Leetcode学习之栈、队列、堆(1)
开宗明义:本系列基于小象学院林沐老师课程《面试算法 LeetCode 刷题班》,刷题小白,旨在理解和交流,重在记录,望各位大牛指点!
Leetcode学习之栈、队列、堆(1)
文章目录
- 1、STL stack(栈、先进后出线性表)
- 2、STL queue(队列、先进先出线性表)
- 3、使用队列实现栈(队列-->栈) Leetcode 225.
- 4、使用栈实现队列(栈-->队列) Leetcode 232.
- 4.1 思路① 临时栈
- 4.2 思路② 双栈法 O(N)
1、STL stack(栈、先进后出线性表)
堆栈是一个线性表,插入和删除只在表的一端进行。这一端称为栈顶( S t a c k T o p Stack \ Top Stack Top),另一端则为栈底( S t a c k B o t t o m Stack \ Bottom Stack Bottom)。堆栈的元素插入称为入栈,元素的删除称为出栈。由于元素的入栈和出栈总在栈顶进行,因此,堆栈是一个后进先出(Last In First Out)表,即 L I F O LIFO LIFO 表。 s t a c k stack stack堆栈容器的 C + + C++ C++标准头文件为 s t a c k stack stack ,必须用宏语句 "#include " 包含进来,才可对 s t a c k stack stack 堆栈的程序进行编译。
测试代码:
#include stack用法总结:
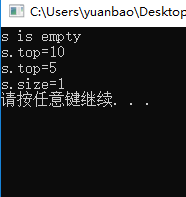
empty() 堆栈为空则返回真
pop() 移除栈顶元素
push() 在栈顶增加元素
size() 返回栈中元素数目
top() 返回栈顶元素
2、STL queue(队列、先进先出线性表)
队列,先进先出的线性表。
测试代码:
#include queue用法总结:
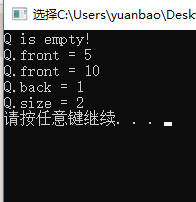
push(x) 将x压入队列的末端
pop() 弹出队列的第一个元素(队顶元素),注意此函数并不返回任何值
front() 返回第一个元素(队顶元素)
back() 返回最后被压入的元素(队尾元素)
empty() 当队列为空时,返回true
size() 返回队列的长度
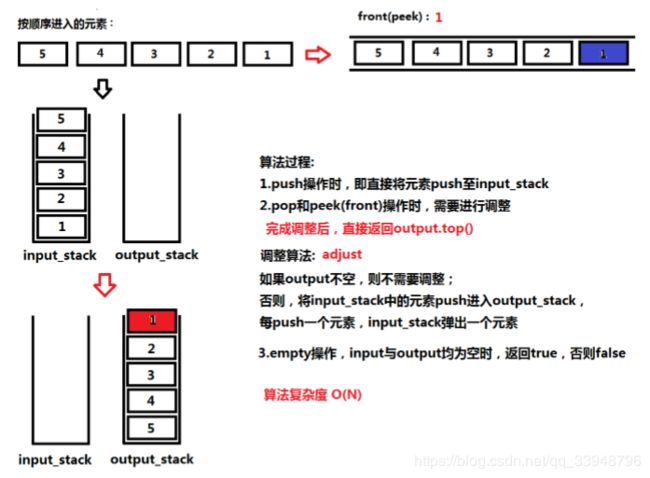
3、使用队列实现栈(队列–>栈) Leetcode 225.
题目来源: L e e t c o d e 225. I m p l e m e n t S t a c k U s i n g Q u e u e s Leetcode \ 225. \ Implement \ Stack \ Using \ Queues Leetcode 225. Implement Stack Using Queues
题目描述:设计一个栈,支持如下操作 p u s h ( x ) 、 p o p ( x ) 、 t o p ( ) 、 e m p t y ( ) push(x)、pop(x)、top()、empty() push(x)、pop(x)、top()、empty(),这些操作算法复杂度需是常数级, O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1),需要实现的栈内部存储数据的结构为队列。
要求描述: 
思路:临时队列
测试代码:
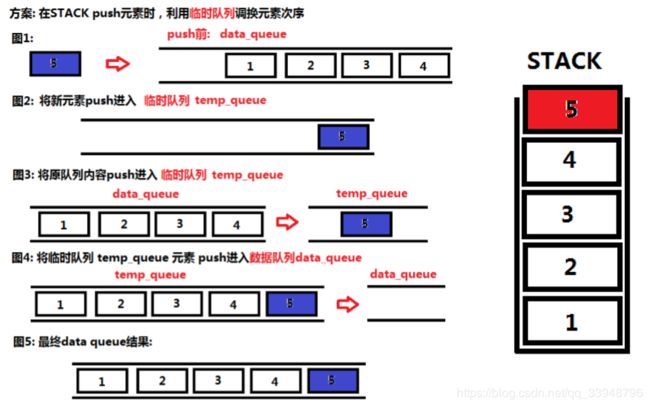
#include 4、使用栈实现队列(栈–>队列) Leetcode 232.
题目来源: L e e t c o d e 232. I m p l e m e n t Q u e u e U s i n g S t a c k s Leetcode \ 232. \ Implement \ Queue \ Using \ Stacks Leetcode 232. Implement Queue Using Stacks
题目描述:设计一个队列,队列支持如下操作,这些操作的算法复杂度为常数级, O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1),需要实现的队列内部存储数据的结构为栈,栈的方法只包括 p u s h 、 t o p 、 p o p 、 s i z e 、 e m p t y push、top、pop、size、empty push、top、pop、size、empty等标准的栈方法。
要求描述:

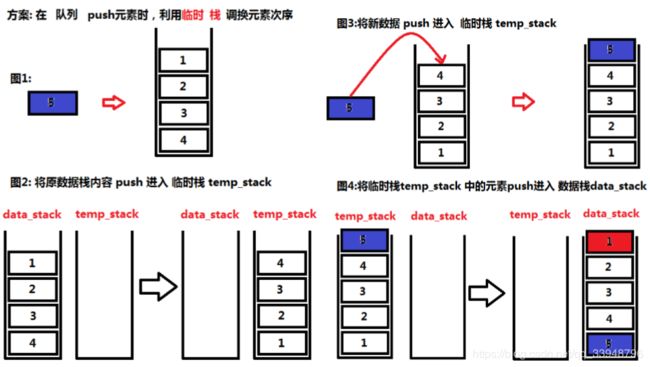
4.1 思路① 临时栈
测试代码:
#include 4.2 思路② 双栈法 O(N)
测试代码:
#include