C++ STL 容器接口使用方法整理
stl 容器的基本知识(常识部分)
容器内元素的条件
(1)必须可以复制(copy)或者搬移(move) (隐含的条件是在拷贝和搬移的过程中应该没有副作用)
struct BadStruct {
BadStruct() : m_id(g_id++) {}
//每次赋值或者搬移都会调用析构函数,因此析构函数中不应该做事
~BadStruct() { std::cout << "bye\n";}
int m_id;
static int g_id;
};
(2) 元素必须可以被赋值操作来复制或者搬移 (因为容器和算法对复写的要求)
=
(3)元素可以被销毁
针对不同的容器还有特殊的要求
- 对于序列式容器,元素必须有默认的构造函数,析构函数不能抛出异常
- 对于某些操作,元素需要定义 == std::find
- 对于关联式容器,排序准则默认的是 <(小于号)
- 无顺序容器,必须要提供一个hash函数 ==
- stl容器里面存的是元素的值而不是引用
容器通用接口
template
void containerAllInterface(T& a, T& b) {
T c;
T d(a); // copy
T e = a; // copy
T f(std::move(a)); // move
auto iterB = b.begin();
auto iterE = b.end();
T g(iterB, iterE); // copy
b.size(); // std::forward_list 不支持size
b.empty(); // return b.size() == 0;
b.max_size();
if(b == c) { // ==
}
if(b != d) { // !(b == d)
}
if(b < e) { // unordered_set unordered_map不支持这种比较
// b <= e
// b > e
// b >= e
}
e = b;
e = std::move(b);
e.swap(g); // std::array 调用swap的时间复杂度是线性的,其余容器调用swap的时间复杂度是 O1
swap(e,g); // 01 除了 std::array
e.cbegin(); //返回值是const迭代器,即 const_iterator
auto ea = e.cbegin();
auto eea = e.begin();
*eea; // -> ???? const &, &
*ea; // -> const &
e.cend();
e.clear(); // std::array 不支持clear
}
array
array 实际上是对c/c++语言中原生数组进行的封装
特点:内存分配在栈(stack),绝对不会重新分配,随机访问元素
//由于我们是按引用传入的参数,因此该函数仅适用于单线程
//多线程情况下会出现数据混乱
template
void checkSize(C& c) {
if(c.size() > 3) {
c[3] = 10;
}
//c.at(3) = 10;
}
void arrayPart() {
// array 实际上是对c/c++语言中原生数组进行的封装
// namespace std {
// template
// class array;
// }
// 特点:内存分配在栈(stack),绝对不会重新分配,随机访问元素
int abc[100]; //未初始化
std::array a; //未初始化
std::array b = {}; //初始化了的
// 以上两者的区别
std::array obj = {1,2,3,4,5};
std::array obj2 = {1,0};
// 接口
a.empty(); // nerver be true if size > 0
a.size();
a.max_size();
// operator == < != > <= >=
auto aa = a;
aa.swap(a); //array是真的每一个元素都去做交换
swap(aa, a); //其他容器通过swap函数交换了指针
// 访问元素
a[1];
a.at(1);
a.front();
a.back();
checkSize(a);
// 迭代器相关
a.begin();
a.end();
a.cbegin();
a.cend();
a.rbegin();
a.rend();
a.crbegin();
a.crend();
// 和C的接口互用
std::array carr;
strcpy(&carr[0], "hello world\n"); // more better use carr.data();
printf("%s", &carr[0]); // more better use carr.data()
// 错误的用法,因为array的迭代器的实现有可能不是指针,因此下面的方式是错误的
printf("%s", carr.begin());
// 特殊的地方 获取特殊位置的值
auto info = std::get<1>(carr);
//对所有的元素进行赋值
carr.fill(0);
// 异常exception
// c.at(pos); 调用at函数的时候有可能会抛出异常
// copy move swap 拷贝、move和swap时,也可能会抛出异常
}
vector
static void vectorPart() {
// vector 是c++98中引入的动态数组(dynamic array)
// namespace std {
// template>
// class vector;
// }
// 特点随机访问元素,末端添加删除元素效率高。前端和中间删除和添加元素效率低,
// 存在当前容器大小和容量的关系
using Group = std::vector; //新式写法
//typedef std::vector Group; //老式写法
Group a;
Group b = a;
Group c(a);
Group d(10);
Group e(10, 1.0f);
