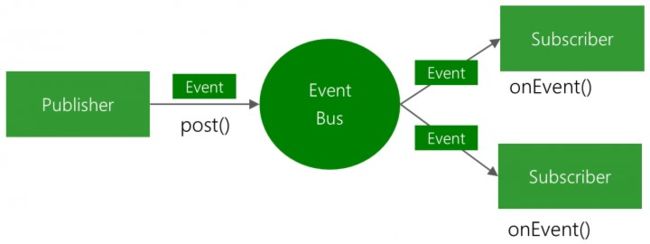
什么是EventBus
EventBus是Android下高效的发布/订阅事件总线机制。作用是可以代替传统的Intent,Handler,Broadcast或接口函数在Fragment,Activity,Service,线程之间传递数据,执行方法,也可以通过调用普通类开启发送消息。特点是代码简洁,是一种发布订阅设计模式(Publish/Subsribe),或称作观察者设计模式。
如何使用EventBus
- Publisher是发布者, 通过post()方法将消息事件Event发布到事件总线
- EventBus是事件总线, 遍历所有已经注册事件的订阅者们,找到里边的onEvent等4个方法,分发Event
- Subscriber是订阅者, 收到事件总线发下来的消息。即onEvent方法被执行。注意参数类型必须和发布者发布的参数一致。
MainActivity.java
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentActivity;
public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
}
activity_main.xml
fragment_left.xml
fragment_right.xml
LeftFragment.java
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.ListFragment;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.ListView;
import de.greenrobot.event.EventBus;
public class LeftFragment extends ListFragment {
@Override
public void onViewCreated(View view, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState);
String[] strs = new String[]{"主线程消息1", "子线程消息1", "主线程消息2","通过普通类发送消息"};
setListAdapter(new ArrayAdapter(getActivity(), android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, strs));
}
@Override
public void onListItemClick(ListView l, View v, int position, long id) {
switch (position) {
case 0:
// 主线程
System.out.println("----------------------主线程发的消息1"
+ " threadName: "+ Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ " threadId: " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
EventBus.getDefault().post(new MsgEvent1("主线程发的消息1"));
break;
case 1:
// 子线程
new Thread(){
public void run() {
System.out.println("----------------------子线程发的消息1"
+ " threadName: "+ Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ " threadId: " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
EventBus.getDefault().post(new MsgEvent1("子线程发的消息1"));
};
}.start();
break;
case 2:
// 主线程
System.out.println("----------------------主线程发的消息2"
+ " threadName: "+ Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ " threadId: " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
EventBus.getDefault().post(new MsgEvent2("主线程发的消息2"));
break;
case 3:
// 子线程2
new Thread(){
public void run() {
System.out.println("----------------------子线程发的类EventBus1消息1"
+ " threadName: "+ Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ " threadId: " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
new EventBus1();//调用类EventBus1传送消息
}
}.start();
}
}
}
RightFragment.java
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;
import de.greenrobot.event.EventBus;
public class RightFragment extends Fragment {
private TextView tv;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// 界面创建时,订阅事件, 接受消息
EventBus.getDefault().register(this);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
// 界面销毁时,取消订阅
EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this);
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_right, null);
tv = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.tv);
return view;
}
/**
* 与发布者在同一个线程
* @param msg 事件1
*/
public void onEvent(MsgEvent1 msg){
String content = msg.getMsg()
+ "\n ThreadName: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "\n ThreadId: " + Thread.currentThread().getId()+"\n onEvent";
System.out.println("onEvent(MsgEvent1 msg)收到" + content);
}
/**
* 执行在主线程。
* 非常实用,可以在这里将子线程加载到的数据直接设置到界面中。
* @param msg 事件1
*/
public void onEventMainThread(MsgEvent1 msg){
String content = msg.getMsg()
+ "\n ThreadName: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "\n ThreadId: " + Thread.currentThread().getId()+"\n onEventMainThread";
System.out.println("onEventMainThread(MsgEvent1 msg)收到" + content);
tv.setText(content);
}
/**
* 执行在子线程,如果发布者是子线程则直接执行,如果发布者不是子线程,则创建一个再执行
* 此处可能会有线程阻塞问题。
* @param msg 事件1
*/
public void onEventBackgroundThread(MsgEvent1 msg){
String content = msg.getMsg()
+ "\n ThreadName: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "\n ThreadId: " + Thread.currentThread().getId()+"\n onEventBackgroundThread";
System.out.println("onEventBackgroundThread(MsgEvent1 msg)收到" + content);
}
/**
* 执行在在一个新的子线程
* 适用于多个线程任务处理, 内部有线程池管理。
* @param msg 事件1
*/
public void onEventAsync(MsgEvent1 msg){
String content = msg.getMsg()
+ "\n ThreadName: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "\n ThreadId: " + Thread.currentThread().getId()+"\n onEventAsync";
System.out.println("onEventAsync(MsgEvent1 msg)收到" + content);
}
/**
* 与发布者在同一个线程
* @param msg 事件2
*/
public void onEvent(MsgEvent2 msg){
String content = msg.getMsg()
+ "\n ThreadName: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "\n ThreadId: " + Thread.currentThread().getId()+"\n msg2";
System.out.println("onEvent(MsgEvent2 msg)收到" + content);
tv.setText(content);
}
}
MsgEvent1.java
public class MsgEvent1 {
private String msg;
public MsgEvent1(String msg) {
super();
this.msg = msg;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
}
MsgEvent2.java
public class MsgEvent2 {
private String msg;
public MsgEvent2(String msg) {
super();
this.msg = msg;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
}
EventBus1.java
import de.greenrobot.event.EventBus;
public class EventBus1 {
public EventBus1() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
EventBus.getDefault().post(new MsgEvent1("类EventBus1发的消息1"));
}
}
效果图:
源码地址:https://git.oschina.net/Fly321/EventBus.git
EventBus的ThreadMode
EventBus包含4个ThreadMode:PostThread,MainThread,BackgroundThread,Async
MainThread我们已经不陌生了;我们已经使用过。
具体的用法,极其简单,方法名为:onEventPostThread, onEventMainThread,onEventBackgroundThread,onEventAsync即可
具体什么区别呢?
- onEventMainThread代表这个方法会在UI线程执行
- onEventPostThread代表这个方法会在当前发布事件的线程执行
- BackgroundThread这个方法,如果在非UI线程发布的事件,则直接执行,和发布在同一个线程中。如果在UI线程发布的事件,则加入后台任务队列,使用线程池一个接一个调用。
Async 加入后台任务队列,使用线程池调用,注意没有BackgroundThread中的一个接一个。