PyQt5 实时获取屏幕界面图像,python3使用matplotlib
由于之前有过C++Qt的基础,加上简单比较python的几个GUI库,最终决定采用PyQt5库。
本程序采用了Python3进行编写,用了PyQt5、matplotlib、pandas等第三方库,其中有一个小功能是实现实时获取放大当前波形图。
话不多说,首先需要安装第三方库的支持,由于使用pip安装像matplotlib库之类的会比较麻烦,安装后将发现使用的时候会报错,网上也找了很多办法,但大部分都是比较麻烦的,哈哈,博主比较nan,就直接装了anaconda3,里面包含了大部分需要使用到的,具体可以百度这个软件,下载安装,安装后大概会占用1个g的内容。
对于PyQt5,就可以简单地使用pip install PyQt5命令直接安装啦!
安装完后,开始入正题,编写程序:
首先编写matplotlib相关的基础父类
class BaseOscillograph(FigureCanvas): # 定义信号 PosChangeSignal = QtCore.pyqtSignal(int,int) WheelChangSignal = QtCore.pyqtSignal(int) def __init__(self, parent=None, width=5, height=4, dpi=100): self.WheelValue = 0 #Wheel Default Value #Matble实现 fig = Figure(figsize=(width, height), dpi=dpi) self.axes = fig.add_subplot(111) self.axes.hold(False) FigureCanvas.__init__(self, fig) self.setParent(parent) # 设置父窗口,添加入窗口容器 FigureCanvas.setSizePolicy(self,QSizePolicy.Expanding,QSizePolicy.Expanding) FigureCanvas.updateGeometry(self) # 改变样式 self.pixmap = QPixmap("./img/border.png") self.scaledPixmap = self.pixmap.scaled(QSize(100, 100), Qt.KeepAspectRatio) # 定义大小 按比例缩放图片 newCursor = QCursor(self.scaledPixmap, -1, -1) self.setCursor(newCursor) def wheelEvent(self, event): delta = event.angleDelta() oriention = delta.y() / 8 if oriention > 0: self.WheelValue -=10 else: self.WheelValue +=10 #Fix Value if self.WheelValue > 100: self.WheelValue =100 if self.WheelValue <-40: self.WheelValue = -40 self.scaledPixmap = self.pixmap.scaled(QSize(120+self.WheelValue, 120+self.WheelValue), Qt.KeepAspectRatio) newCursor = QCursor(self.scaledPixmap, -1, -1) self.setCursor(newCursor) self.WheelChangSignal.emit(self.WheelValue) # Send Signal To Provide Current WhellValue def mouseMoveEvent(self, event): pos =event.globalPos() self.curX = pos.x() self.curY = pos.y() self.PosChangeSignal.emit(self.curX,self.curY) super().mouseMoveEvent(event)
大部分本文讨论的核心功能将在父类实现,重载wheelEvent方法,用于获取鼠标滚动事件,采用self.WheelValue属性用于记录当前鼠标滚轮的值,用于发送到主窗体,主窗体获取后动态改变显示大小的倍率,实现放大缩小的效果。每次滚动增减值为10,读者也可以自行添加个全局变量,或后期使用读取配置文件的方式,动态改变这一值。
每次改变后,使用emit将这个值发送出去,供主窗口程序获取并作出改变。
同样的方式,采用复写mouseMoveEvent的方法,将获取的当前鼠标位置保存起来,并发送给主界面
接下来就需要编写子类功能实现窗口了,继承自BaseOscillograph
#全局变量 i=0 j=200 data = pd.read_excel(r'./data/signalData.xlsx') data = np.array(data) class MatplotOscillograph(BaseOscillograph): def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): BaseOscillograph.__init__(self, *args, **kwargs) #调用父类的构造器 self.timer = QtCore.QTimer(self) self.timer.timeout.connect(self.update_figure) # FIXME : 改用开启线程的方式 self.timer.start(100) def update_figure(self): # TODO : 此代码需要放在线程上 涉及线程通信 global i,j self.axes.plot(data[i,j-200:j], 'r') self.axes.set_ylim([data[i,:].min(),data[i,:].max()]) j = j + 5 if j > 4096: j = 0 i = i + 1 self.draw() def stopRun(self): self.timer.stop() def beginRun(self): self.timer.start(100)
这里首先采用简单的测试方法,将excel文件里面的内容当做仪器发送过来的信号,进行读取(这里的读取只是测试用,后期需要采用线程的方式进行动态获取,动态改变波形图,不在本文章详细介绍),子类使用简单的定时器功能,定时获取数据,并将数据读取显示成为波形图,当然,这里是需要修改的,只做测试用。
excel的数据内容很简单,其实就是仿到时候仪器发送过来的数据。由于没有开启线程动态获取,开启程序的时候会因为读取过长,显示界面比较缓慢。后续采用动态获取仪器发送过来的数据将不会有这种现象。
主程序类实现:
class ApplicationWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): QMainWindow.__init__(self) self.Init() def Init(self): # InitWindowAttribute self.setAttribute(QtCore.Qt.WA_DeleteOnClose) self.setWindowFlags(Qt.FramelessWindowHint) #去掉标题栏 # 添加状态栏 重载,参数二为状态持续时间 self.statusBar().showMessage(u"心电信号波形图") # self.SetStyle() self.InitData() self.InitProperty() self.InitLayout() def SetStyle(self): qssFile = open("qss\style.qss").read() self.setStyleSheet(qssFile) self.setWindowIcon(QIcon("img/15d.ico")) def InitData(self): # Param self.WheelValue = 0 #默认为0 self.FitstMove = 1 self.bImgRun = 1 self.curX = -1 self.curY = -1 # Control self.image = QPixmap() self.picture = QLabel() self.minBtn = QPushButton() self.exitBtn = QPushButton() self.aboutBtn = QPushButton() self.analyResText = QTextEdit() # Others self.timer = QtCore.QTimer(self) # 定时器 def InitProperty(self): self.image.scaled(QSize(300, 300), Qt.KeepAspectRatio) # self.picture.setFixedSize(300, 300) self.picture.setScaledContents(1) # self.analyResText.setAttribute(Qt.WA_TranslucentBackground, 1) # Updata self.timer.timeout.connect(self.updateCurImg) # #### # Init ToolBar self.minBtn.setIcon(QIcon("img/btn_mini_normal.png")) self.minBtn.setMaximumSize(20, 20) self.minBtn.setIconSize(QSize(30, 30)) self.minBtn.clicked.connect(self.windowMin) # self.exitBtn.setIcon(QIcon("img/btn_close_normal.png")) self.exitBtn.setMaximumSize(20, 20) self.exitBtn.setIconSize(QSize(30, 30)) self.exitBtn.clicked.connect(self.fileQuit) # self.aboutBtn.setIcon(QIcon("img/list_icon_b.png")) self.aboutBtn.setMaximumSize(20, 20) self.aboutBtn.setIconSize(QSize(30, 30)) self.aboutBtn.clicked.connect(self.about) # #### # def InitLayout(self): ### # Main Frame And Layout frame = QWidget() frameLayout = QVBoxLayout(frame) # ### # TitleLayout titleLayout = QHBoxLayout() toolBarLayout = QHBoxLayout() # ico = QToolButton() ico.setIcon(QIcon("img/15d.ico")) title = QLabel(u"心电信号波形界面") # toolBarLayout.addWidget(QLabel()) toolBarLayout.addWidget(self.aboutBtn, 1) toolBarLayout.addWidget(self.minBtn, 1) toolBarLayout.addWidget(self.exitBtn, 1) # titleLayout.addWidget(ico) titleLayout.addWidget(title) titleLayout.addLayout(toolBarLayout) # ### # CenterLayout centerLayout = QHBoxLayout() rightLayout = QVBoxLayout() # MatbalWindow matplotWindow = MatplotOscillograph(frame, width=5, height=4, dpi=100) matplotWindow.PosChangeSignal.connect(self.showCurImg) matplotWindow.WheelChangSignal.connect(self.wheelChange) # rightLayout.addWidget(self.picture) rightLayout.addWidget(QLabel(u"分析结果:")) rightLayout.addWidget(self.analyResText) # centerLayout.addWidget(matplotWindow, 2) centerLayout.addLayout(rightLayout, 1) # ### # ButtonLayout bottonLayout = QHBoxLayout() # Buttons stopBtn = QPushButton(u"暂停波形图") beginBtn = QPushButton(u"波形图运动") self.beginImgBtn = QPushButton(u"观察动图") self.analyCom = QComboBox() # # TODO : 改模式名称 self.analyCom.addItem(u"分析1") self.analyCom.addItem(u"分析2") self.analyCom.addItem(u"分析3") self.analyCom.addItem(u"分析4") self.analyCom.addItem(u"分析5") # Signals and slots