写在前面:
1.相关https具体内容本篇就不再描述。
2.前几天公司项目要求配置https双向认证,由于是银行业务,证书是cfca(中国金融认证中心)颁发的,因此 在这里我就不描述自签名证书的具体。iOS自签名证书,我没有调试,据说是不认自签名的。自签名证书中,这里有篇博客讲的非常好,这篇帮我在本地搭建了双向认证的tomcat服务器。http://blog.csdn.net/jerryvon/article/details/8548802
3.这篇博客侧重于 iOS客户端相关内容的描述,OC语言,基于AFNetwork3.0版本。
本篇内容
1.https双向认证中,iOS客户端需要哪两个证书,什么格式的。
2.ATS设置
3.普通https请求证书验证代码 与 uiwebview请求https页面时验证代码
4.html中ajax请求https
1.服务器公钥和p12文件。服务器公钥网上很多代码是 .cer格式的,但是在AF3.0版本中,支持的是.der格式,这个坑请注意了。
p12证书 对应的是服务器上的 .pfx证书(应该是,不太确定),pfx格式的可以转换成p12证书,它里面包括了公钥和私钥,客户端用p12证书应该是在做客户端的验证。
注意:在添加读取证书的时候,Xcode7有个bug 但不是必现。当证书拖到项目中时,路径读不出来,找不到这个文件,但是Bundle Resource中却偏偏存在,当时我一直认为是证书的问题,纠结了很久。
2.ATS设置
这个也是我一个不是特别能想的通的问题,按道理说,这个是设置在iOS9之后请求http才会设置的,但是在请求https的时候我发现 不设置的话,证书并没有进行验证。
因此还是要设置一下。
3.请求https服务源代码
```
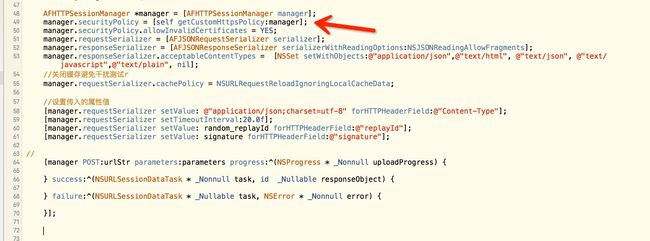
-(AFSecurityPolicy*) getCustomHttpsPolicy:(AFHTTPSessionManager*)manager{
//https 公钥证书配置
NSString *certFilePath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"custom" ofType:@"der"];
NSData *certData = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:certFilePath];
NSSet *certSet = [NSSet setWithObject:certData];
AFSecurityPolicy *policy = [AFSecurityPolicy policyWithPinningMode:AFSSLPinningModeCertificate withPinnedCertificates:certSet];
policy.allowInvalidCertificates = YES;
policy.validatesDomainName = NO;//是否校验证书上域名与请求域名一致
//https回调 客户端验证
[manager setSessionDidBecomeInvalidBlock:^(NSURLSession * _Nonnull session, NSError * _Nonnull error) {
NSLog(@"setSessionDidBecomeInvalidBlock");
}];
__weak typeof(manager)weakManger = manager;
__weak typeof(self)weakSelf = self;
//客户端请求验证 重写 setSessionDidReceiveAuthenticationChallengeBlock 方法
[manager setSessionDidReceiveAuthenticationChallengeBlock:^NSURLSessionAuthChallengeDisposition(NSURLSession*session, NSURLAuthenticationChallenge *challenge, NSURLCredential *__autoreleasing*_credential) {
NSURLSessionAuthChallengeDisposition disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengePerformDefaultHandling;
__autoreleasing NSURLCredential *credential =nil;
if([challenge.protectionSpace.authenticationMethod isEqualToString:NSURLAuthenticationMethodServerTrust]) {
if([weakManger.securityPolicy evaluateServerTrust:challenge.protectionSpace.serverTrust forDomain:challenge.protectionSpace.host]) {
credential = [NSURLCredential credentialForTrust:challenge.protectionSpace.serverTrust];
if(credential) {
disposition =NSURLSessionAuthChallengeUseCredential;
} else {
disposition =NSURLSessionAuthChallengePerformDefaultHandling;
}
} else {
disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengeCancelAuthenticationChallenge;
}
} else {
// client authentication
SecIdentityRef identity = NULL;
SecTrustRef trust = NULL;
NSString *p12 = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"client"ofType:@"p12"];
NSFileManager *fileManager =[NSFileManager defaultManager];
if(![fileManager fileExistsAtPath:p12])
{
NSLog(@"client.p12:not exist");
}
else
{
NSData *PKCS12Data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:p12];
if ([[weakSelf class]extractIdentity:&identity andTrust:&trust fromPKCS12Data:PKCS12Data])
{
SecCertificateRef certificate = NULL;
SecIdentityCopyCertificate(identity, &certificate);
const void*certs[] = {certificate};
CFArrayRef certArray =CFArrayCreate(kCFAllocatorDefault, certs,1,NULL);
credential =[NSURLCredential credentialWithIdentity:identity certificates:(__bridge NSArray*)certArray persistence:NSURLCredentialPersistencePermanent];
