SpringMVC源码解析
SpringMVC源码解析
Spring Web MVC是基于Servlet API构建的原始Web框架,从一开始就包含在Spring框架中。
其正式名称“Spring Web MVC”来自它的源模块(Spring -webmvc)的名称,但它更常见的名称是“Spring MVC”。
本节介绍Spring Web MVC。
(1)servlet3.0新特性
通过上图可以知道,servlet3.0给我们提供了一个非常牛逼的规范,只要我们按照这个规范,我们就能在tomcat启动的时候去掉web.xml,而且还能初始化spring环境。
- 定义了一个新的规范,即在资源文件的META-INF/services文件夹下面,有一个以javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer命名的文件,里面定义一个你自己的类的全类名。同时该类实现javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer接口,并重写onStartup方法
- 在上面这个规范下,所有按照这个规范的servlet服务器,例如:tomcat,在服务启动的时候,会自己反射执行这个类的onStartup()方法
- 通过这个新的规范,我们就不需要按照传统的方法,需要在web.xml文件中,初始化spring等配置和环境,这样做就能实现零配置,springboot就是按照这个思想实现零配置的。
(2)模拟SpringBoot零配置,内嵌tomcat
通过上图,可以看到模拟springboot零配置和内嵌tomcat,主要要注意几点:
- tomcat.addContext和tomcat.addWebapp的区别:
(1) addWebapp表示该项目是一个web项目,tomcat启动的时候,就会默认去加载jsp视图解析器,然后没有添加jsp视图解析器的依赖,就会报错。
(2) addContext表示的仅仅是往tomcat的webapps目录添加一个context,tomcat不会加载jsp视图解析器,也就不会报找不到jsp视图解析器依赖的错了。
(3) springboot基本上是已经默认不再使用jsp技术,例如:thymeleaf,freemarker…等,所以springboot的底层,肯定不会使用addWebapp这个方法。
- 这里不使用上面提到的servlet3.0新特性的规范,主要实现WebApplicationInitializer这个接口,tomcat启动要执行到这个类的代码,一定要在web项目的情况下,才会执行到。即在使用addContext这个方式的情况下,是不会执行到我们的类。那么这里的唯一做法:只能在一个软方法里面,同时初始化spring ioc,spring mvc和tomcat等环境。
在开始spring mvc的源码解析之前,我们先要有这样的一个概念:
- 通过浏览器发起的一个请求,只能请求到一个servlet的方法,它是无法直接请求到一个java类的某个方法,也就是我们经常使用的controller类的方法。
- 那么spring mvc框架可以让一个请求,执行到对应的controller类的某个方法,肯定是先让一个请求去到servlet,然后这个servlet再调用到我们的controller类的某个方法。
request ----> ! servlet.class(这是不可能实现的)
request ----> servlet ----> controller(只能是方法调用,不然无法实现)(方法调用,底层一定是反射技术:indexController:index())
- DispatcherServlet这个servlet,就是spring mvc的核心类。
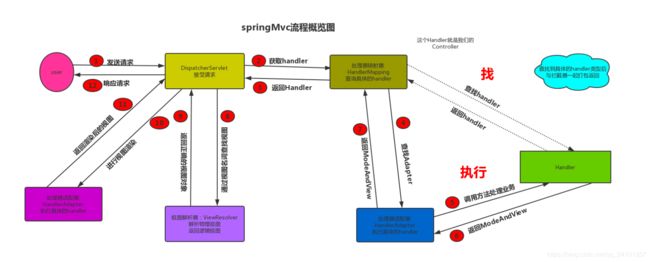
(3)Spring MVC源码解析
总结:
(1) 首先请求进入DispatcherServlet 由DispatcherServlet 从HandlerMappings中提取对应的Handler。
(2) 此时只是获取到了对应的Handle,然后得去寻找对应的适配器,即:HandlerAdapter。
(3) 拿到对应HandlerAdapter时,这时候开始调用对应的Handler处理业务逻辑了。
(这时候实际上已经执行完了我们的Controller) 执行完成之后返回一个ModeAndView
(4) 这时候交给我们的ViewResolver通过视图名称查找出对应的视图然后返回。
(5) 最后 渲染视图 返回渲染后的视图 -->响应请求。
3.1Spring MVC初始化阶段
我们要从哪里入手呢?
