漫画算法-小灰的算法之旅-树(三)
1. 树
2. 二叉树
2.1 满二叉树
2.2 完全二叉树
3. 二叉树的应用
3.1 查找
3.2 维持相对顺序(插入)
4. 二叉树的遍历
5. 二叉堆
6. 优先队列
1. 树
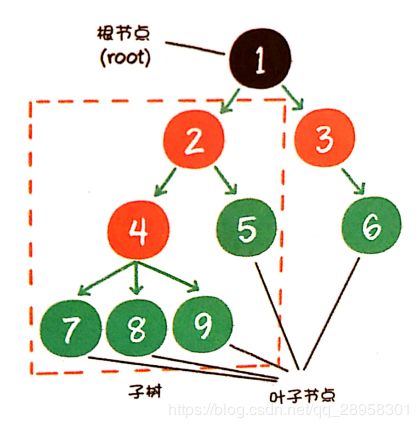
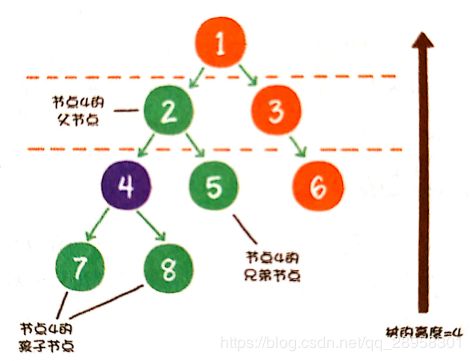
树是n个节点的有限集。当n=0时,称为空树。在任意一个非空树中,有如下特点:
- 有且仅有一个特定的称为根的节点;
- 当n>1时,其余节点可分为m个互不相交的有限集,每一个集合本身又是一个树,并称为根的子树。
树的最大层级数,称为树的高度或深度。
2. 二叉树
树的每个节点最多有2个孩子节点。
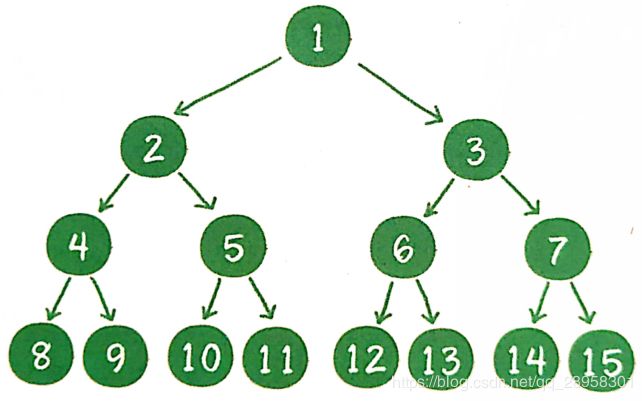
2.1 满二叉树
一个二叉树的所有非叶子节点都存在左右孩子,并且所有叶子节点都在同一层级上。
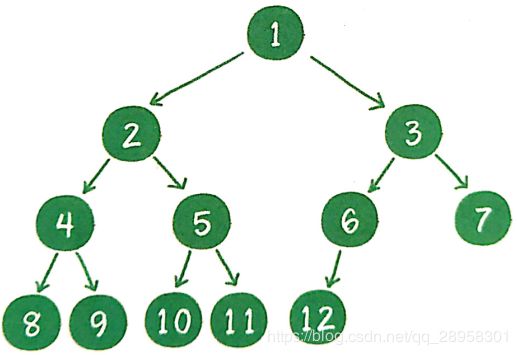
2.2 完全二叉树
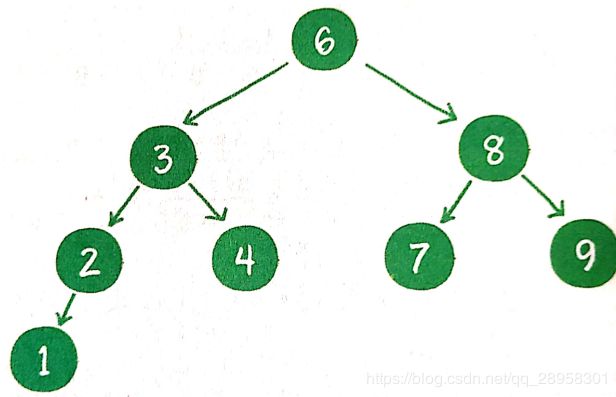
对一个有n个节点的二叉树,按层级顺序编号,则所有节点的编号为1到n。要求这个树所有节点和同样深度的满二叉树的编号为从1到n的节点位置相同。完全二叉树只需保证最后一个节点之前的节点都齐全即可。
3. 二叉树的应用
3.1 查找
二叉查找树在二叉树的基础上增加了以下几个条件:
- 如果左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值均小于根节点的值;
- 如果右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值均大于根节点的值;
- 左、右子树也都是二叉查找树。
对于一个节点分布相对均衡的二叉查找树来说,如果节点总数是n,那么搜索节点的时间复杂度都是O(logn),和树的深度是一样的。
3.2 维持相对顺序(插入)
二叉查找树的特性保证了二叉树的有序性,因此还有另外一个名字:二叉排序树。
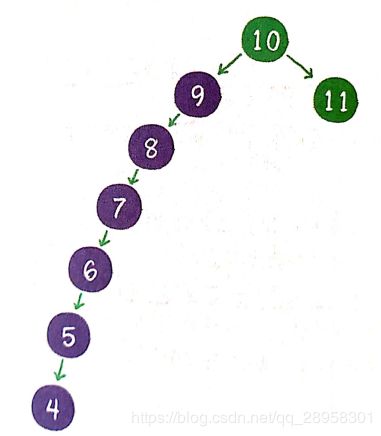
插入的过程中,可能会出现需要二叉树进行自平衡,例如下图的情况:
二叉树的自平衡的方式有很多种,如红黑树、AVL树、树堆等。
4. 二叉树的遍历
- 深度优先遍历
- 前序遍历
- 中序遍历
- 后序遍历
- 广度优先遍历
- 层序遍历
public class TreeTest {
/**
* 二叉树节点
*/
private static class TreeNode {
int data;
TreeNode leftChild;
TreeNode rightChild;
public TreeNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
/**
* 构建二叉树
* 注意这里构建的顺序和前序遍历的顺序相同
* @param inputList
* @return
*/
public static TreeNode createBinaryTree(LinkedList inputList) {
TreeNode node = null;
if (inputList == null || inputList.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
Integer data = inputList.removeFirst();
if (data != null) {
node = new TreeNode(data);
node.leftChild = createBinaryTree(inputList);
node.rightChild = createBinaryTree(inputList);
}
return node;
}
/**
* 二叉树的层序遍历
* @param root
*/
public static void levelOrderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
System.out.println(node.data);
if (node.leftChild != null) {
queue.offer(node.leftChild);
}
if (node.rightChild != null) {
queue.offer(node.rightChild);
}
}
}
/**
* 二叉树的前序遍历递归实现
* @param node
*/
public static void preOrderTraveralByRecursion(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
System.out.println(node.data);
preOrderTraveralByRecursion(node.leftChild);
preOrderTraveralByRecursion(node.rightChild);
}
/**
* 二叉树的前序遍历栈实现
* @param root