stopBtn.clicked.connect(matplotWindow.stopRun) beginBtn.clicked.connect(matplotWindow.beginRun) self.beginImgBtn.clicked.connect(self.beginImgRun) self.analyCom.currentIndexChanged.connect(self.analyFunction) # bottonLayout.addWidget(stopBtn) bottonLayout.addWidget(beginBtn) bottonLayout.addWidget(self.beginImgBtn) bottonLayout.addWidget(self.analyCom) # ### # MainLayout frameLayout.addLayout(titleLayout) frameLayout.addWidget(QLabel().setMaximumHeight(20)) frameLayout.addLayout(centerLayout) frameLayout.addLayout(bottonLayout) # ### Others # setFocus And CentralWindow frame.setFocus() self.setCentralWidget(frame) # ### # # Slot Functions # # def fileQuit(self): self.close() def windowMin(self): self.showMinimized( ) def closeEvent(self, ce): self.fileQuit() def about(self): QMessageBox.about(self, u"心电信号波形图", """心电信号波形图使用程序 旨为医生提供更便捷的服务 """ ) def mousePressEvent(self, event): if event.button() == Qt.LeftButton: self.dragPosition = event.globalPos() - self.frameGeometry().topLeft() QApplication.postEvent(self, QEvent(174)) event.accept() def mouseMoveEvent(self, event): if event.buttons() == Qt.LeftButton: self.move(event.globalPos() - self.dragPosition) event.accept() def showCurImg(self,x,y): self.curX = x self.curY = y screen = QGuiApplication.primaryScreen() distance = self.WheelValue + 80 self.image = QPixmap(screen.grabWindow(0, x-distance,y-distance,distance*2, distance*2)) self.picture.setPixmap(self.image) self.picture.update() def wheelChange(self,wheelValue): self.WheelValue = wheelValue def updateCurImg(self): self.showCurImg(self.curX,self.curY) def beginImgRun(self): if(self.bImgRun): if self.curX == -1: self.statusBar().showMessage(u"请先用鼠标获取波形图再尝试",2000) return self.bImgRun = 0 self.beginImgBtn.setText(u"停止动图") self.timer.start(500) # Don't Too Quick. It is important for CPU else: self.bImgRun =1 self.beginImgBtn.setText(u"观察动图") self.timer.stop()
哈哈,由于受到了Duilib的影响,现在做界面什么的都喜欢采用自绘的方式,同样的思想被我应用到了PyQt中,采用
self.setAttribute(QtCore.Qt.WA_DeleteOnClose) self.setWindowFlags(Qt.FramelessWindowHint) #去掉标题栏去掉标题栏,然后重写下面两个方法以实现窗口的拖动,
def mousePressEvent(self, event): def mouseMoveEvent(self, event):简单地实现了布局后,我们进入到本文重点,就是动态获取屏幕信息
由于MATLAB窗口那边发送了信号,我们在主窗口类实现上,将信号和槽连接起来,一旦信号发生了,槽方法将被调用,槽函数的实现我们详细再看一遍
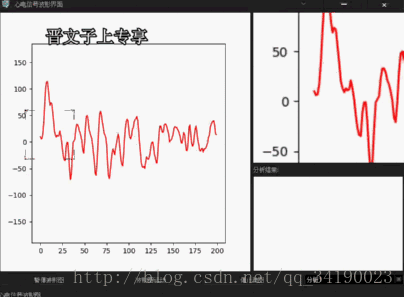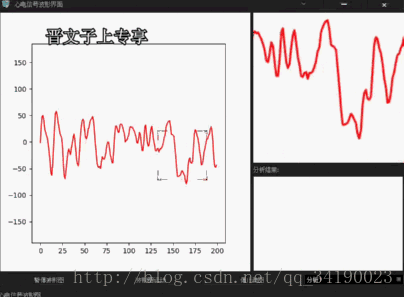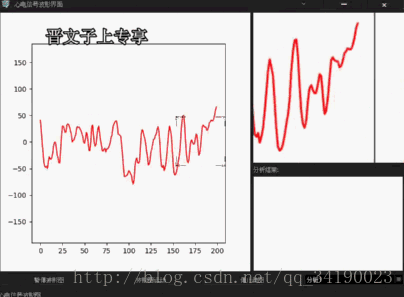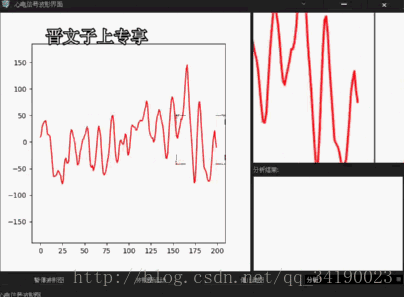
def showCurImg(self,x,y): self.curX = x self.curY = y screen = QGuiApplication.primaryScreen() distance = self.WheelValue + 80 self.image = QPixmap(screen.grabWindow(0, x-distance,y-distance,distance*2, distance*2)) self.picture.setPixmap(self.image) self.picture.update() def wheelChange(self,wheelValue): self.WheelValue = wheelValue由于MATLAB窗口发送信号的同时,我们将鼠标当前的位置也发送过来了,所以,在主界面类中,我们先保存当前的鼠标坐标,供后面使用,然后调用Qt封装好的API,获取屏幕,根据滚轮的值,动态获取这个QPixmap,然后,只需要简答地setPixmap,update后就可以了。
功能很简单,没有太强大的功能,但是可以根据同样的思路,实现截图程序,以及屏幕录屏程序等。
就介绍这么多了,对于python博主也是使用不久,主要是因为Qt有了python的实现,所以也那么幸运,可以使用到python制作一个Gui程序。
好了,功能实现的结果就如下了:还有不完善的地方后续将更改,也会分享出来,一方面可以增强自己的记忆,也可以供以后忘了的时候阅读