Linux系统编程:代码实现多重管道功能
代码功能介绍
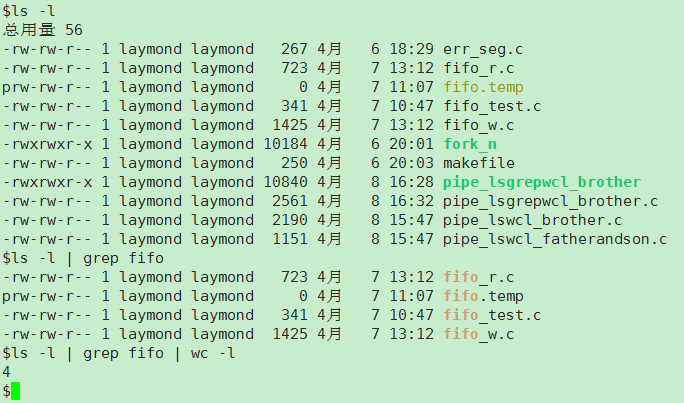
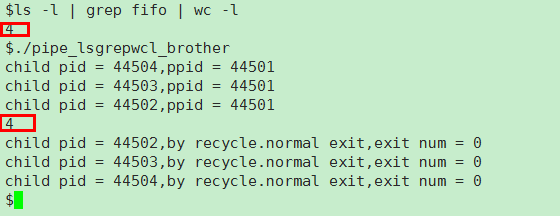
我们在linux命令中可以使用 | 进行数据的流动,比如命令 ls -l | grep fifo | wc -l 如下图。这就是多重管道,今天我们用代码来实现类似的功能。
代码实现思路
管道 | 的实现当然要用到pipe函数 用来创建管道,每条单独的命令 用一个子进程来实现,linux命令默认是STDIN_FILENO作为输入端,STDOUT_FILENO作为输出端。故此,会用到dup2文件描述符重定向。父进程负责回收子进程。只要思路清晰代码实现就不难了。当然如果是 3重、4重管道,思路都一样。需要注意的是,pipe的创建一定是在fork子进程之前,为了保证管道单向流动每个进程必须将没有用到的读写端close掉。
代码展示
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
//利用管道实现 ls -l | grep "fifo" | wc -l 功能
//所以需要2 根管道
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
{
pid_t pid,wpid;
int i,fd[2],fd2[2],status;
pipe(fd);
pipe(fd2);
for( i = 0; i < 3; i++ )
{
if((pid = fork()) == 0)
{
//子进程
break;
}else if( pid < 0 )
{
perror("fork error");
exit(1);
}
}
if( i == 0 )
{
printf("child pid = %d,ppid = %d\n",getpid(),getppid());
//将管道不相关的端口关闭
close(fd2[0]);
close(fd2[1]);
close(fd[0]);
//子进程1 执行ls 将结果写出到管道1
dup2(fd[1],STDOUT_FILENO);
execlp("ls","ls","-l",NULL);
perror("ls error");
}
else if( i == 1 )
{
printf("child pid = %d,ppid = %d\n",getpid(),getppid());
close(fd[1]);
close(fd2[0]);
//子进程2 grep "fifo*" 从管道1中读入数据,并输出到管道2
dup2(fd[0],STDIN_FILENO);
dup2(fd2[1],STDOUT_FILENO);
execlp("grep","grep","fifo",NULL);
perror("cat error");
}
else if( i == 2 )
{
printf("child pid = %d,ppid = %d\n",getpid(),getppid());
close(fd[0]);
close(fd[1]);
close(fd2[1]);
//子进程3 wc -l 从管道2中读入数据,将最终结果输出的屏幕
dup2(fd2[0],STDIN_FILENO);
execlp("wc","wc","-l",NULL);
perror("wc error");
}
else
{
//父进程2根管道的 2端都要关闭 为了不影响子进程的管道通信 ,而且必须放在fork完子进程后才可以关闭。
close(fd[0]);
close(fd[1]);
close(fd2[0]);
close(fd2[1]);
// 父进程 回收子进程
while( (wpid = waitpid(-1,&status,WNOHANG)) != -1 )
{
if(wpid > 0)
{
printf("child pid = %d,by recycle.",wpid);
if(WIFEXITED(status))
{
//程序正常退出
printf("normal exit,exit num = %d\n",WEXITSTATUS(status));
}else if( WIFSIGNALED(status) )
{
//程序被信号终止
printf("terminate by signal,signal num = %d\n",WTERMSIG(status));
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}