*/
public static void preOrderTraveralByStack(TreeNode root) {
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode node = root;
while (node != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (node != null) {
stack.push(node);
System.out.println(node.data);
node = node.leftChild;
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
node = stack.pop();
node = node.rightChild;
}
}
}
/**
* 二叉树的中序遍历递归实现
* @param node
*/
public static void inOrderTraveralByRecursion(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
inOrderTraveralByRecursion(node.leftChild);
System.out.println(node.data);
inOrderTraveralByRecursion(node.rightChild);
}
/**
* 二叉树的中序遍历栈实现
* @param root
*/
public static void inOrderTraveralByStack(TreeNode root) {
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode node = root;
while (node != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (node != null) {
stack.push(node);
node = node.leftChild;
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
node = stack.pop();
System.out.println(node.data);
node = node.rightChild;
}
}
}
/**
* 二叉树的后序遍历递归实现
* @param node
*/
public static void postOrderTraveralByRecursion(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
postOrderTraveralByRecursion(node.leftChild);
postOrderTraveralByRecursion(node.rightChild);
System.out.println(node.data);
}
/**
* 二叉树的后序遍历栈实现
* @param root
*/
public static void postOrderTraveralByStack(TreeNode root) {
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode node = root;
TreeNode tempNode = null;
while (node != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (node != null) {
stack.push(node);
node = node.leftChild;
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
node = stack.pop();
tempNode = node.rightChild;
if (tempNode != null) {
node.rightChild = null;
stack.push(node);
} else {
System.out.println(node.data);
}
node = tempNode;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList inputList = new LinkedList<>(Arrays.asList(3, 2, 9, null, null, 10, null, null, 8, null, 4));
TreeNode node = createBinaryTree(inputList);
System.out.println("层序遍历:");
levelOrderTraversal(node);
System.out.println("前序遍历递归实现:");
preOrderTraveralByRecursion(node);
System.out.println("前序遍历栈实现:");
preOrderTraveralByStack(node);
