Spring注解
1、@Primary
@Primary的含义是告诉Spring IoC容器,当发现多个同样类型的Bean时,请优先使用我进行注入。
@Component
@Primary
public class Cat implements Animal{
...
}
@Component
public class Dog implements Animal{
...
}
@Component
public class PersonService{
//表示Spring优先将Cat注入进来(如果Cat没有使用@Primary注解,那么Spring不知道是将Cat还是Dog注入进来,导致Spring抛出异常)
@Autowired
private Animal animal;
}
注意:如果在多个同样类型的Bean中都使用了@Primary注解后,Spring也不知道到底优先注入谁,这也会导致Spring抛出异常。
2、@Autowired
该注解表示将一个组件依赖注入到另一个组件的属性中。默认情况下,如果找到多个相同的被注入的组件或者没有找到被注入的主键Spring都会抛出异常。
@Autowired有个属性required表示组件是否允许不为空,默认是true,表示默认必须要有相关注入组件。
3、@Qualifier
该注解结合@Autowired一起使用,表示如果有相同的多个注入组件类型,可以通过@Qualifier来指定特定id名的组件进行注入
@Component
public class PersonService{
@Autowired
@Qualifier("dog")
private Animal animal;
}
4、@ComponentScan
该注解表示配置Spring的自动扫描路径,默认是被该注解的类的当前包及其子包。
常用的属性:
value:自定义扫描的包
basePackages:自定义扫描的包
basePackageClasses:自定义扫描的类
nameGenerator:Bean name生成器
scopeResolver:作用域解析器
scopedProxy:作用域代理模式
resourcePattern:资源匹配模式
useDefaultFilters:是否启用默认的过滤器
includeFilters:当满足过滤器的条件时扫描
excludeFilters:当不满足过滤器的条件时扫描
lazyInit:是否延迟初始化,如果为false表示Spring IoC容器初始化时,就执行了实例化和依赖注入;如果为true表示在使用对应的Bean时,Spring 才为我们完成实例化和依赖注入
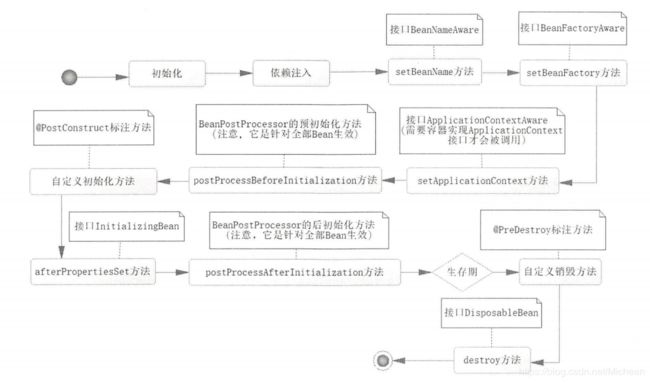
5、Bean的生命周期
6、@Value
改注解是将配置文件的值自动映射到java属性中。可以用在属性上也可以用在方法上
database.driverName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
database.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
database.username=root
database.password=root
/*
此依赖文件的作用是将application.properties位置文件自动加载到项目中
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-configuration-processor
true
*/
@Component
public class DatabaseProperties{
@Value("${database.driverName}")
private String driverName;
@Value("${database.url}")
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
@Value("${database.username}")
public void setUsername(String username){
this.username = username;
}
@Value("${database.password}")
public void setPassword(String password){
this.password = password;
}
...
