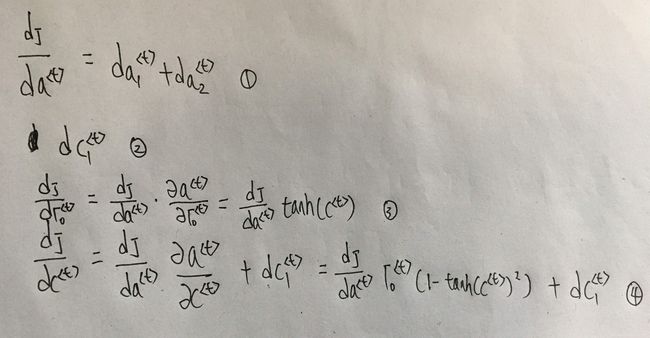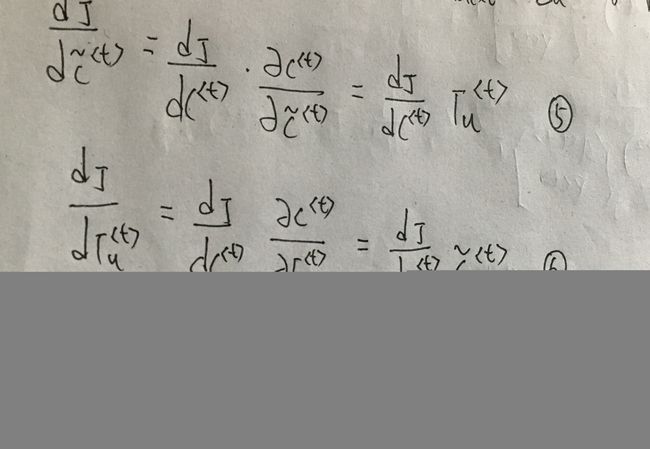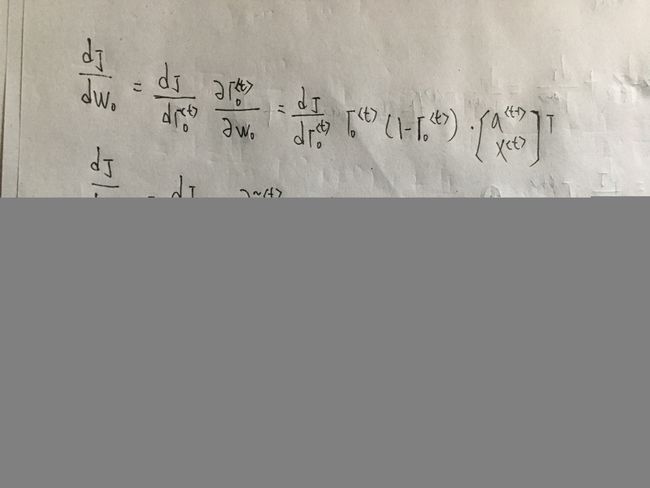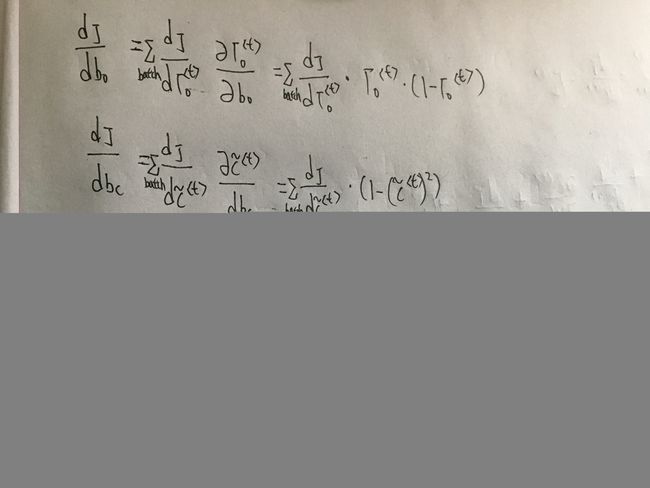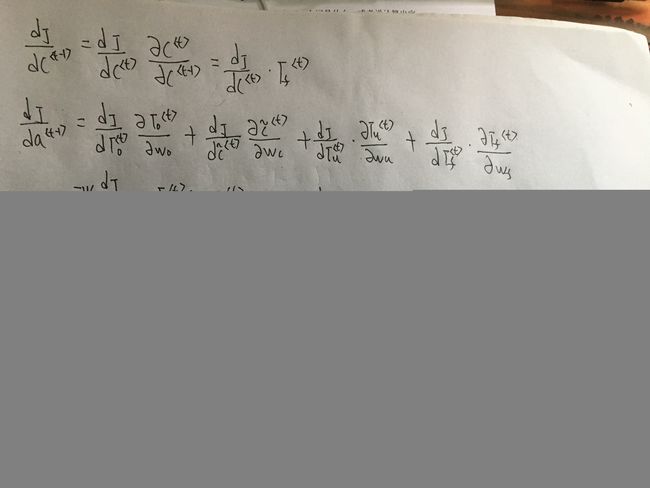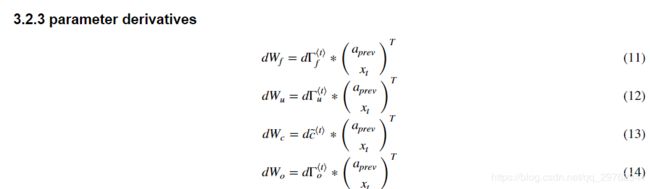RNN、LSTM反向传播推导详解
在做吴恩达深度学习课程相关作业时,顺便进行了RNN和LSTM的反向传播推导。顺便记录如下,希望能对你有所帮助~
RNN前向与反向:
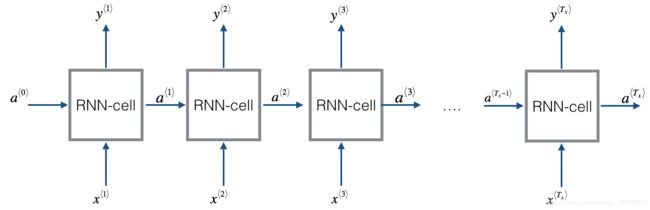
模型的整体结构如下图所示,输入的是序列x、输出y,长度为Tx。
BasicRNN 前向传播
现在我们单独对每个cell进行公式推导,最终整个模型的公式其实就是单个cell的循环调用。
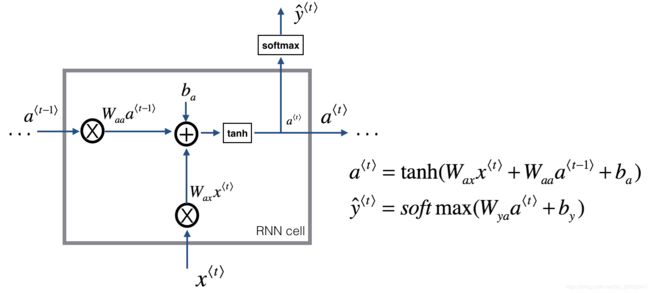
下图是单个cell的具体结构图,以及前向传播的公式,非常的简洁明了
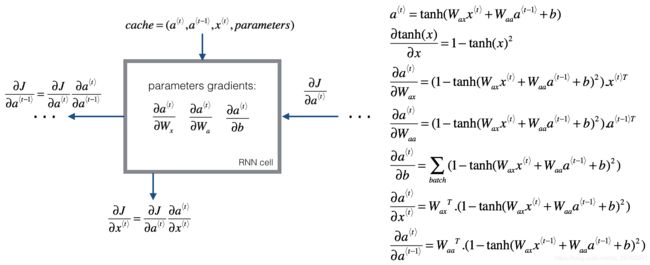
Basic RNN的反向传播很简单,直接上图:
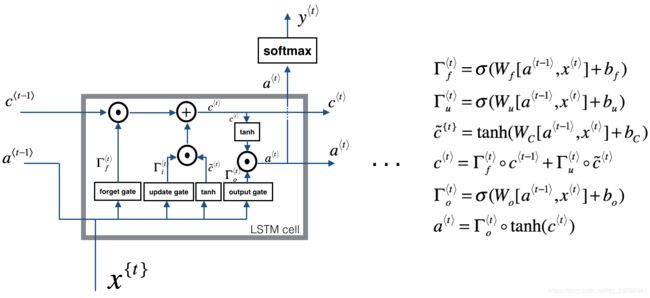
LSTM前向传播
LSTM单个cell的反向传播比Basic RNN看起来要复杂很多,主要变化就是添加了三个门:遗忘门、更新门和输出门。但是我们理清楚单个cell接收到的所有梯度,就很容易理解了。
(1)当前cell中a< t >通过反向传播得到的梯度同样有两个部分
- 当前输出y^< t >代入损失函数,对a< t >求导得到的da< t >1
