JAVA数据结构与算法之————平衡二叉树
JAVA数据结构与算法之————平衡二叉树
平衡二叉树 又称AVL树,平衡二叉树具有的特性是:它是一 棵空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树。
本文将从以下几个方面进行介绍:
- TreeNode结构介绍。
- 向平衡二叉树中插入元素,然后调整二叉树使其仍然为平衡二叉树。
- 创建平衡二叉树。
- 删除平衡二叉树中的节点。
介绍TreeNode结构:
由于我在博客JAVA数据结构与算法之————二叉树中给出了TreeNode的结构,这里就不多重复了。
向平衡二叉树中插入元素,然后调整二叉树使其仍然为平衡二叉树:
向平衡二叉树中插入可能造成以下4种不平衡的情况:
1:如图1

节点5的平衡因子为2,所以应该进行右旋调整,调整后如图2:

具体实现过程看右旋代码(结合上图进行解释):
// 右旋操作
public TreeNode<E> rightRotate(TreeNode<E> T) {
// T为上图1中的节点5,p为节点3
TreeNode<E> p = T.getlChild();
// 结点4作为结点5的左子树接入
T.setlChild(p.getrChild());
// 结点5作为结点3的的右子树接入
p.setrChild(T);
// 如果结点4存在,则设置4的父节点为结点5
if (T.getlChild() != null) {
T.getlChild().setParent(T);
}
// 让3变成5的父节点
p.setParent(T.getParent());
if (p.getParent() != null) {
if (T == T.getParent().getlChild()) {
p.getParent().setlChild(p);
} else {
p.getParent().setrChild(p);
}
}
T.setParent(p);
/*这里有一个需要注意的点是,要先跟新结点5的高度和平衡因子,在跟新结点3的*/
T.setDepth(calDepth(T));
T.setBalance(calBalance(T));
p.setDepth(calDepth(p));
p.setBalance(calBalance(p));
return p;
}
图1不平衡的二叉树经过右旋调整变成图2的平衡二叉树。
2,如图3

图3中2的平衡因子为-2,需要进行左旋操作,调整后如图4:

具体看代码(左旋和右旋类似):
// 左旋 ,基本和右旋类似
public TreeNode<E> leftRotate(TreeNode<E> T) {
TreeNode<E> p = T.getrChild();
T.setrChild(p.getlChild());
p.setlChild((T));
if (T.getrChild() != null) {
T.getrChild().setParent(T);
}
p.setParent(T.getParent());
if (p.getParent() != null) {
if (T == T.getParent().getlChild()) {
p.getParent().setlChild(p);
} else {
p.getParent().setrChild(p);
}
}
T.setParent(p);
T.setDepth(calDepth(T));
T.setBalance(calBalance(T));
p.setDepth(calDepth(p));
p.setBalance(calBalance(p));
return p;
}
3,如图5:
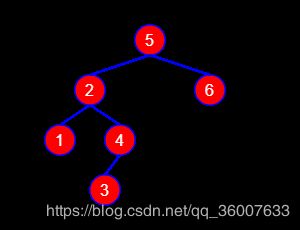
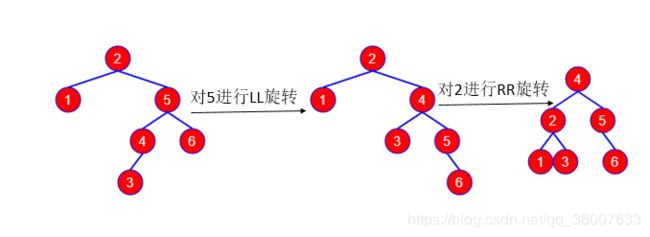
如图5,结点5的平衡因子为2,结点2的平衡因子为-1,它们的平衡因子符号相反,这种情况应该对根结点为2的子树进行左旋炒作,然后对根节点为5的子树进行右旋操作,调整后如图6:

4,如图7:

如图7,结点5的平衡因子为-2,结点2的平衡因子为1,它们的平衡因子符号相反,这种情况应该对根结点为5的子树进行右旋操作,然后对根节点为2的子树进行左旋操作,调整后如图8:
上代码:
public void adjust(TreeNode<E> T){
// 如果T的平衡因子大于等于2,或者小于等于-2,,都需要对以T为跟节点的子树进行旋转调整
if (T.getBalance() >= 2) {
// 当T的平衡因和T左子树的平衡因子符号相反,需要先对T的左子树进行左旋操作,再对T进行右旋操作
if (T.getlChild().getBalance() == -1) {
leftRotate(T.getlChild());
}
rightRotate(T);
}
// 与T的平衡因子为2的情况相似,先对T的右子树进行右旋操作,再对T进行左旋操作
if (T.getBalance() <= -2) {
if (T.getrChild().getBalance() == 1) {
rightRotate(T.getrChild());
}
leftRotate(T);
}
}
下面就正式进入插入代码:
/*
*向平衡二叉树中插入元素
* */
public void insert(TreeNode<E> T, E data) {
//如果data小于T的值,进入T的左子树
if (data.compareTo(T.getData()) < 0) {
if (T.getlChild() != null) {
//如果左子树不为空,这递归左子树
insert(T.getlChild(), data);
} else {
// 如果左子树为空,插入,作为T的左子树
T.setlChild(new TreeNode<E>(data));
T.getlChild().setParent(T);