Group f(e.begin(), e.end());
Group g({1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f});
Group h = {1.0f, 3.0f, 4.0f}; // initialize list
d.empty();
d.size();
d.max_size(); //相对于其他容器来说,返回值会比较小
d.capacity();
d.reserve(100); //预先的生成并保留这些空间
d.shrink_to_fit(); // c++11
// operator == != < > <= >=
// 赋值
b = g;
b.assign(3, 1.0f); // { 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f}
b.assign(g.begin(), g.end()); //等价于: b = g
b.assign({1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f}); //
// 交换
b.swap(a); // swap十分高效且不会抛出异常
std::swap(a,b);
// 元素访问
b[0];
// at函数访问相应位置的元素,如果元素位置不合法,则会抛出异常 std::out_of_range
b.at(0);
if(b.empty()) {
b.front(); // undefined
b.back(); // undefined
}
b.front();
b.back();
// 迭代器相关
a.begin();
a.end();
a.cbegin();
a.cend();
a.rbegin();
a.rend();
a.crbegin();
a.crend();
// 当vector中没有元素的时候,会出现undefined行为
a.pop_back();
// single thread
// multithread maybe wrong
if(!a.empty()) a.pop_back();
//erase删除掉特定位置的元素之后,后面的元素会依次往前移动
//由于stl追求效率,因此对于传入的参数不会进行检查。因此这块的正确性需要我们来把控
//erase返回我要删除的元素的下一个位置。如果vector后面没有元素了,则erase会返回一个end
auto iterAfter=b.erase(b.begin());
b.erase(b.begin(), b.end());
b.push_back(10.0f);
b.pop_back();
//在特定位置插入新元素
auto iter = b.insert(b.end(), 100.0f);
//insert函数的返回值是插入新元素之后,新元素所在位置的迭代器
iter = b.insert(b.end(), 10, -10.0f);
b.insert(b.end(), h.begin(), h.end());
b.emplace(b.end(), 10.0f); // c++11,emplace是原位生成
b.emplace_back(10.0f); // c++11 && move copy&&
// b.size() == 100
b.resize(10); //将vector的尺寸设置成10
// b.size() == 10
b.resize(100, 1.0f);
b.resize(100000);
b.clear(); // 清空vector中的元素,并调用元素的析构函数。但是vector所占内存不会发生变化
b.shink_to_fit(); // c++11 让vector中所占内存根据所含元素个数来进行调整
// 和C的接口互用
std::vector carr(100, 0);
strcpy(&carr[0], "hello world\n"); // more better use carr.data();
printf("%s", &carr[0]); // more better use carr.data()
// 错误的用法
printf("%s", carr.begin());
// 异常
// (1) push_back发生异常的时候,vector本身不会发生变化
// (2) 元素 move/copy 没有异常的话, insert、 emplace、 emplace_back、 push_back都不会出现任何问题
// (3) pop_back肯定不会发生异常
// (4) 元素 move/copy 没有异常的话,erase也不会抛出异常
// (5) swap clear 也不会抛出异常
// 特殊——不要将bool类型的值存入vector中
// std::vector never use it
}
deque
static void dequePart() {
// deque 是c++98中引入的动态数组(dynamic array)
// namespace std {
// template>
// class deque;
// }
// 特点随机访问元素,末端和头部添加删除元素效率高。中间删除和添加元素效率低,
// 元素的访问和迭代比vector要慢,迭代器不能是普通的指针
using Group = std::deque;
Group a;
Group b = a;
Group c(a);
Group d(10);
Group e(10, 1.0f);
Group f(e.begin(), e.end());
Group g({1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f});
Group h = {1.0f, 3.0f, 4.0f};
d.empty();
d.size();
d.max_size();
// 和vector不同,deque不提供以下的函数
//d.capacity();
//d.reserve(100);
d.shrink_to_fit(); //存在该函数
// operator == != < > <= >=