- 输入到下一个cell的a< t >传回的梯度da< t >2
(2)当前cell还要接受输入到下一个cell的c< t >传回的梯度dc< t >1
为了便于理解,现在图上标记一些符号:
注意其中的 da
LSTM反向传播详细推导(第一种推导法)
PS:这里是本人根据吴恩达作业结合自己理解推导出来的。之所以自己宁愿手撕推导一遍,再(二)中讲明原因。
第二步计算反向传播:
第三步计算反向传播:
第四步计算反向传播:
第五步计算反向传播:
注意第五步这里的 W前 W 后要分别对应 a 和 x 的维数。
至此,整个LSTM反向传播完成~~~
LSTM反向传播详细推导(第二种推导法)
PS: 之所以手推了上面的(一)。是因为一开始看吴恩达作业列的式子时,有些不明白式子怎么会这样,例如dot = da_next * np.tanh(c_next) * ot * (1 - ot),但是后来结合了代码去看,发现ot * (1 - ot)是把应该在后面才求导的式子中部分计算直接在前面给计算了,例如dwf的求导,这里就不用ot * (1 - ot)。。。当然这样结果是对的,只是一开始真把我搞糊涂了。(这里的dc并没有像上面那样直接单独算出整体结果)
注意: 图中标记的1部分是计算dWo时才用到的,但是下面的dWo没列出,这里提前列出来了。。。(8)(9)(10)后面的下划线部分都是一样提前计算了,真正的反向求导只是中扩号里面的。一开始觉得很奇怪,后来结合整体结合才看明白了。至于为什么提前计算,就是为了后面的公式写起来简单吧~
(8)式中画叉的应该是图错了,把那个去掉。
实现代码如下:
def lstm_cell_backward(da_next, dc_next, cache):
"""
Implement the backward pass for the LSTM-cell (single time-step).
