Spring boot成长系列三、Springboot配置文件详解(application.properties/application.yaml)(为什么Spring boot可以做到零配置)
前言:在使用Spring boot 的时候肯定听说过Spring boot可以做到零配置,其实创建Spring boot 确实可以做到零配置,它在内部其实帮你默认配置基础的参数,但是它确实配置方便,所以集成的配置参数都可以在Spring boot 提供的配置文件中自己设置,除了在Spring boot提供的配置文件中配置以为还可以做到使用java文件的方式去注册bean,这就可以做到了Spring boot的简化配置,不需要集成第三方功能的时候去单独写xml的bean。
1、Spring boot配置文件介绍
spring boot之所以能简化开发,其配置文件起到了很重要的作用,第三方集成配置都可以写在这个配置文件里面,这个配置文件有2个格式,application.properties和application.yaml(yml)都可以。下面来介绍2中配置文件的情况。
application.properties
格式:key-value
演示:
server.port=8080
logging.level.root=errorapplication.yaml(yml)
格式:类似于JSON格式的形式,因为这个格式就是JSON的超集
演示:
server:
port: 8080
logging:
level:
root: info个人比较喜欢下面这种有层级显示的格式,后面的例子就以下面这个层级的作演示。
2、通过不同的方式获取配置文件的自定义值
第一种:通过@Value注解获取配置文件里面的值
1、在配置文件里面创建你需要的数据
cx:
name: cx
age: 232、测试
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringbootConfigApplicationTests {
@Value("${cx.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${cx.age}")
private String age;
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
}
}第二种:通过@ConfigurationProperties注解获取配置文件里面的值生成对象
1、在配置文件里面创建你需要的对象数据
json:
str1: "双引号直接输出" #双引号字符串
str2: '单引号可以转义' #单引号字符串
boole: false #boolean值
intNum: 666 #整形
doubleScore: 88.88 #小数
list: #list集合
- one
- two
- two
arr: [1,2,2,3] #数组
map: {boy: 1, girl: 2} #map
person: #集合对象
- name: zhangsan
age: 18
- name: lisi
age: 192、创建实体类
@Data
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "json")
public class Cx {
private String str1;
private String str2;
private Boolean boole;
private Integer intNum;
private Double doubleScore;
private List list;
private Integer[] arr;
private Map map;
private List person;
} 3、测试
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@EnableConfigurationProperties({Cx.class}) //选择需要注册的类
public class SpringbootConfigApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Cx cx;
@Test
public void testConfig(){
System.out.println(cx);
}
}第三种:通过@PropertySource从指定的配置文件中读取,这个文件只能是以properties结尾的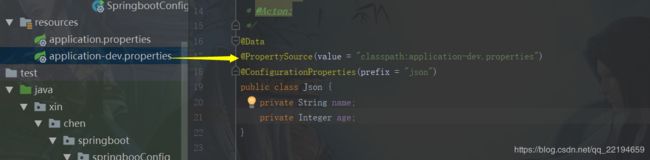
通过上面的几种情况,我们可以根据开发中的不同情况进行不同的选择。
@Value 简单快捷,适合少数配置,少数取值,而且支持的值的类型比较少
@ ConfigurationProperties,适合当做对象取值,多数取值,支持的类型较多,基本的类型都支持
@PropertySource,适合多个配置文件,从不同的配置文件里面加载不同的值
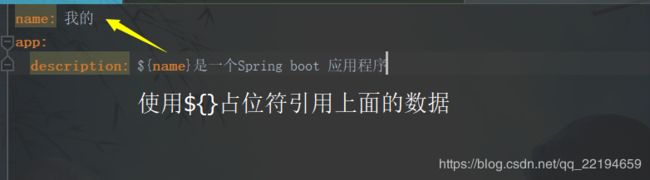
3、 配置文件中的占位符
4、配置文件中配置随机值
配置:
cx:
age: ${random.int(10)} #int值,后面括号是指多少以内
score: ${random.long(100)} #long值,后面括号是指多少以内
secretKey: ${random.value} #秘匙
uuid: ${random.uuid} #uuid测试:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringbootConfigApplicationTests {
@Value("${cx.age}")
private Integer age;
@Value("${cx.score}")
private String score;
@Value("${cx.secretKey}")
private String secretKey;
@Value("${cx.uuid}")
private String uuid;
@Test
public void testConfig(){
System.out.println("秘匙:" + secretKey + ",成绩:" + score + "年龄:" + age + ",uuid"+uuid);
}
}
5、配置多种不同的环境开发文件

这个就像找对象一样,是找个女朋友还是找老婆,找到谁我就娶谁(可以使用它里面的内容)