// 赋值
b = g;
b.assign(3, 1.0f);
b.assign(g.begin(), g.end());
b.assign({1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f});
// 交换
b.swap(a);
std::swap(a,b);
// 元素访问
b[0];
b.at(0); //有可能会抛出异常
b.front();
b.back();
// 迭代器相关
a.begin();
a.end();
a.cbegin();
a.cend();
a.rbegin();
a.rend();
a.crbegin();
a.crend();
a.pop_back(); // maybe wrong
if(!a.empty()) a.pop_back();
b.erase(b.begin());
b.erase(b.begin(), b.end());
b.push_back(10.0f);
b.pop_back();
b.push_front(1.2f);
b.emplace_front(1.3f);
b.pop_front();
auto iter = b.insert(b.end(), 100.0f);
iter = b.insert(b.end(), 10, -10.0f);
b.insert(b.end(), h.begin(), h.end());
b.emplace(b.end(), 10.0f);
b.emplace_back(10.0f);
b.resize(10);
b.resize(100, 1.0f);
b.clear(); // notice
b.shink_to_fit();
// 异常
// (1) push_back push_front 不会抛出异常
// (2) 元素 move/copy 没有异常的话, insert 、emplace、 emplace_back、 push_back、emplace_front也不会抛出异常
// (3) pop_back、pop_front
// (4) 元素 move/copy 没有异常的话,erase也不会抛出异常
// (5) swap clear
}
list
static void listPart() {
// list 是c++98中引入的双向串列(doubley linked list)
// namespace std {
// template>
// class list;
// }
// 特点不支持随机访问元素,访问头部和尾部元素速度快
// 任何位置插入删除元素都很快,常量时间内完成
// 插入和删除不会造成迭代器失效
// 对于异常支持的好,出现异常对于list而言,要不成功,要不什么影响没有
using Group = std::list;
Group a;
Group b = a;
Group c(a);
Group d(10);
Group e(10, 1.0f);
Group f(e.begin(), e.end());
Group g({1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f});
Group h = {1.0f, 3.0f, 4.0f};
d.empty();
d.size();
d.max_size();
//和vector不同,list不提供以下的函数
//d.capacity();
//d.reserve(100);
//d.shrink_to_fit();
// operator == != < > <= >=
// 赋值
b = g;
b.assign(3, 1.0f);
b.assign(g.begin(), g.end());
b.assign({1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f});
// 交换
b.swap(a);
std::swap(a,b);
// 元素访问,不能随机访问
//b[0];
//b.at(0);
b.front();
b.back();
// 迭代器相关
a.begin();
a.end();
a.cbegin();
a.cend();
a.rbegin();
a.rend();
a.crbegin();
a.crend();
//下面代码是获取第五个元素的两种方法:
//第一种方法,遍历到第五个元素
auto iterBegin = a.begin();
assert(a.size() >= 10);
for(int i = 0;i < 5; ++i) ++iterBegin;
//第二种方法,通过advance函数直接获取第五个元素
std::advance(iterBegin, 4);
//cpp 11 中使用next函数来获取第五个元素
auto iter5 = std::next(iterBegin, 4);
/*
advance和next的区别:
std::advance
modifies its argument
returns nothing
works on input iterators or better (or bi-directional iterators if a negative distance is given)
std::next
leaves its argument unmodified
returns a copy of the argument, advanced by the specified amount
works on forward iterators or better (or bi-directional iterators if a negative distance is given))
*/
a.pop_back(); // maybe wrong
if(!a.empty()) a.pop_back();
b.erase(b.begin());
b.erase(b.begin(), b.end());
b.push_back(10.0f);
b.pop_back();
b.push_front(1.2f);
