微服务:简述微服务架构中的配置中心之Apollo
微服务:简述微服务架构中的配置中心之Apollo
《微服务:简述微服务架构中的配置中心选型》
Github : https://github.com/ctripcorp/apollo
Apollo(阿波罗)是携程框架部门研发的分布式配置中心,能够集中化管理应用不同环境、不同集群的配置,配置修改后能够实时推送到应用端,并且具备规范的权限、流程治理等特性,适用于微服务配置管理场景。
- 服务端基于Spring Boot和Spring Cloud开发,打包后可以直接运行,不需要额外安装Tomcat等应用容器。
- Java客户端不依赖任何框架,能够运行于所有Java运行时环境,同时对Spring/Spring Boot环境也有较好的支持。
- .Net客户端不依赖任何框架,能够运行于所有.Net运行时环境。
如果想要深入了解,可以到github上参见Apollo配置中心,官网的介绍很详细。本文主要讲述Spring Boot 2.0 整合Apollo配置中心。
一、Apollo配置中心服务端
Apollo服务端使用的是官网提供的 Quick Start(针对本地测试使用)。
1.1 准备工作
- Java
Apollo服务端要求Java 1.8+,客户端要求Java 1.7+。 - MySQL
Apollo的表结构对timestamp使用了多个default声明,所以需要5.6.5以上版本。 - 下载 Quick Start
官网为我们准备了 Quick Start 安装包,只需要下载到本地,就可以直接使用,免去了编译、打包过程。大家可以到github下载,也可以通过百度云盘下载
1.2 安装步骤
1.2.1 创建数据库
Apollo服务端共需要两个数据库:ApolloPortalDB和ApolloConfigDB,官网把数据库、表的创建和样例数据都分别准备了sql文件(在下载的 Quick Start 安装包的sql目录下),只需要导入数据库即可。
- 创建ApolloPortalDB
通过各种Mysql客户端(Navicat,DataGrip等)导入sql/apolloportaldb.sql即可。导入成功后,可以通过执行下述sql语句来验证:
select 'Id', 'AppId', 'Name' from ApolloPortalDB.App;
| Id | AppId | Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | SampleApp | Sample App |
- 创建ApolloConfigDB
通过各种Mysql客户端(Navicat,DataGrip等)导入sql/apolloconfigdb.sql即可。导入成功后,可以通过执行下述sql语句来验证:
select ‘NamespaceId’, ’Key‘, ’Value‘, ‘Comment’ from ApolloConfigDB.Item;
| NamespaceId | Key | Value | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | timeout | 100 | sample |
1.2.2配置数据库连接信息
Apollo服务端需要知道如何连接到前面创建的数据库,所以需要编辑 demo.sh,修改ApolloPortalDB和ApolloConfigDB相关的数据库连接串信息。
#apollo config db info
apollo_config_db_url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ApolloConfigDB?characterEncoding=utf8
apollo_config_db_username=用户名
apollo_config_db_password=密码(如果没有密码,留空即可)
# apollo portal db info
apollo_portal_db_url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ApolloPortalDB?characterEncoding=utf8
apollo_portal_db_username=用户名
apollo_portal_db_password=密码(如果没有密码,留空即可)
1.2.3 启动Apollo配置中心
1.2.3.1 确保端口未被占用
Quick Start脚本会在本地启动3个服务,分别使用8070, 8080, 8090端口,请确保这3个端口当前没有被使用。例如,在Linux/Mac下,可以通过命令【lsof -i:8080】检查;在windows下,可以通过命令【netstat -aon|findstr “8080”】检查:
1.2.3.2 执行启动脚本
在Quick Start目录下执行命令【./demo.sh start】。当看到如下输出后,就说明启动成功了!
==== starting service ====
Service logging file is ./service/apollo-service.log
Started [10768]
Waiting for config service startup.......
Config service started. You may visit http://localhost:8080 for service status now!
Waiting for admin service startup....
Admin service started
==== starting portal ====
Portal logging file is ./portal/apollo-portal.log
Started [10846]
Waiting for portal startup......
Portal started. You can visit http://localhost:8070 now!