通过上面的分析,我们知道spring mvc的核心类是DispatcherServlet,这是一个servlet类,那么看这个类,就从这个类的init方法开始。
# 1.执行父类HttpServletBean的init()方法
//tomcat启动,就会执行该方法,初始化DispatcherServlet
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw ex;
}
}
//初始化web环境(重要)
initServletBean();
}
# 2.执行子类FrameworkServlet类的initServletBean()方法
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
//初始化web环境
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
throw ex;
}
}
# 3.执行FrameworkServlet类的initWebApplicationContext()方法
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
//配置和刷新spring容器(重要)
//这个无非就是初始化spring ioc的环境,创建bean和实例化bean等操作
//这个方法最终也是调用refresh()方法,已在spring源码解析中解析过了
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
//初始化DispatcherServlet的配置initStrategies() (重点)
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
# 4.执行DispatcherServlet类的onRefresh()方法,初始化springmvc的配置
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
//初始化springmvc的配置
initStrategies(context);
}
(1)通过上面代码分析,可以得到在执行DispatcherServlet的init方法,会执行父类的HttpServletBean的init方法,然后调用了FrameworkServlet的initServletBean()方法。
HttpServletBean#init() —> FrameworkServlet#initServletBean()
(2)执行initWebApplicationContext()方法,就是对spring ioc环境的初始化。那么这里就衍生出了一个面试题:spring容器和spring mvc的容器的区别?通过源码的分析,spring和spring mvc底层,都是调用了同一个refresh()方法,所以spring容器和spring mvc容器是没有区别的,都是指的是同一个容器。
(3)执行到onRefresh()方法,就是开始初始化DispatcherServlet了,也就是开始初始化spring mvc。
# 1.执行DispatcherServlet类的initStrategies()方法
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);//上传文件
initLocaleResolver(context);//国际化
initThemeResolver(context);//前段的主题样式
initHandlerMappings(context);//初始化HandlerMappings(请求映射器)重点
initHandlerAdapters(context);//初始化HandlerAdapters(处理适配器)
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);//视图转换器
initFlashMapManager(context);//重定向数据管理器
}
# 2.执行initHandlerMappings()方法
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
}
//通过配置文件中的配置信息,得到handlerMappings
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
//使用defaultStrategies获取数据
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
}
}
# 3.执行getDefaultStrategies()方法
protected <T> List<T> getDefaultStrategies(ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) {
String key = strategyInterface.getName();
// defaultStrategies 是DispatcherServlet.properties 配置文件,在static静态代码块初始化
String value = defaultStrategies.getProperty(key);
if (value != null) {
String[] classNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(value);
List<T> strategies = new ArrayList<>(classNames.length);
for (String className : classNames) {
try {
// 获取class字节码文件
Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.forName(className, DispatcherServlet.class.getClassLoader());
// 底层是通过调用spring的getBean的方式创建该对象(可以进行bean的属性装配)
// 请求映射就是在这个方法实现装配的
Object strategy = createDefaultStrategy(context, clazz);
strategies.add((T) strategy);
}
}
return strategies;
}
else {
return new LinkedList<>();
}
}
(1) initHandlerMappings方法,就是初始化我们的handlerMapping(请求映射器)。
(2) handlerMapping的主要作用是,找到请求路径对应的controller的方法。例如:请求的路径 “/index”,然后这个handlerMapping,在初始化的时候,已经将所有controller的请求路径映射保存在一个map集合,当请求过来的时候,就将"/index"作为一个key,从map集合中找到对应的controller的index方法。
(3) 这里初始化handlerMappings ,默认是有两个handlerMappings ,是直接在defaultStrategies配置文件中获取。
(4) 那么defaultStrategies的值是什么时候初始化的呢?通过查看源码,defaultStrategies这个值,是DispatcherServlet类的静态代码块初始化的。
全世界都知道,当一个类被初始化的时候,会执行该类的static静态代码块的。
# 1.DispatcherServlet类的static静态代码块
static {
try {
/**
* 从属性文件加载默认策略实现
* 说白了这里的意思就是从DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH这个文件当中拿出所有的配置
* 可以去数一下一共有8个: DispatcherServlet.properties == DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH
*/
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, DispatcherServlet.class);
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
}
# 2.DispatcherServlet.properties文件
//这里就贴出HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter的类
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=
org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
从DispatcherServlet.properties配置文件,可以看出handlerMapping默认是有两个:
1.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping (主要处理object)
2.RequestMappingHandlerMapping(主要处理method)
3.2Spring MVC请求阶段分析
用户的一个请求过来,会由servlet接收到,然后一步一步调用到DispatcherServlet的doService方法。
# 1.DispatcherServlet类的doService()方法
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
try {
//核心方法(重点)
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}
# 2.调用DispatcherServlet类的doDispatch()方法
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
//异步编程
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
//定义变量
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
//检查请求中是否有文件上传操作
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
//确定当前请求的处理程序(重点),推断controller和handler的类型,
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