}
} else {//如果data小于T的值,进入T的右子树
if (T.getrChild() != null) {
//如果右子树不为空,这递归右子树
insert(T.getrChild(), data);
} else {
// 如果右子树为空,插入,作为T的右子树
T.setrChild(new TreeNode<>(data));
T.getrChild().setParent(T);
}
}
// 回溯更新平衡因子
T.setDepth(calDepth(T));
T.setBalance(calBalance(T));
// 调整树的平衡
adjust(T);
}
// 计算T的高度
public int calDepth(TreeNode<E> T) {
if (T == null) {
return 0;
}
int depth = 0;
if (T.getlChild() != null) {
// 如果T的左子树不为空,则depth的值为T左子树的高度
depth = T.getlChild().getDepth();
} else {
// 否则为0
depth = 0;
}
// 如果T的右子树不为空且右子树的高度比左子树高,则depth的值为右子树的高度
if (T.getrChild() != null && T.getrChild().getDepth() > depth) {
depth = T.getrChild().getDepth();
}
// T的高度为子树中高度最高的值加1
depth++;
return depth;
}
// 平衡因子=T左子树的高度-T右子树的高度
public int calBalance(TreeNode<E> T) {
return calDepth(T.getlChild()) - calDepth(T.getrChild());
}
创建平衡二叉树
这里涉及到的BinaryTree请移步:[JAVA数据结构与算法之————二叉树]
(https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36007633/article/details/89429077)
// 创建平衡二叉树
public void createAVLTree(E[] a) {
BinaryTree<E> bt = new BinaryTree<>();
this.root = new TreeNode<E>(a[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
insert(this.root, a[i]);
//每次都需要找到跟节点从上往下插入
this.root = bt.findRoot(this.root);
}
}
删除平衡二叉树中的节点
平衡二叉树结点的删除和我们前面提到过的JAVA数据结构与算法之————排序二叉树很类似,无非就是平衡二叉树删除节点后还有对节点进行调整,使其平衡。
删除节点T
// 删除节点T
public TreeNode<E> delete(TreeNode<E> T) {
TreeNode<E> q, s = null;
TreeNode<E> parent = null;
// 如果T为叶子节点,则直接删除
if(T.getlChild() == null && T.getrChild() == null){
if(T == T.getParent().getlChild()){
T.getParent().setlChild(null);
}else{
T.getParent().setrChild(null);
}
parent = T.getParent();
T.delete();
return parent;
}else if(T.getlChild() == null){ //如果T只有右子树,则将T的右子树接入T的父节点
T.getrChild().setParent(T.getParent());
if(T == T.getParent().getlChild()){
T.getParent().setlChild(T.getrChild());
}else{
T.getParent().setrChild(T.getrChild());
}
parent = T.getParent();
T.delete();
return parent;
}else if(T.getrChild() == null){ //如果T只有左子树,则将T的左子树接入T的父节点
T.getlChild().setParent(T.getParent());
if(T == T.getParent().getlChild()){
T.getParent().setlChild(T.getlChild());
}else{
T.getParent().setrChild(T.getlChild());
}
parent = T.getParent();
T.delete();
return parent;
}else{
// 如果T的左右子树都有,则找到T的前驱节点,用T的前驱节点的data与T节点的data替换,然后删除T的前驱节点
q = T;
s = T.getlChild();
while (s.getrChild() != null) {
q = s;
s = s.getrChild();
}
T.setData(s.getData());
if (q == T) {
q.setlChild(s.getlChild());
} else {
q.setrChild(s.getlChild());
}
if (s.getlChild() != null) {
s.getlChild().setParent(q);
}
s.delete();
return q;//返回删除节点的父节点,便于回溯调整节点的平衡
}
}
删除平衡二叉树中的节点:
public void deleteAVL(TreeNode<E> T, E e) {
if (T == null) {
return;
}
if (T.getData().compareTo(e) == 0) {
TreeNode<E> q= null;
q = delete(T);
while (q != null) {
q.setDepth(calDepth(q));
q.setBalance(calBalance(q));
// 调整,使树平衡
adjust(q);
// 一直往到根节点
q = q.getParent();
}
} else if (T.getData().compareTo(e) < 0) {
deleteAVL(T.getrChild(), e);
} else {
deleteAVL(T.getlChild(), e);
}
// 更新根节点
this.root = new BinaryTree<E>().findRoot(this.root);
}
整体代码:
package tree;
public class AVLTree<E extends Comparable<E>> {
private TreeNode<E> root = null;
// 设置根节点
public void setRoot(TreeNode<E> rtn) {
this.root = rtn;
}
//获取根节点
public TreeNode<E> getRoot() {
return this.root;
}
// 创建平衡二叉树
public void createAVLTree(E[] a) {
BinaryTree<E> bt = new BinaryTree<>();
this.root = new TreeNode<E>(a[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
insert(this.root, a[i]);
//每次都需要找到跟节点从上往下插入
this.root = bt.findRoot(this.root);
}
}
// 右旋操作
public TreeNode<E> rightRotate(TreeNode<E> T) {
TreeNode<E> p = T.getlChild();
T.setlChild(p.getrChild());
p.setrChild(T);
if (T.getlChild() != null) {
T.getlChild().setParent(T);
}
// p变成T的父节点
p.setParent(T.getParent());
if (p.getParent() != null) {
if (T == T.getParent().getlChild()) {
p.getParent().setlChild(p);
} else {
p.getParent().setrChild(p);
}
}
T.setParent(p);
/*要先跟新T的高度和平衡因子,在跟新p的*/
T.setDepth(calDepth(T));
T.setBalance(calBalance(T));
p.setDepth(calDepth(p));
p.setBalance(calBalance(p));
return p;
}
// 左旋 ,基本和右旋类似
public TreeNode<E> leftRotate(TreeNode<E> T) {
TreeNode<E> p = T.getrChild();
T.setrChild(p.getlChild());
p.setlChild((T));
if (T.getrChild() != null) {
T.getrChild().setParent(T);
}
p.setParent(T.getParent());
if (p.getParent() != null) {
if (T == T.getParent().getlChild()) {
p.getParent().setlChild(p);
} else {
p.getParent().setrChild(p);
}
}
T.setParent(p);
T.setDepth(calDepth(T));
T.setBalance(calBalance(T));
p.setDepth(calDepth(p));
p.setBalance(calBalance(p));
return p;
}
/*
*向平衡二叉树中插入元素
* */
public void insert(TreeNode<E> T, E data) {
//如果data小于T的值,进入T的左子树
if (data.compareTo(T.getData()) < 0) {
if (T.getlChild() != null) {
//如果左子树不为空,这递归左子树
insert(T.getlChild(), data);
} else {
// 如果左子树为空,插入,作为T的左子树
T.setlChild(new TreeNode<E>(data));
T.getlChild().setParent(T);
}
} else {//如果data小于T的值,进入T的右子树
if (T.getrChild() != null) {
//如果右子树不为空,这递归右子树
insert(T.getrChild(), data);
} else {
// 如果右子树为空,插入,作为T的右子树
T.setrChild(new TreeNode<>(data));
T.getrChild().setParent(T);
}
}
// 递归回溯跟新平衡因子,比如插入
T.setDepth(calDepth(T));
T.setBalance(calBalance(T));
// 调整树的平衡
adjust(T);
}
// 删除节点
public TreeNode<E> delete(TreeNode<E> T) {