b.emplace_front(1.3f);
auto iter = b.insert(b.end(), 100.0f);
iter = b.insert(b.end(), 10, -10.0f);
b.insert(b.end(), h.begin(), h.end());
b.emplace(b.end(), 10.0f);
b.emplace_back(10.0f);
b.resize(10);
b.resize(100, 1.0f);
// 算法
b.remove(1.0f); //删除list中所有的1.0f
b.remove_if([](auto v) { return v > 100.0f;}); //删除满足条件的所有元素
b.reverse(); //反转链表 1 2 3 4 -> 4 3 2 1
//std::sort(a.begin(), a.end());
b.sort(); // list自己实现的sort算法,算法sort对于list不实用
g.sort(); //
b.merge(g); //排好序的两个list
c.unique(); //排好序的两个list 1 1 2 2 1 1 3 4 -> 1 2 1 3 4
c.splice(c.begin(), b); //将b作为一块安插到c的头部
}
forward_list
static void forwardListPart() {
// forward_list 是c++11中引入的单向串列(singly linked list)
// namespace std {
// template>
// class forward_list;
// }
// 特点不支持随机访问元素,访问头部元素速度快
// "forward_list 和自己手写的c-style singly linked list相比,
// 没有任何时间和空间上的额外开销。任何性质如果和这个目标抵触,我们放弃该特征。"
// 任何位置插入删除元素都很快,常量时间内完成
// 插入和删除不会造成迭代器失效
// 对于异常支持的好,出现异常对于forward_list而言,要不成功,要不什么影响没有
using Group = std::forward_list;
Group a;
Group b = a;
Group c(a);
Group d(10);
Group e(10, 1.0f);
Group f(e.begin(), e.end());
Group g({1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f});
Group h = {1.0f, 3.0f, 4.0f};
d.empty();
//d.size(); 不存在size函数
d.max_size();
// 和vector不同,forward_list不提供以下的函数
//d.capacity();
//d.reserve(100);
//d.shrink_to_fit();
// operator == != < > <= >=
// 赋值
b = g;
b.assign(3, 1.0f);
b.assign(g.begin(), g.end());
b.assign({1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f});
// 交换
b.swap(a);
std::swap(a,b);
// 元素访问,不能随机访问
//b[0];
//b.at(0);
b.front();
//b.back(); 不能直接访问最后一个元素
// 迭代器相关
a.begin();
a.end();
a.cbegin();
a.cend();
//auto iter = a.before_begin();
//*iter; // undefined
a.before_begin(); //返回第一个有效位置的前一个位置
c.cbefore_begin(); //返回第一个有效位置的前一个位置
// a.rbegin();
// a.rend();
// a.crbegin();
// a.crend();
auto iterBegin = a.begin();
//a.pop_back(); // maybe wrong
//if(!a.empty()) a.pop_back();
// list的erase函数会返回下一个元素的位置,forward_list的这些函数返回void
b.erase_after(b.before_begin()); // return void 删除下一个位置的元素
b.erase_after(b.before_begin(), b.end()); // return void
//b.push_back(10.0f); 不支持push_back
//b.pop_back();
b.push_front(1.2f);
b.emplace_front(1.3f);
auto iter = b.insert_after(b.before_begin(), 100.0f);
iter = b.insert_after(b.before_begin(), 10, -10.0f);
b.insert_after(b.before_begin(), h.begin(), h.end());
//b.emplace(b.end(), 10.0f);
//b.emplace_back(10.0f);
b.resize(10);
b.resize(100, 1.0f);
// 算法
b.remove(1.0f);
b.remove_if([](auto v) { return v > 100.0f;});
b.reverse(); // 1 2 3 4 -> 4 3 2 1
//std::sort(a.begin(), a.end());
b.sort(); // <
g.sort(); //
b.merge(g);
c.unique(); // 1 1 2 2 1 1 3 4 -> 1 2 1 3 4
c.splice_after(c.before_begin(), b); //将b作为一块安插到c的头部