//推断适配器,不同的controller类型,交给不同的适配器去处理
//如果是一个bean,mappedHandler.getHandler()返回的是一个对象
//如果是一个method,mappedHandler.getHandler()返回的是一个方法
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
//到这里,spring才确定我要怎么反射调用
//前置拦截器处理
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
//通过适配器,处理请求(可以理解为,反射调用方法)(重点)
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
}
通过对DispatcherServlet的分析,得到请求的核心处理方法是doDispatch(),主要是分了几步:
(1) 检查请求中是否有文件上传操作
(2) 确定当前请求的处理的handler(重点)
(3) 推断适配器,不同的controller类型,交给不同的适配器去处理
(4) 执行前置拦截器处理interceptor
(5) 通过找到的HandlerAdapter ,反射执行相关的业务代码controller的方法。
(6) 返回结果。
# 1.DispatcherServlet类的getHandler()方法
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
//循环所有的HandlerMappings
//this.handlerMappings这个是什么时候初始化的?(重点)
//在handlerMappings初始化的时候
for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) {
//把请求传过去看能不能得到一个handler
//注意:怎么得到handler和handlerMapping自己实现的逻辑有关系
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
# 2.执行到AbstractHandlerMapping的getHandler()方法
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//获取handler(重点)
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.globalCorsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
(1) getHandler()方法,主要是遍历在DispatcherServlet初始化是,初始化的handlerMappings。
(2) 这个方法的主要思想是,通过request的路径,去匹配对应的controller去处理。
(3) SpringMVC自己自带了2个HandlerMapping 来供我们选择 至于 为什么要有2个呢?
- 我们用2种方式来注册Controller 分别是:
- (1) 作为Bean的形式:实现Controller接口,重写handleRequest方法,请求路径为"/test"
@Component("/test")
public class TesrController implements org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller{
@Override
public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
System.out.println("1");
return null;
}
}
- (2) 以Annotation形式:
@Controller
public class AnnotationController {
@RequestMapping("/test2")
public Object test(){
System.out.println("test");
return null;
}
}
(1) 经过测试,可以得到以Bean方式的controller,是通过BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping去匹配
(2)以注解方法的controller,是通过RequestMappingHandlerMapping去匹配
- BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping处理bean方式的源码分析:
# 1.执行到AbstractUrlHandlerMapping的getHandlerInternal()方法
protected Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//获取请求的路径
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
//找到对应的handler(重点)
Object handler = lookupHandler(lookupPath, request);
if (handler == null) {
Object rawHandler = null;
if ("/".equals(lookupPath)) {
rawHandler = getRootHandler();
}
if (rawHandler == null) {
rawHandler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (rawHandler != null) {
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (rawHandler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) rawHandler;
rawHandler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
validateHandler(rawHandler, request);
handler = buildPathExposingHandler(rawHandler, lookupPath, lookupPath, null);
}
}
return handler;
}
# 2.执行到AbstractUrlHandlerMapping的lookupHandler()方法
protected Object lookupHandler(String urlPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//通过请求的路径,在handlerMap中去匹配。
//handlerMap这个值,什么时候填充值?在init初始化的时候,就已经存放在这个handlerMap种
Object handler = this.handlerMap.get(urlPath);
if (handler != null) {
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
validateHandler(handler, request);
return buildPathExposingHandler(handler, urlPath, urlPath, null);
}
....忽略....
}
(1) 以Bean方式的controller,匹配请求的路径,是通过一个handlerMap去匹配,比较简单。
(2) 这里的问题是,这个handlerMap的值,是什么时候放进去的?通过源码分析,BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping是实现了ApplicationContextAware接口。
如果你精通spring的源码,就知道spring的实例bean的时候,会回调这些类的setApplicationContext()方法。
# 1.执行父类的ApplicationObjectSupport的setApplicationContext()方法
public final void setApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext context) throws BeansException {
if (context == null && !isContextRequired()) {
// Reset internal context state.
this.applicationContext = null;
this.messageSourceAccessor = null;
}
else if (this.applicationContext == null) {
this.applicationContext = context;
this.messageSourceAccessor = new MessageSourceAccessor(context);
//初始化ApplicationContext,就会执行到子类的方法(重点)
initApplicationContext(context);
}
}
# 2.执行到AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping类的initApplicationContext()方法
@Override
public void initApplicationContext() throws ApplicationContextException {
super.initApplicationContext();
// 检测出handler
detectHandlers();
}
# 3.执行到AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping类的detectHandlers()方法
protected void detectHandlers() throws BeansException {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = obtainApplicationContext();
//获取spring ioc所有的beanName,然后判断beanName,那些是以 "/" 开头
String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlersInAncestorContexts ?
