【基于opencv3.4.1的Mobilenet_SSD深度学习模型的调用与目标识别】
目前,常见的目标检测算法,如Faster R-CNN,存在着速度慢的缺点。该论文提出的SSD方法,不仅提高了速度,而且提高了准确度。SSD:
该论文的核心思想:
本文中我们主要总结前人工作,通过opencv调用ssd生成模型,实现对图像或视频流中目标的识别。
其中mobile_net的模型文件与描述文件位于opencv安装路径的C:\opencv\opencv\sources\samples\data\dnn\...中。
在opencv的dnn模块中,输入到神经网络的图像需要以一种叫bolb的格式保存。读取了输入图片或者视频流的一帧图像后,这帧图像需要经过bolbFromImage()函数处理为神经网络的输入类型bolb。在这个过程中,图像像素以一个1/255的比例因子,被缩放到0到1之间。另一个参数是图像平均值(比如[0,0,0]),用途不明。保持swapRB参数到默认值1。
其中有几个重要的函数:
1. dnn::blobFromImage函数解读(这个很重要,参数不对,直接影响预测结果)
opencv中的函数声明
CV_EXPORTS_W Mat blobFromImage(InputArray image, double scalefactor=1.0, const Size& size = Size(), const Scalar& mean = Scalar(), bool swapRB=true, bool crop=true);对于各参数的文档解释
第一个参数,InputArray image,表示输入的图像,可以是opencv的mat数据类型。
第二个参数,scalefactor,这个参数很重要的,如果训练时,是归一化到0-1之间,那么这个参数就应该为0.00390625f (1/256),否则为1.0
第三个参数,size,应该与训练时的输入图像尺寸保持一致。
第四个参数,mean,这个主要在caffe中用到,caffe中经常会用到训练数据的均值。tf中貌似没有用到均值文件。
第五个参数,swapRB,是否交换图像第1个通道和最后一个通道的顺序。
第六个参数,crop,如果为true,就是裁剪图像,如果为false,就是等比例放缩图像。
其他地方的解释:
参数:
[1] - image: cv2.imread 读取的图片数据;
[2] - scalefactor: 缩放像素值,如 [0, 255] - [0, 1].
[3] - size: 输出图像的尺寸,如 (netInWidth, netInHeight).
[4] - mean: 从各通道减均值. 如果输入 image 为 BGR 次序,且swapRB=True,则通道次序为 (mean-R, mean-G, mean-B).
[5] - swapRB: 交换 3 通道图片的第一个和最后一个通道,如 BGR - RGB.
[6] - crop: 图像尺寸 resize 后是否裁剪. 如果crop=True,则,输入图片的尺寸调整resize后,一个边对应与 size 的一个维度,而另一个边的值大于等于 size 的另一个维度;然后从 resize 后的图片中心进行 crop. 如果crop=False,则无需 crop,只需保持图片的长宽比.
[7] - ddepth: 输出 blob 的 Depth. 可选: CV_32F 或 CV_8U
关于Net函数:https://docs.opencv.org/master/db/d30/classcv_1_1dnn_1_1Net.html
主要代码如下:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::dnn;
using namespace std;
int main() {
Net net = readNetFromCaffe("MobileNetSSD_deploy.prototxt", "MobileNetSSD_deploy.caffemodel");
const char* classNames[] = { "background", "aeroplane", "bicycle", "bird", "boat", "bottle", "bus", "car", "cat", "chair","cow", "diningtable", "dog", "horse", "motorbike", "person", "pottedplant", "sheep", "sofa", "train", "tvmonitor" };
float detect_thresh = 0.24;
VideoCapture cap("vtest.avi");
if (!cap.isOpened()) return -1;
while (true) {
Mat frame;
cap >> frame;
if (frame.empty()) break;
clock_t start_t = clock();
//预测
Mat inputblob = blobFromImage(frame, 1.0 / 127.5, Size(300, 300), Scalar(127.5, 127.5, 127.5), true, false);
net.setInput(inputblob, "data");
Mat detetmat = net.forward("detection_out");
cout << "Cost time: " << clock() - start_t << endl;
}
}
imshow("test", frame);
waitKey(50);
}
return 0;
}
main函数中数预测部分,然后需要对预测的内容进行绘制。
//绘制
Mat detectionMat(detetmat.size[2], detetmat.size[3], CV_32F, detetmat.ptr());
float confidence_th = 0.2;
for (int i = 0; i < detectionMat.rows; i++) {
//int obj_class = detectionMat.at(i, 1);
float confidence = detectionMat.at(i, 2);
if (confidence > confidence_th) {
size_t objectClass = (size_t)(detectionMat.at(i, 1));
int xLeftBottom = static_cast(detectionMat.at(i, 3) * frame.cols);
int yLeftBottom = static_cast(detectionMat.at(i, 4) * frame.rows);
int xRightTop = static_cast(detectionMat.at(i, 5) * frame.cols);
int yRightTop = static_cast(detectionMat.at(i, 6) * frame.rows);
Rect object((int)xLeftBottom, (int)yLeftBottom, (int)(xRightTop - xLeftBottom), (int)(yRightTop - yLeftBottom));
rectangle(frame, object, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2);
putText(frame, classNames[objectClass], Point(xLeftBottom, yLeftBottom - 10), 3, 0.5, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2);
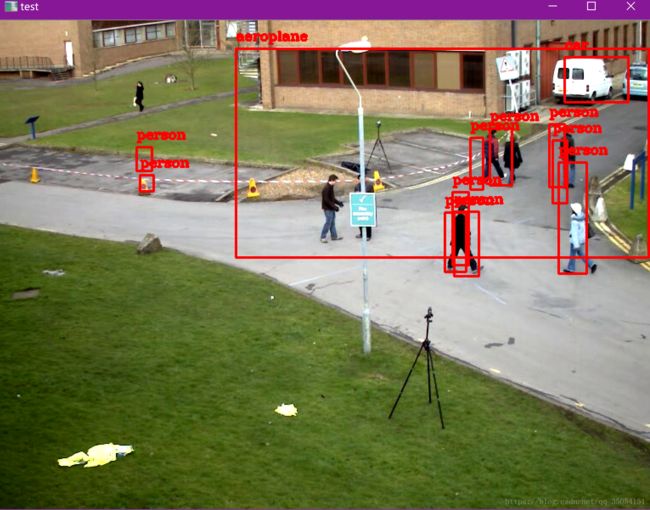
detectionMat输入图像后经过网络前向传播后的输出7*10的结果矩阵,其定义盗用别人一张图来说明前向运行输出的图像结果矩阵,prob层的输出:实际意义为测试图片所对应与标签的概率值。resize成一个列向量,然后排序,输出最大值和最大值所对应的位置。
上图中置信概率最高(0.999)的目标数组下标为2,对应的是bicycle自行车,只要大于设置的阈值(变量confidenceThreshold),就会在图像上标记出目标的位置(detectionMat行向量的3,4,5,6元素)。比如将阈值confidenceThreshold设置为0.5,则识别结果只有一个是大于0.5的,则只会在图像上标记出自行车,如下图:
参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/KayChanGEEK/article/details/79978851
https://blog.csdn.net/samylee/article/details/80548323
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_15947787/article/details/78436995
https://www.jianshu.com/p/f3b027e7a406