//在第三个元素前插入一个元素的例子
Group forlist = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
auto fiter = forlist.before_begin();
for(int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) ++fiter;
forlist.insert_after(fiter, 10);
}
set
static void setPart() {
// set multiset 是c++98中引入的二叉树数据结构
// namespace std {
// template, typename Allocator = allocator>
// class set;
// template, typename Allocator = allocator>
// class multiset;
// }
// 特点自动将元素排序
// 插入、删除、查找的时间复杂度O(logn)
// 插入的元素必须支持严格的弱顺序
// (1) x < y == true, y < x == false
// (2) x < y == true, y < z == true, x < z == true
// (3) x < x === false
// (4) a == b, b == c, c == a
// 不能改变元素的值
//
// 辅助的类——pair
// namespace std {
// template
// struct pair {
// T1 first;
// T2 second;
// };
// }
using Group = std::set;
Group a;
Group b = a;
Group c(a);
Group d(c.begin(), c.end());
Group g({ 1.0f, 4.0f, 3.0f });
// 1.0f
// 1.0f 4.0f
// 1.0f 3.0f 4.0f -> 1.0f 4.0f 3.0f
Group h = { 1.0f, 3.0f, 4.0f };
d.empty();
d.size();
d.max_size();
// operator == != < > <= >=
// special
auto keycomp = c.key_comp(); //没用过
auto valuecomp = c.value_comp(); //没用过
// 赋值
b = g;
// 交换
b.swap(a);
std::swap(a, b);
// 迭代器相关
a.begin();
a.end();
a.cbegin();
a.cend();
a.rbegin();
a.rend();
a.crbegin();
a.crend();
auto iterBegin = a.begin();
//算法函数
//count的返回值0表示不存在这个值,1代表存在这个值
// multiset中count函数的返回值是>= 0的,如果不存在,则返回0;如果存在,则会将出现的数量返回给你
auto num = a.count(1.0f);
//find的返回值是迭代器
auto findIter = a.find(1.0f);
if (findIter == a.end()) {
// not finded
} else {
*findIter;
}
//lower_bound——返回的位置的值大于等于你要插入的值
auto lower = a.lower_bound(1.0f);
if (lower != a.end()) {
if (*lower == 1.0f) {
// has 1.0f
}
}
//返回的位置的值大于你要插入的值
auto high = a.upper_bound(1.0f);
//equal_range的返回值 std::make_pair(a.lower_bound(1.0f), a.upper_bound(1.0f));
auto range = a.equal_range(1.0f);
auto eraseIter = b.erase(b.begin());
eraseIter = b.erase(b.begin(), b.end());
//insert的返回值是一个pair
auto state = b.insert(100.0f);
auto insertIter = b.insert(c.begin(), c.end());
b.emplace(10.0f);
b.emplace_hint(b.end(), 100.0f);
}
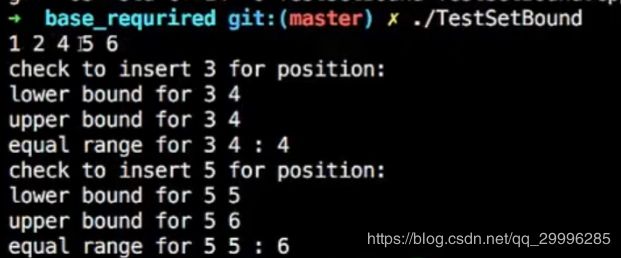
TestSetBound——测试set的各种bound函数
注意:对于迭代器的返回值,一定要判断其是否有效。
#include
#include
int main() {
using Group = std::set;
Group a = {1,4,2,5,6};
for(auto& v : a) {
std::cout << v << " "; // 1 2 4 5 6
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "check to insert 3 for position:\n";
auto lb = a.lower_bound(3);
auto ub = a.upper_bound(3);
auto er = a.equal_range(3);
std::cout << "lower bound for 3 " << *lb << std::endl; // 4
std::cout << "upper bound for 3 " << *ub << std::endl; // 4
std::cout << "equal range for 3 " << *(er.first) << " : " // 4 :4
<< *(er.second) << std::endl;
std::cout << "check to insert 5 for position:\n";
