非线性逻辑回归的代码实现(梯度下降法)
非线性逻辑回归的代码实现(梯度下降法)

当我们需要分类这样的数据集的时候,线性的逻辑回归就派不上用场了
前期的代码模块都与线性逻辑回归的步骤一致。
线性逻辑回归的代码实现:
https://mp.csdn.net/mdeditor/90899227#
载入数据
data = np.genfromtxt(r'data.txt',delimiter=',')
x_data = data[:, :-1]
y_data = data[:, -1, np.newaxis]
对原始数据画图
def plot():
x0 = []
x1 = []
y0 = []
y1 = []
# 切分不同数据
for i in range(len(x_data)):
if y_data[i] == 0:
x0.append(x_data[i, 0])
y0.append(x_data[i, 1])
else:
x1.append(x_data[i, 0])
y1.append(x_data[i, 1])
# 画图
scatter0 = plt.scatter(x0, y0, c='b', marker='o')
scatter1 = plt.scatter(x1, y1, c='r', marker='x')
#画图例
plt.legend(handles=[scatter0, scatter1], labels=['label0', 'label1'], loc='best')
plot()
plt.show()
生成非线性项:
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
# 定义多项式回归,degree的值可以调节多项式的特征
poly_reg = PolynomialFeatures(degree=3)
# 特征处理
x_poly = poly_reg.fit_transform(x_data)
利用sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures来构建特征项,其中degree控制多项式的度。
例如,如果有a,b两个特征,那么它的2次多项式为(1,a,b,a^2,ab, b^2)
利用代码来看一看,这里a=2,b=3,degree=3,

所以它打印出来的是1,a,b,a²,ab,b²,a³,a²b,ab²,b³
![]()
定义sigmoid函数、代价函数、梯度下降法
def sigmoid(x):
return 1.0/(1+np.exp(-x))
def cost(xMat, yMat, ws):
left = np.multiply(yMat, np.log(1-sigmoid(xMat*ws)))
right = np.multiply(1-yMat, np.log(1-sigmoid(xMat * ws)))
return np.sum(left + right) / -(len(xMat))
def gradDscent(xArr, yArr):
if scale == True:
xArr = preprocessing(xArr)
xMat = np.mat(xArr)
yMat = np.mat(yArr)
lr = 0.03
epochs = 50000
costList = []
#计算数据列数,有几列就有几个权值
m, n = np.shape(xMat)
#初始化权值
ws = np.mat(np.ones((n, 1)))
for i in range(epochs+1):
# xMat和weights矩阵相乘
h = sigmoid(xMat*ws)
# 计算误差
ws_grad = xMat.T*(h-yMat)/m
ws = ws - lr * ws_grad
if i % 50 == 0:
costList.append(cost(xMat, yMat, ws))
return ws, costList
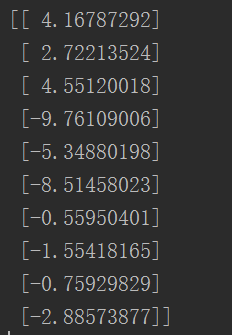
得到degree=3时各项的权值
#训练模型,得到权值和cost值的变化
ws, costList = gradDscent(x_poly, y_data)
print(ws)
作图
# 获取数据所在的范围
x_min, x_max = x_data[:, 0].min() - 1, x_data[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = x_data[:, 1].min() - 1, x_data[:, 1].max() + 1
# 生成网格矩阵
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.02), np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.02))
# 进行判断
z = sigmoid(poly_reg.fit_transform(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]).dot(np.array(ws)))
# ravel与flatten类似,多维数据转一维
for i in range(len(z)):
if z[i] > 0.5:
z[i] = 1
else:
z[i] = 0
z = z.reshape(xx.shape)
注:ravel与flatten类似,多维数据转一维
flatten不会改变原始数据,ravel会改变原始数据
做等高线图观察
z的值只会是0或1,在等高线图中,z代表高度,所以属于不同类的数据可以很直观地观察出来。
cs = plt.contourf(xx, yy, z)
plot()
plt.show()
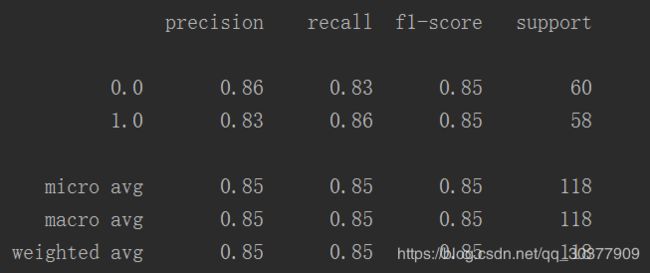
预测
def predict(x_data, ws):
xMat = np.mat(x_data)
ws = np.mat(ws)
return [1 if x >= 0.5 else 0 for x in sigmoid(xMat*ws)]
predictions = predict(x_poly, ws)
print(classification_report(y_data, predictions))