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, Object.class) :
applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
//然后判断beanName,那些是以 "/" 开头
String[] urls = determineUrlsForHandler(beanName);
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(urls)) {
//注册handler(重点)
registerHandler(urls, beanName);
}
}
}
# 4.执行到AbstractUrlHandlerMapping的registerHandler()方法
protected void registerHandler(String[] urlPaths, String beanName) throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
Assert.notNull(urlPaths, "URL path array must not be null");
for (String urlPath : urlPaths) {
registerHandler(urlPath, beanName);
}
}
# 5.AbstractUrlHandlerMapping的registerHandler()方法
protected void registerHandler(String urlPath, Object handler) throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
Object resolvedHandler = handler;
//最终put到map集合中(省略其他无关代码)
this.handlerMap.put(urlPath, resolvedHandler);
}
BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping处理bean方式的源码分析,其实是很简单:
(1) 在类初始化的时候,就已经将所有实现了Controller接口的controller类,拿到他们的@Componet(’/test’)
(2) 然后将’/test’这个作为key,controller类作为value,放入到一个map集合。
(3) 当一个请求过来的时候,拿到这个请求的uri,在map里面找,找到了即表示匹配上
- RequestMappingHandlerMapping处理注解方式的源码分析:
# 1.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#getHandlerInternal
// 对于RequestMappingHandlerMapping,indexController.index(),方法的请求路径映射
@Override
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//获取请求路径
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
//通过请求路径,获取handler
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
# 2.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#lookupHandlerMethod
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>();
//从mappingRegistry的urlLookup,匹配请求路径
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
// No choice but to go through all mappings...
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
matches.sort(comparator);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found " + matches.size() + " matching mapping(s) for [" + lookupPath + "] : " + matches);
}
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous handler methods mapped for HTTP path '" +
request.getRequestURL() + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
//返回handler
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
}
else {
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
# 3.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.MappingRegistry#getMappingsByUrl
public List<T> getMappingsByUrl(String urlPath) {
return this.urlLookup.get(urlPath);
}
RequestMappingHandlerMapping处理注解方式的源码分析,比较复杂,用一个MappingRegistry维护所有的请求路径映射。
MappingRegistry的初始化,也是在该bean实例化的时候,就已经做好的了。
原理也是和上一个差不多,都是从一个map集合里面匹配。所以这里就不再做解析了。
总结:getHandler()
- 接下来到找Apapter适配器了
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
for (HandlerAdapter ha : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Testing handler adapter [" + ha + "]");
}
if (ha.supports(handler)) {
return ha;
}
}
}
}
其实能看见他是从一个handlerAdapters属性里面遍历了我们的适配器 这个handlerAdapters哪来的呢? 跟我们的HandlerMappings一样 在他的配置文件里面有写,就是我们刚刚所说的 。
至于什么是适配器,我们结合Handler来讲, 就如我们在最开始的总结时所说的, 一开始只是找到了Handler 现在要执行了,但是有个问题,Handler不止一个, 自然而然对应的执行方式就不同了, 这时候适配器的概念就出来了:对应不同的Handler的执行方案。当找到合适的适配器的时候, 基本上就已经收尾了,因为后面在做了一些判断之后(判断请求类型之类的),就开始执行了你的Handler了,上代码:
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
这个mv就是我们的ModlAndView 其实执行完这一行 我们的Controller的逻辑已经执行完了, 剩下的就是寻找视图 渲染图的事情了。
总结:
其实我们的SpringMVC关键的概念就在于Handler(处理器) 和Adapter(适配器)
通过一个关键的HandlerMappings 找到合适处理你的Controller的Handler
然后再通过HandlerAdapters找到一个合适的HandlerAdapter 来执行Handler即Controller里面的逻辑。
最后再返回ModlAndView…
总的来说,springmvc的源码,还是很复杂,本博客只是大概的描述了主要的执行流程。
源码注释下载地址:https://github.com/llsydn/spring-framework