lb = a.lower_bound(5);
ub = a.upper_bound(5);
er = a.equal_range(5);
std::cout << "lower bound for 5 " << *lb << std::endl; // 5
std::cout << "upper bound for 5 " << *ub << std::endl; //6
std::cout << "equal range for 5 " << *(er.first) << " : " // 5 : 6
<< *(er.second) << std::endl;
} - lower_bound——返回的位置是大于等于你要插入的值
- upper_bound——返回的位置是大于你要插入的值
- equal_range——返回一个pair,第一个值是lower_boud的返回值,第二个值是upper_bound的返回值
map
static void mapPart() {
// map multimap是c++98中引入的二叉树数据结构。key是const key,因此无法修改
// namespace std {
// template, typename Allocator = allocator>
// class map;
// template, typename Allocator =locator>
// class multimap;
// }
// 特点自动将元素排序
// 插入和删除查找O(logn)
// 必须Key元素必须支持严格的弱顺序
// (1) x < y == true, y < x == false
// (2) x < y == true, y < z == true, x < z == true
// (3) x < x === false
// (4) a == b, b == c, c == a
// 不能改变Key元素的值
using Group = std::map;
Group a;
Group b = a;
Group c(a);
Group d(c.begin(), c.end());
Group g({ {1, "a"}, {2,"test"}, {3, "test"} });
d.empty();
d.size();
d.max_size();
// operator == != < > <= >=
// special
auto keycomp = c.key_comp();
auto valuecomp = c.value_comp();
// 赋值
b = g;
// 交换
b.swap(a);
std::swap(a, b);
// 迭代器相关
a.begin();
a.end();
a.cbegin();
a.cend();
a.rbegin();
a.rend();
a.crbegin();
a.crend();
auto iterBegin = a.begin();
//算法函数
// map count 0 1
// multimap count >= 0
auto num = a.count(1);
auto findIter = a.find(1);
if (findIter == a.end()) {
// not finded
}
else {
//*findIter; // 解引用之后得到的std::pair&
//注意key是const int类型,因此无法修改
}
auto lower = a.lower_bound(1);
if (lower != a.end()) {
if (*lower.first == 1) {
// has 1
}
}
auto high = a.upper_bound(1);
auto range = a.equal_range(1); // return std::make_pair(a.lower_bound(1), a.upper_bound(1));
auto eraseIter = b.erase(b.begin());
eraseIter = b.erase(b.begin(), b.end());
// insert返回值是一个pair,第一个元素指向插入的迭代器的位置,第二个参数表示是否插入成功
//state is a pair
auto state = b.insert(std::make_pair(100, "good"));
auto insertIter = b.insert(c.begin(), c.end());
//emplace是按原位插入。由于cpp11引入了move才有的这些操作
b.emplace(std::make_pair(10, "has it"));
// 这句和下面那句等价—b.emplace( std::pair(11, std::string("again"));
b.emplace(11, std::string("again"));
//这句和下面那句等价—b.emplace(std::pair(12, "third"));
b.emplace(12, "third");
b.emplace_hint(b.end(), 13, "haha");
// map重载了[]。如果搜索的键值对不存在,则会创建一个这样的键值对,插入map中
//插入过程为auto iter = b.insert(std::make_pair(13, std::string())).first; return (*iter).second;
// auto这里的类型是string
auto& info = b[10];
// at 使用at查找,找到的情况下返回一个引用,没有的情况下返回一个异常
//因此使用的时候需要用一个try catch将语句包起来。
//这样的其实不如下面的更推荐的方式
try {
auto& findInfo = b.at(10); // 既可以是const,也可以是非const
}
catch (...) {}
//更推荐使用这种方式来进行查找
auto findIter = b.find(10);
