu.net | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
#Ansible: date
*/5 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate 120.25.108.11 &>/dev/null
2.3.15 hostname 模块
- 作用:管理主机名
- 参数:
- name: 指明主机名(永久修改)
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web01.yu.net -m hostname -a 'name=web03.yu.net'
web01.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_domain": "yu.net",
"ansible_fqdn": "web03.yu.net",
"ansible_hostname": "web03",
"ansible_nodename": "web03.yu.net"
},
"changed": true,
"name": "web03.yu.net"
}2.3.16 script 模块
- 作用: 将管理端的脚本,移动到远端主机(不需指明路径),系统会自动移动,执行。一般是移动到
/root/.ansible/tmp下,然后自动给予其权限,然后再开个子shell运行,运行后删除脚本。
[root@ansible ~]# cat test.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo "hello,ansible" >/tmp/ansible_script.txt
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m script -a '/root/test.sh'
web02.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"rc": 0,
"stderr": "",
"stderr_lines": [],
"stdout": "",
"stdout_lines": []
}
web01.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"rc": 0,
"stderr": "",
"stderr_lines": [],
"stdout": "",
"stdout_lines": []
}
//测试
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m shell -a 'cat /tmp/ansible_script.txt'
web02.yu.net | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
hello,ansible
web01.yu.net | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
hello,ansible2.3.17 setup 模块
- 作用: 收集远程主机信息(内核,操作系统,cpu等),需要时,直接调用即可
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m setup > /tmp/setup.txt
web01.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_all_ipv4_addresses": [
"192.168.137.135"
],
"ansible_all_ipv6_addresses": [
"fe80::20c:29ff:fee4:b423"
]
"ansible_apparmor": {
"status": "disabled"
...2.3.18 fetch 模块
- 作用:从远程主机拉取数据
- 参数:
- dest: 从远程主机上拉取的文件存放在本地的位置,一般只能是目录
- src= : 指明远程主机上要拉取的文件,只能是文件,不能是目录
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m fetch -a 'src=/etc/hosts dest=/root'
web01.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "8a4e06f4db39707f47fa1db58954f977481fa2a8",
"dest": "/root/web01.yu.net/etc/hosts",
"md5sum": "4cab68d7daf7e70979423242114195c7",
"remote_checksum": "8a4e06f4db39707f47fa1db58954f977481fa2a8",
"remote_md5sum": null
}
web02.yu.net | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "74b152f8ef49444ceba5f20f44de736cb4662a47",
"dest": "/root/web02.yu.net/etc/hosts",
"md5sum": "07788d5144f7e4e69ab31ab1885ad86e",
"remote_checksum": "74b152f8ef49444ceba5f20f44de736cb4662a47",
"remote_md5sum": null
}
[root@ansible ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg install.log.syslog
ansible_test.txt test.sh
curl-test.sh web01.yu.net
install.log web02.yu.net3、playbook使用方法
3.1 playbook 介绍
Playbooks 是定义ansible任务的配置文件,可以将多个任务定义在一个剧本中,由ansible自动执行,剧本执行支持多个任务,可以由控制主机运行多个任务,同时对多台远程主机进行管理。
3.2 playbook 基础组件
- hosts: 运行指定任务的目标主机,多个主机用“:”分隔。
- remote_user:在远程主机上执行任务的用户,可以全局指定,也可以单个任务指定
- sudo_user: 表示sudo方式运行任务时,切换为哪个用户身份运行
- tasks: 任务列表
- handlers: 在发生改变时执行的操作
3.3 playbook 语法
- ansible-playbook –syntax-check test.yml 测试文件语法
- ansible-playbook –check test.yml 测试执行(不是正式执行)
3.4 playbook 案例
- 用于配置系统基本信息的playbook
---
- hosts: mysql
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: stop selinux
shell: setenforce 0
- name: configure the file of selinux config
- name: stop iptables
service: name=iptables state=stopped enabled=no
- name: copy rc.local
copy: src=/etc/rc.local dest=/etc/rc.local //若selinux未关,会报错
- name: copy hosts
copy: src=/etc/hosts dest=/etc/hosts
- name: make directory /mnt/dvd //若已存在,会报错
shell: mkdir /mnt/dvd
- name: mount CDrom //若已挂载,会报错
shell: mount /dev/sr0 /mnt/dvd
- name: rm /etc/yum.repos.d
shell: rm -rf /etc/yum.repos.d/
- name: configure yum
copy: src=/etc/yum.repos.d dest=/etc/yum.repos.d
- name: make memcache
shell: yum clean all & yum makecache
- name: install vim
yum: name=vim state=present
- name: install wget
yum: name=wget state=present
- name: install curl
yum: name=curl state=present
- name: install tree
yum: name=tree state=present
- name: install lrzsz telnet
yum: name=telnet state=present- 运行结果
[root@ansible ansible_playbook]# ansible-playbook os_init.yaml
PLAY [mysql] *******************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************************************
ok: [mysql01.yu.net]
ok: [mysql03.yu.net]
ok: [mysql02.yu.net]
TASK [stop iptables] ***********************************************************************************
ok: [mysql01.yu.net]
ok: [mysql03.yu.net]
ok: [mysql02.yu.net]
TASK [copy rc.local] ***********************************************************************************
changed: [mysql01.yu.net]
changed: [mysql02.yu.net]
changed: [mysql03.yu.net]
TASK [copy hosts] **************************************************************************************
changed: [mysql01.yu.net]
changed: [mysql02.yu.net]
changed: [mysql03.yu.net]
TASK [make directory /mnt/dvd] *************************************************************************
[WARNING]: Consider using the file module with state=directory rather than running mkdir. If you need
to use command because file is insufficient you can add warn=False to this command task or set
command_warnings=False in ansible.cfg to get rid of this message.
changed: [mysql01.yu.net]
changed: [mysql02.yu.net]
changed: [mysql03.yu.net]
......
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************************************
mysql01.yu.net : ok=12 changed=9 unreachable=0 failed=0
mysql02.yu.net : ok=12 changed=9 unreachable=0 failed=0
mysql03.yu.net : ok=12 changed=9 unreachable=0 failed=0
- 报错
TASK [copy rc.local] ***********************************************************************************
fatal: [mysql03.yu.net]: FAILED! => {"changed": false, "checksum": "ae15fe0530d07dd80da29903726da141617660be", "msg": "Aborting, target uses selinux but python bindings (libselinux-python) aren't installed!"}
fatal: [mysql01.yu.net]: FAILED! => {"changed": false, "checksum": "ae15fe0530d07dd80da29903726da141617660be", "msg": "Aborting, target uses selinux but python bindings (libselinux-python) aren't installed!"}
fatal: [mysql02.yu.net]: FAILED! => {"changed": false, "checksum": "ae15fe0530d07dd80da29903726da141617660be", "msg": "Aborting, target uses selinux but python bindings (libselinux-python) aren't installed!"}
//这个报错是因为selinux未关,如果关了以后,要重启机器