System.out.println("中序遍历递归实现:");
inOrderTraveralByRecursion(node);
System.out.println("中序遍历栈实现:");
inOrderTraveralByStack(node);
System.out.println("后序遍历递归实现:");
postOrderTraveralByRecursion(node);
System.out.println("后序遍历栈实现:");
postOrderTraveralByStack(node);
}
} 5. 二叉堆
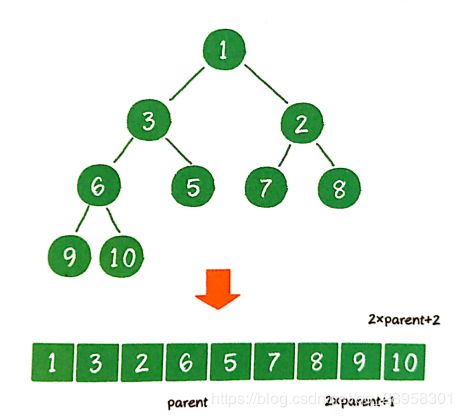
二叉堆本质上是一种完全二叉树,分为2个类型:
- 最大堆:任何一个父节点的值,都大于或等于它左、右孩子节点的值;
- 最小堆:任何一个父节点的值,都小于或等于它左、右孩子节点的值。
二叉堆虽然是一个完全二叉树,但它的存储方式并不是链式存储,而是顺序存储,如下图所示:
假设父节点的下标是parent,那么它的左孩子的下标就是2 * parent + 1,右孩子的下标就是2 * parent + 2。
二叉堆的3种操作(假设是最小堆):
- 插入节点
插入节点是通过“上浮”操作完成的:当二叉堆插入节点时,插入位置是完全二叉树的最后一个位置,将该节点与它的父节点进行比较,如果该节点小于它的父节点,那么该与它的父节点交换位置,直到比较到堆顶位置。
时间复杂度O(logn)。
public class HeapTest {
/**
* 插入节点
* @param array
* @param node
* @return
*/
public static int[] insert(int[] array, int node) {
int[] newArray = new int[array.length + 1];
System.arraycopy(array, 0, newArray, 0, array.length);
newArray[newArray.length - 1] = node;
upAdjust(newArray);
return newArray;
}
/**
* “上浮”调整
* @param array
*/
private static void upAdjust(int[] array) {
int childIndex = array.length - 1;
int parentIndex = (childIndex - 1) / 2;
int temp = array[childIndex];
while (childIndex > 0 && temp < array[parentIndex]) {
array[childIndex] = array[parentIndex];
childIndex = parentIndex;
parentIndex = (childIndex - 1) / 2;
}
array[childIndex] = temp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = new int[]{1, 3, 2, 6, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(insert(array, 0)));
}
}- 删除节点
删除节点是通过“下沉”操作完成的:将要删除的节点看作是堆顶,只看该节点及它下面的部分。因为堆顶元素要进行删除,将最后一个节点元素替换堆顶元素,将替换后的元素与它的左、右子树进行比较,如果左、右孩子节点中最小的一个比该节点小,那么该节点“下沉”,直到叶子节点。
时间复杂度O(logn)。
public class HeapTest {
/**
* 删除节点
* @param array
* @param deleteIndex
* @return
*/
public static int[] delete(int[] array, int deleteIndex) {
array[deleteIndex] = array[array.length - 1];
int[] newArray = new int[array.length - 1];
System.arraycopy(array, 0, newArray, 0, array.length - 1);
downAdjust(newArray, deleteIndex);
return newArray;
}
/**
* “下沉”操作
* @param array
* @param index
*/
public static void downAdjust(int[] array, int index) {
int parentIndex = index;
int leftChildIndex = parentIndex * 2 + 1;
int rightChildIndex = parentIndex * 2 + 2;
int temp = array[parentIndex];
while (leftChildIndex <= array.length - 1) {
int minIndex;
//如果右孩子存在且右孩子小于左孩子