Arguments:
da_next -- Gradients of next hidden state, of shape (n_a, m)
dc_next -- Gradients of next cell state, of shape (n_a, m)
cache -- cache storing information from the forward pass
Returns:
gradients -- python dictionary containing:
dxt -- Gradient of input data at time-step t, of shape (n_x, m)
da_prev -- Gradient w.r.t. the previous hidden state, numpy array of shape (n_a, m)
dc_prev -- Gradient w.r.t. the previous memory state, of shape (n_a, m, T_x)
dWf -- Gradient w.r.t. the weight matrix of the forget gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x)
dWi -- Gradient w.r.t. the weight matrix of the input gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x)
dWc -- Gradient w.r.t. the weight matrix of the memory gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x)
dWo -- Gradient w.r.t. the weight matrix of the save gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x)
dbf -- Gradient w.r.t. biases of the forget gate, of shape (n_a, 1)
dbi -- Gradient w.r.t. biases of the update gate, of shape (n_a, 1)
dbc -- Gradient w.r.t. biases of the memory gate, of shape (n_a, 1)
dbo -- Gradient w.r.t. biases of the save gate, of shape (n_a, 1)
"""
# Retrieve information from "cache"
(a_next, c_next, a_prev, c_prev, ft, it, cct, ot, xt, parameters) = cache
### START CODE HERE ###
# Retrieve dimensions from xt's and a_next's shape (≈2 lines)
n_x, m = xt.shape
n_a, m = a_next.shape
# Compute gates related derivatives, you can find their values can be found by looking carefully at equations (7) to (10) (≈4 lines)
dot = da_next * np.tanh(c_next) * ot * (1 - ot)
dcct = (dc_next * it + ot * (1 - np.square(np.tanh(c_next))) * it * da_next) * (1 - np.square(cct))
dit = (dc_next * cct + ot * (1 - np.square(np.tanh(c_next))) * cct * da_next) * it * (1 - it)
dft = (dc_next * c_prev + ot *(1 - np.square(np.tanh(c_next))) * c_prev * da_next) * ft * (1 - ft)
# Compute parameters related derivatives. Use equations (11)-(14) (≈8 lines)
dWf = np.dot(dft,np.concatenate((a_prev, xt), axis=0).T)
dWi = np.dot(dit,np.concatenate((a_prev, xt), axis=0).T)
dWc = np.dot(dcct,np.concatenate((a_prev, xt), axis=0).T)
dWo = np.dot(dot,np.concatenate((a_prev, xt), axis=0).T)
dbf = np.sum(dft, axis=1 ,keepdims = True)
dbi = np.sum(dit, axis=1, keepdims = True)
dbc = np.sum(dcct, axis=1, keepdims = True)
dbo = np.sum(dot, axis=1, keepdims = True)
# Compute derivatives w.r.t previous hidden state, previous memory state and input. Use equations (15)-(17). (≈3 lines)
da_prev = np.dot(parameters['Wf'][:,:n_a].T,dft)+np.dot(parameters['Wi'][:,:n_a].T,dit)+np.dot(parameters['Wc'][:,:n_a].T,dcct)+np.dot(parameters['Wo'][:,:n_a].T,dot)
dc_prev = dc_next*ft+ot*(1-np.square(np.tanh(c_next)))*ft*da_next
dxt = np.dot(parameters['Wf'][:,n_a:].T,dft)+np.dot(parameters['Wi'][:,n_a:].T,dit)+np.dot(parameters['Wc'][:,n_a:].T,dcct)+np.dot(parameters['Wo'][:,n_a:].T,dot)
# parameters['Wf'][:, :n_a].T 每一行的 第 0 到 n_a-1 列的数据取出来
# parameters['Wf'][:, n_a:].T 每一行的 第 n_a 到最后列的数据取出来
### END CODE HERE ###
# Save gradients in dictionary
gradients = {"dxt": dxt, "da_prev": da_prev, "dc_prev": dc_prev, "dWf": dWf,"dbf": dbf, "dWi": dWi,"dbi": dbi,
"dWc": dWc,"dbc": dbc, "dWo": dWo,"dbo": dbo}
return gradients