if (findIter != std::end(b) /* b.end() */) {
auto& v = (*findIter).second;
}
else {}
//调用下面自己写的辅助函数来进行键值对查找
auto info = get_default(b, 10);
if (info.empty()) {}
else {}
}
//写一个辅助函数,帮助我们查找键值对
template
typename Map::mapped_type get_default(
const Map &map, const typename Map::key_type &key,
const typename Map::mapped_type &dflt = typename Map::mapped_type()) {
auto pos = map.find(key);
return (pos != map.end() ? pos->second : dflt);
}
unordered_set和unordered_map
static void unorderedSetAndMapPart() {
// unordered_multiset unordered_set
// unordered_map unordered_multimap是c++11中以hash table为基础的,内部元素没有明确的顺序的容器
//namespace std {
// template, typename
// EqPred = equal_to, typename Allocator =
// allocator>
// class unorderd_map;
// template, typename
// EqPred = equal_to, typename Allocator =
// allocator>
// class multimap;
// template, typename
// EqPred = equal_to, typename Allocator =
// allocator>
// class unorderd_set;
// template, typename
// EqPred = equal_to, typename Allocator =
// allocator>
// class unorderd_multiset;
//}
// 插入和删除查找O(1)
// 不能改变Key元素的值
using Group = std::unordered_map;
Group a;
Group b = a;
Group c(a);
Group d(c.begin(), c.end());
Group g({ {1, "a"}, {2,"test"}, {3, "test"} });
d.empty();
d.size();
d.max_size();
// operator == !=
// special
// 赋值
b = g;
// 交换
b.swap(a);
std::swap(a, b);
// 迭代器相关
a.begin();
a.end();
a.cbegin();
a.cend();
a.rbegin();
a.rend();
a.crbegin();
a.crend();
auto iterBegin = a.begin();
//算法函数
// map count 0 1
// multimap count >= 0
auto num = a.count(1);
auto findIter = a.find(1);
if (findIter == a.end()) {
// not finded
}
else {
const std::pair& obj = *findIter;
//*findIter; // std::pair&
}
auto lower = a.lower_bound(1);
if (lower != a.end()) {
if (*lower.first == 1) {
// has 1
}
}
auto high = a.upper_bound(1);
auto range = a.equal_range(1); // return std::make_pair(a.lower_bound(1), a.upper_bound(1));
auto eraseIter = b.erase(b.begin());
eraseIter = b.erase(b.begin(), b.end());
auto state = b.insert(std::make_pair(100, "good")); // state is a pair
auto insertIter = b.insert(c.begin(), c.end());
b.emplace(std::make_pair(10, "has it"));
// b.emplace( std::pair(10, std::string("again"));
b.emplace(11, std::string("again"));
b.emplace(12, "third"); // b.emplace(std::pair(10, "third"));
b.emplace_hint(b.end(), 13, "haha");
// 重载[]
// auto string
auto& info = b[10];
//如果没找到,则执行[]之后的操作等价于:
//auto iter = b.insert(std::make_pair(13, std::string())).first; return (*iter).second;
// at
try {
auto& findInfo = b.at(10); // const
}
catch (...) {}
auto findIter = b.find(10);
if (findIter != std::end(b) /* b.end() */) {
auto& v = (*findIter).second;
}
else {}
auto info = get_default(b, 10);
if (info.empty()) {}
else {}
}