}
7、@ConfigurationProperties
此注解的作用是将配置文件的值映射到java属性中。此注解于@Value不同的是@ConfigurationProperties作用在类上,将类的所有属性都映射上相关的值;而@Value是作用在方法或者某个属性上,表示将某一个属性映射上相关的值;
/*
注解@ConfigurationProperties中配置的字符串database,将与POJO的属性名组成属性的全限定名去配置文件中查找,这样就能将对应的属性读入到POJO当中
*/
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties("database")
public class DatabaseProperties{
private String driverName;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
/** Setter Getter*/
}
8、@PropertySource
此注解的作用是将我们自定义的配置文件加载到项目中。其中有两个属性value和ignoreResourceNotFound。value是要加载的配置文件路径(可以设置多个配置文件);ignoreResourceNotFound则是是否忽略配置文件找不到的问题,默认是false表示没有找到属性文件就会抛出异常。
/*
比如我们将上面的数据库配置信息单独存放在jdbc.properties文件中
*/
@Component
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:jdbc.properties"}, ignoreResourceNotFound = true)
@ConfigurationProperties("database")
public class DatabaseProperties{
private String driverName;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
/** Setter Getter*/
}
9、@Conditional
满足条件时才装配Bean,此注解要和Condition(org.springframework.context.annotation.Condition)接口一起使用。
/*
满足DatabaseConditional类所实现的条件判断时才装配Bean
*/
@Bean
@Conditional(DatabaseConditional.class)
public DataSource dataSource(@Value("${database.driverName}") String driverName, @Value("${database.url}") String url, @Value("${database.username}") String username, @Value("${database.password}") String password){
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("driver", driverName);
props.setProperty("url", url);
props.setProperty("username", username);
props.setProperty("password", password);
return BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(props);
}
/*
数据库装配条件
@Param context 条件上下文
@Param metadata 注解类型的元数据
@return 返回true表示装配Bean, 否则不装配
*/
public class DatabaseConditional implements Condition{
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata){
//取出环境配置
Environment env = context.getEnvironment();
//判断属性文件是否存在对应的数据库配置
return env.containsProperty("database.driverName") && env.containsProperty("database.url") && env.containsProperty("database.username") && env.containsProperty("database.password")
}
}
10、@Scope
此注解定义Bean的作用域,Spring默认的Bean作用域是单例形式。下面是Bean作用域

ConfigurableBeanFactory 中定义了singleton和prototype两种作用域。
WebApplicationContext中定义了request、session、application作用域
@Component
@Scope(ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
//@Scope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_REQUEST) 在Spring MVC环境中使用
public class ScopeBean{
...
}
11、@Profile
此注解可以定义多个环境,可以实现各个环境之间的切换。在Spring中使用spring.profiles.active或者spring.profiles.default配置指定启用那个环境。前则的优先级更高。如果这两种配置都没有使用,那么Spring将不会装配带有@Profile注解的Bean到IoC容器中。
/*
开发环境
*/
@Bean(name = "dataSource")
@Profile("dev")
public DataSource getDevDataSource(){
...
}
/*
生产环境
*/
@Bean(name = "dataSource")
@Profile("prod")
public DataSource getProdDataSource(){
...
}
在application.properties文件中设置启用哪个环境
spring.profiles.active=dev
或者设置环境变量-Dspring.profiles.active=dev
12、@ImportResource
此注解用于引入XML文件对Bean的配置。
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages="com.spring.test.*")
@ImportResource(value = {"classpath:spring-other.xml"})
public class AppConfig{
...
}
13、@Aspect
此注解用于定义AOP中的切面,使用此注解时,Spring就会知道这是一个切面,然后我们就可以通过各类注解来定义各类的通知。例如(@Before/@After/@AfterReturning/@AfterThrowing/@Around)
14、@Pointcut
切点定义,切点的作用就是向Spring描述哪些类的哪些方法需要启用AOP编程。切点定义后,需要将其运用在AOP通知注解上(@Before/@After/@AfterReturning/@AfterThrowing/@Around)
@Aspect
public class MyAspect{
/*
定义切点
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* com.springboot.test.aspect.service.impl.TestServiceImpl.printTest(..))")
public void pointCut(){
}
/*
可以获取连接点的参数
通过连接点参数的getArgs方法也可以获取所有的参数
*/
@Before("pointCut() && args(user)")
public void before(JoinPoint point, User user){
System.out.println(" before . ..... ");
}
@After("pointCut()")
public void after () {
System.out.prntln(" after . .. . .. ");
}
@AfterReturning("pointCut()")
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("afterReturning .. .. . . ") ;
}
@Around("pointCut ()")
public void around (ProceedngJoinPont jp) throws Throwable {
System . o ut.pr int ln (" around before . .....");
//回调目标对象的原有方法
jp.proceed();
System.out.println( "around after . . . . " );
}
...