TreeNode<E> q, s = null;
TreeNode<E> parent = null;
// 如果T为叶子节点,则直接删除
if(T.getlChild() == null && T.getrChild() == null){
if(T == T.getParent().getlChild()){
T.getParent().setlChild(null);
}else{
T.getParent().setrChild(null);
}
parent = T.getParent();
T.delete();
return parent;
}else if(T.getlChild() == null){ //如果T只有右子树,则将T的右子树接入T的父节点
T.getrChild().setParent(T.getParent());
if(T == T.getParent().getlChild()){
T.getParent().setlChild(T.getrChild());
}else{
T.getParent().setrChild(T.getrChild());
}
parent = T.getParent();
T.delete();
return parent;
}else if(T.getrChild() == null){ //如果T只有左子树,则将T的左子树接入T的父节点
T.getlChild().setParent(T.getParent());
if(T == T.getParent().getlChild()){
T.getParent().setlChild(T.getlChild());
}else{
T.getParent().setrChild(T.getlChild());
}
parent = T.getParent();
T.delete();
return parent;
}else{
// 如果T的左右子树都有,则找到T的前驱节点,用T的前驱节点的data与T节点的data替换,然后删除T的前驱节点
q = T;
s = T.getlChild();
while (s.getrChild() != null) {
q = s;
s = s.getrChild();
}
T.setData(s.getData());
if (q == T) {
q.setlChild(s.getlChild());
} else {
q.setrChild(s.getlChild());
}
if (s.getlChild() != null) {
s.getlChild().setParent(q);
}
s.delete();
return q;//返回删除节点的父节点,便于回溯调整节点的平衡
}
}
// 删除节点
public void deleteAVL(TreeNode<E> T, E e) {
if (T == null) {
return;
}
if (T.getData().compareTo(e) == 0) {
TreeNode<E> q= null;
q = delete(T);
while (q != null) {
q.setDepth(calDepth(q));
q.setBalance(calBalance(q));
// 调整,使树平衡
adjust(q);
// 一直往到根节点
q = q.getParent();
}
} else if (T.getData().compareTo(e) < 0) {
deleteAVL(T.getrChild(), e);
} else {
deleteAVL(T.getlChild(), e);
}
// 更新根节点
this.root = new BinaryTree<E>().findRoot(this.root);
}
// 计算T的高度
public int calDepth(TreeNode<E> T) {
if (T == null) {
return 0;
}
int depth = 0;
if (T.getlChild() != null) {
// 如果T的左子树不为空,则depth的值为T左子树的高度
depth = T.getlChild().getDepth();
} else {
// 否则为0
depth = 0;
}
// 如果T的右子树不为空且右子树的高度比左子树高,则depth的值为右子树的高度
if (T.getrChild() != null && T.getrChild().getDepth() > depth) {
depth = T.getrChild().getDepth();
}
// T的高度为子树中高度最高的值加1
depth++;
return depth;
}
// 平衡因子=T左子树的高度-T右子树的高度
public int calBalance(TreeNode<E> T) {
return calDepth(T.getlChild()) - calDepth(T.getrChild());
}
public void adjust(TreeNode<E> T){
// 如果T的平衡因子大于等于2,或者小于等于-2,,都需要对以T为跟节点的子树进行旋转调整
if (T.getBalance() >= 2) {
// 当T的平衡因和T左子树的平衡因子符号相反,需要先对T的左子树进行左旋操作,再对T进行右旋操作
if (T.getlChild().getBalance() == -1) {
leftRotate(T.getlChild());
}
rightRotate(T);
}
// 与T的平衡因子为2的情况相似
if (T.getBalance() <= -2) {
if (T.getrChild().getBalance() == 1) {
rightRotate(T.getrChild());
}
leftRotate(T);
}
}
}
代码拙劣,请多指教。