1.2.3.3 异常排查
如果启动遇到了异常,可以分别查看service和portal目录下的log文件排查问题。
注: 在启动apollo-configservice的过程中会在日志中输出eureka注册失败的信息,如com.sun.jersey.api.client.ClientHandlerException: java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused。需要注意的是,这个是预期的情况,因为apollo-configservice需要向Meta Server(它自己)注册服务,但是因为在启动过程中,自己还没起来,所以会报这个错。后面会进行重试的动作,所以等自己服务起来后就会注册正常了。
1.2.4 使用Apollo配置中心 – 查看样例配置
浏览器访问http://localhost:8070。Quick Start集成了Spring Security简单认证,更多信息可以参考Portal 实现用户登录功能。输入用户名apollo,密码admin登录。
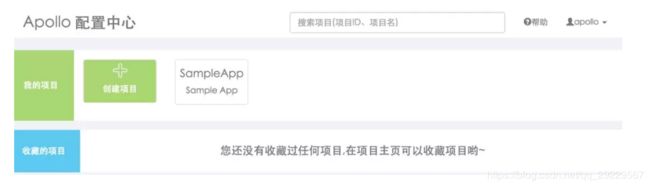
配置中心中包含一个默认的项目SampleApp。
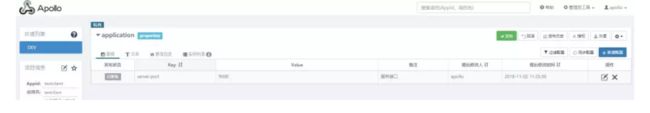
点击SampleApp进入配置界面,可以看到当前有一个配置timeout=100。如果提示系统出错,请重试或联系系统负责人,请稍后几秒钟重试一下,因为通过Eureka注册的服务有一个刷新的延时。

1.2.5 使用Apollo配置中心 – 新增项目配置
我们的客户端使用apollo需要新增相关的项目配置。
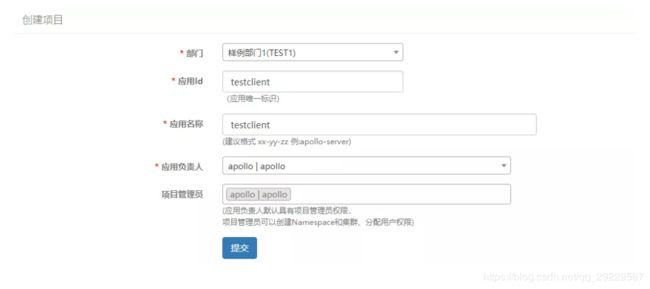
1.2.5.1点击新建项目,填写信息
点击提交,创建完成 。
应用ID:这个ID是应用的唯一标识
应用名称:应用的名称,会展示在配置中心的首页上
1.2.5.2 新增配置信息
1.2.5.3 发布配置
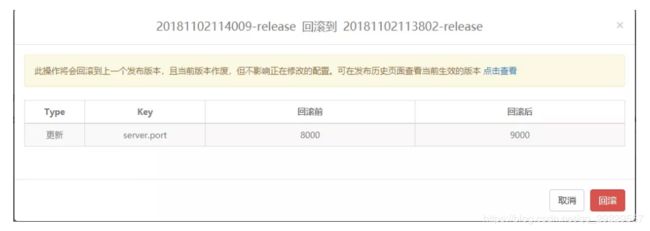
1.2.5.4 回滚
如果配置做了修改之后,发现配置更改错误,这个时候可以使用回滚功能,回到上一个配置。
二、Apollo配置中心客户端
Apollo客户端基于Spring Boot 2.0搭建,开发工具是InteIIij IDEA。新建一个项目,项目名称为apollo-client
2.1 客户端搭建
- 添加Apollo客户端依赖
com.ctrip.framework.apollo
apollo-client
1.1.1
- 添加配置信息
# 应用ID(在Apollo服务端新增项目添加的应用ID)
app.id=testclient
# apollo-configservice地址
apollo.meta=http://127.0.0.1:8080开启Apollo客户端
-
在项目的启动类上添加@EnableApolloConfig注解
-
新增一个测试接口
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String hello(){
return "hello man";
}
- 启动服务测试
在Apollo配置中心中,我们对该项目有一条配置server.port = 9000,启动服务,访问http://localhost:9000/index,返回hello man。证明,客户端是从服务端获取的配置。
2.2 客户端用法
上面我们简单的搭建了客户端,成功的使用服务端配置。Apollo为我们提供的使用方式有很多种,下面只介绍Spring Boot 2.0环境下的使用方式。
2.2.1 Spring Placeholder的使用
Spring应用通常会使用Placeholder来注入配置,使用的格式形如【$ {someKey:someDefaultValue}】,如${timeout:100}。冒号前面的是key,冒号后面的是默认值(建议在实际使用时尽量给出默认值,以免由于key没有定义导致运行时错误)。
Apollo从v0.10.0开始的版本支持placeholder在运行时自动更新。如果需要关闭placeholder在运行时自动更新功能,可以通过以下两种方式关闭:
- 通过设置System Property apollo.autoUpdateInjectedSpringProperties,如启动时传入-Dapollo.autoUpdateInjectedSpringProperties=false
- 通过设置META-INF/app.properties中的apollo.autoUpdateInjectedSpringProperties=false
2.2.1.1 Java Config使用方式
- 新建配置类JavaConfigBean如下:
/**
* Java Config方式
**/
@Configuration
public class JavaConfigBean {
@Value("${timeout:20}")
private int timeout;
public int getTimeout() {
return timeout;
}
}
- 新增访问端点
@Autowired
JavaConfigBean javaConfigBean;
@RequestMapping("/index1")
public String hello1(){
return javaConfigBean.getTimeout()+"";
}
- 测试
浏览器访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/index1,正确返回配置的值
2.2.1.2 ConfigurationProperties使用方式
Spring Boot提供了@ConfigurationProperties把配置注入到bean对象中。Apollo也支持这种方式,下面的例子会把redis.cache.expireSeconds和redis.cache.commandTimeout分别注入到SampleRedisConfig的expireSeconds和commandTimeout字段中。