}
15、@DeclarePents
此注解的作用的作用是引入新的类来增强服务,它有两个必须配置的属性value和defaultImpl
- value:指向你需要增强功能的目标对象
- defaultImpl:引入增强功能的类
样例:比如在UserServiceImpl.printUser(User)中增加一个参数验证的方法,同时我们又不能修改原有的类。这时我们就可以引入一个新类使用AOP技术将其引入。
/*
引入接口
*/
public interface UserValidator{
//检测用户对象是否为空
boolean validate(User user);
}
/*
引入接口的实现
*/
public class UserValidatorImpl implements UserValidator{
@Override
public boolean validate(User user){
System.out.println("引入新的接口");
return user != null;
}
}
/*
切面定义
*/
@Aspect
public class MyAspect{
/*
将引入类定义到切面中
*/
@DeclareParents(value="com.springboot.test.aspect.service.impl.TestServiceImpl+", defaultImpl=UserValidatorImpl.class)
public UserValidator userValidator;
/*
定义切点
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* com.springboot.test.aspect.service.impl.TestServiceImpl.printTest(..))")
public void pointCut(){
}
@Before("pointCut()")
public void before(){
System.out.println(" before . ..... ");
}
...
}
//使用方法
//强制转换
UserValidator userValidator = (UserValidator)TestService;
if (userValidator.validate(user) ) {
userService.printUser(user) ;
}
16、@Order
如果多个切面对应同样的切点是,可以使用@Order或者继承Ordered接口实现群的执行顺序。
@Compont
@Aspect
@Order(1)
public class MyAspect1{
....
}
//////////////////////////////
@Compont
@Aspect
@Order(2)
public class MyAspect2{
....
}
//////////////////////////
@Compont
@Aspect
public class MyAspect3 implements Ordered{
@Override
public int getOrder(){
return 3;
}
....
}
17、@Transient
此注解所注解的方法,表示不持久化,防止它与其他属性一起持久化
18、@Conditional
条件装配Bean,此注解在类和方法上
- value 实现Condition接口的子类,接口的matches方法返回true则装配该Bean
例如:根据配置文件信息,选择装配对应的Bean
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Condition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionContext;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata;
/**
* 条件加载文件存储
* 判断使用哪种方式存储文件ftp还是FsClient
*/
public class FtpStorageCondition implements Condition {
/**
* 通过配置文件设置
*
* @param context 判断条件能使用的上下文(环境)
* @param annotatedTypeMetadata 注释信息
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata annotatedTypeMetadata) {
//获取环境变量
Environment environment = context.getEnvironment();
String fileStorageMethod = environment.getProperty("fileStorageMethod", "");
if ("FTP".equals(fileStorageMethod)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Condition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionContext;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata;
/**
* 条件加载文件存储
* 判断使用哪种方式存储文件ftp还是FsClient
*/
public class MongDBStorageCondition implements Condition {
/**
* 通过配置文件设置
* @param context 判断条件能使用的上下文(环境)
* @param annotatedTypeMetadata 注释信息
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata annotatedTypeMetadata) {
//获取环境变量
Environment environment = context.getEnvironment();
String fileStorageMethod = environment.getProperty("fileStorageMethod", "");
if("MongoDB".equals(fileStorageMethod)){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
/**
* Configuration - 文件配置
*/
@Configuration("mongoDbFsAutoConfiguration")
@AutoConfigureAfter(MongoDataAutoConfiguration.class)
public class FileConfiguration {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FsAutoConfiguration.class);
/**
* @param gridFsOperations GridFS操作
* @return FS客户端
*/
@Conditional({MongDBStorageCondition.class})
@Bean("mongoDbFsClient")
public FsClient fsClient(GridFsOperations gridFsOperations, @Value("${systemUrl}") String systemUrl) {
logger.info("启动MongoDB存储文件...");
if(StringUtils.isBlank(systemUrl)){
throw new RuntimeException("系统URL为空");
}
return new FsClient(gridFsOperations, systemUrl);
}
/**
* 根据条件装配FtpTemplate
*/
@Conditional({FtpStorageCondition.class})
@Bean
public FtpTemplate ftpTemplate() {
logger.info("启动FTP存储文件...");
return new FtpTemplate();
}
}