if (rightChildIndex <= array.length - 1 && array[rightChildIndex] < array[leftChildIndex]) {
minIndex = rightChildIndex;
} else {
minIndex = leftChildIndex;
}
if (temp > array[minIndex]) {
array[parentIndex] = array[minIndex];
parentIndex = minIndex;
leftChildIndex = parentIndex * 2 + 1;
rightChildIndex = parentIndex * 2 + 2;
} else {
break;
}
}
array[parentIndex] = temp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(delete(array, 0)));
}
}- 构建二叉堆
构建二叉堆就是把一个无序的完全二叉树调整为二叉堆,本质就是让所有非叶子节点依次“下沉”。
时间复杂度O(n)。
public class HeapTest {
/**
* “下沉”操作
* @param array
* @param index
*/
public static void downAdjust(int[] array, int index) {
int parentIndex = index;
int leftChildIndex = parentIndex * 2 + 1;
int rightChildIndex = parentIndex * 2 + 2;
int temp = array[parentIndex];
while (rightChildIndex <= array.length - 1) {
int minIndex;
if (array[leftChildIndex] < array[rightChildIndex]) {
minIndex = leftChildIndex;
} else {
minIndex = rightChildIndex;
}
if (temp > array[minIndex]) {
array[parentIndex] = array[minIndex];
parentIndex = minIndex;
leftChildIndex = parentIndex * 2 + 1;
rightChildIndex = parentIndex * 2 + 2;
} else {
break;
}
}
array[parentIndex] = temp;
}
/**
* 构建二叉堆
* @param array
*/
public static void build(int[] array) {
for (int i = (array.length - 2) / 2; i >= 0; i--) {
downAdjust(array, i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] newArray = new int[]{7, 1, 3, 10, 5, 2, 8, 9, 6};
build(newArray);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(newArray));
}
}二叉堆是实现堆排序及优先队列的基础。
6. 优先队列
优先队列不再遵循先入先出的原则,而是分为两种情况:
- 最大优先队列,无论入队顺序如何,都是当前最大的元素优先出队;
- 最小优先队列,无论入队顺序如何,都是当前最小的元素优先出队。
public class PriorityQueue {
private static int[] array;
static {
array = new int[0];
}
public static void enQueue(int key) {
array = HeapTest.insert(array, key);
}
public static int deQueue() throws Exception {
if (array.length <= 0) {
throw new Exception("the queue is is empty");
}
int result = array[0];
array = HeapTest.delete(array, 0);
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
PriorityQueue.enQueue(3);
PriorityQueue.enQueue(5);
PriorityQueue.enQueue(4);
PriorityQueue.enQueue(2);
PriorityQueue.enQueue(7);
System.out.println("出队: " + PriorityQueue.deQueue());
System.out.println("出队: " + PriorityQueue.deQueue());
}
}