- 新增配置类SampleRedisConfig如下:
redis.cache.commandTimeout=3000
redis.cache.expireSeconds=20
/**
* ConfigurationProperties使用方式
**/
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "redis.cache")
public class SampleRedisConfig {
private int expireSeconds;
private int commandTimeout;
public void setExpireSeconds(int expireSeconds) {
this.expireSeconds = expireSeconds;
}
public void setCommandTimeout(int commandTimeout) {
this.commandTimeout = commandTimeout;
}
public int getExpireSeconds() {
return expireSeconds;
}
public int getCommandTimeout() {
return commandTimeout;
}
}
- 新增访问端点
@Autowired
SampleRedisConfig sampleRedisConfig;
@RequestMapping("/index2")
public String hello2(){
return sampleRedisConfig.getCommandTimeout()+"--"+sampleRedisConfig.getExpireSeconds();
}
- 测试
浏览器访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/index2,正确返回配置的值
注: @ConfigurationProperties如果需要在Apollo配置变化时自动更新注入的值,需要配合使用EnvironmentChangeEvent或RefreshScope。
2.2.2 Spring Annotation支持
Apollo同时还增加了几个新的Annotation来简化在Spring环境中的使用。
- @ApolloConfig用来自动注入Config对象
- @ApolloConfigChangeListener用来自动注册ConfigChangeListener
- @ApolloJsonValue用来把配置的json字符串自动注入为对象
2.2.2.1 @ApolloConfig的使用
- 新增访问端点
@ApolloConfig
private Config config;
@RequestMapping("/index3")
public String hello3(){
Set propertyNames = config.getPropertyNames();
propertyNames.forEach(key -> {
System.err.println(key+"="+config.getIntProperty(key,0));
});
return propertyNames.toString();
}
- 测试
浏览器访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/index3,正确打印配置的值
redis.cache.commandTimeout=3000
redis.cache.expireSeconds=20
server.port=800
timeout=200
2.2.2.2 @ApolloConfigChangeListener的使用
- 新增以下代码
@ApolloConfigChangeListener
private void someOnChange(ConfigChangeEvent changeEvent) {
//update injected value of batch if it is changed in Apollo
if (changeEvent.isChanged("timeout")) {
System.out.println(config.getIntProperty("timeout", 0));
}
}
- 测试
在Apollo服务端修改timeout配置的值为300,发布后,控制台打印300。
2.2.2.3 @ApolloJsonValue的使用
- 新增User如下:
/**
* 用户
**/
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
-
服务端新增配置
jsonBeanProperty=[ { “username”: “john”, “password”: “1234” }, { “username”: “simon”, “password”: “222132” } ] -
客户端获取配置
@ApolloJsonValue("${jsonBeanProperty:[]}")
private List anotherJsonBeans;
@RequestMapping("/index4")
public void hello4(){
anotherJsonBeans.forEach(item -> {
System.err.println(item.getUsername()+"--"+item.getPassword());
});
}
- 测试
浏览器访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/index4,正确打印配置的值
参考:
- https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QgW6WqjDI6zeMkLqNges-A