disposition =NSURLSessionAuthChallengeUseCredential;
}
}
}
*_credential = credential;
return disposition;
}];
return policy;
}
```
```
+ (BOOL)extractIdentity:(SecIdentityRef*)outIdentity andTrust:(SecTrustRef *)outTrust fromPKCS12Data:(NSData *)inPKCS12Data {
OSStatus securityError = errSecSuccess;
//client certificate password
NSDictionary*optionsDictionary = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithObject:@"111111"
forKey:(__bridge id)kSecImportExportPassphrase];
CFArrayRef items = CFArrayCreate(NULL, 0, 0, NULL);
securityError = SecPKCS12Import((__bridge CFDataRef)inPKCS12Data,(__bridge CFDictionaryRef)optionsDictionary,&items);
if(securityError == 0) {
CFDictionaryRef myIdentityAndTrust =CFArrayGetValueAtIndex(items,0);
const void*tempIdentity =NULL;
tempIdentity= CFDictionaryGetValue (myIdentityAndTrust,kSecImportItemIdentity);
*outIdentity = (SecIdentityRef)tempIdentity;
const void*tempTrust =NULL;
tempTrust = CFDictionaryGetValue(myIdentityAndTrust,kSecImportItemTrust);
*outTrust = (SecTrustRef)tempTrust;
} else {
NSLog(@"Failedwith error code %d",(int)securityError);
return NO;
}
return YES;
}
```
UIWebview加载双向认证https页面
设置,请求忽略本地缓存在性能上会有所牺牲。在https请求中,据说90%多cpu消耗都是花费在证书的校验过程当中。但是,当html页面中使用的ajax请求方式也是https的时候,这个就必须重新验证。原因是,当uiwebview验证完证书,之后,再次启动app,webview会根据connection返回的验证历史信息,直接认为客户端是安全的,不再进行证书校验,这个时候,html页面里面的ajax请求就不能正常的发送,会导致无法正常运行。
主要代码:
```
#pragma mark - UIWebViewDelegate
- (BOOL)webView:(UIWebView *)webView shouldStartLoadWithRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request navigationType:(UIWebViewNavigationType)navigationType {
NSString *tmp = [request.URL absoluteString];
NSLog(@"request url :%@",tmp);
if ([request.URL.scheme rangeOfString:@"https"].location != NSNotFound) {
//开启同步的请求去双向认证
if (!_Authenticated) {
originRequest = request;
NSURLConnection *conn = [NSURLConnection connectionWithRequest:request delegate:self];
[conn start];
[webView stopLoading];
return false;
}
}
return YES;
}
```
```
#pragma NSURLConnectionDelegate
- (void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection willSendRequestForAuthenticationChallenge:(NSURLAuthenticationChallenge *)challenge {
NSURLCredential * credential;
assert(challenge != nil);
credential = nil;
NSLog(@"----received challenge----");
NSString *authenticationMethod = [[challenge protectionSpace] authenticationMethod];
if ([authenticationMethod isEqualToString:NSURLAuthenticationMethodServerTrust]) {
NSLog(@"----server verify client----");
NSString *host = challenge.protectionSpace.host;
SecTrustRef serverTrust = challenge.protectionSpace.serverTrust;
BOOL validDomain = false;
NSMutableArray *polices = [NSMutableArray array];
if (validDomain) {
[polices addObject:(__bridge_transfer id)SecPolicyCreateSSL(true, (__bridge CFStringRef)host)];
}else{
[polices addObject:(__bridge_transfer id)SecPolicyCreateBasicX509()];
}
SecTrustSetPolicies(serverTrust, (__bridge CFArrayRef)polices);
//pin mode for certificate
NSString *path = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"custom" ofType:@"der"];
NSData *certData = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:path];
NSMutableArray *pinnedCerts = [NSMutableArray arrayWithObjects:(__bridge_transfer id)SecCertificateCreateWithData(NULL, (__bridge CFDataRef)certData), nil];
SecTrustSetAnchorCertificates(serverTrust, (__bridge CFArrayRef)pinnedCerts);
credential = [NSURLCredential credentialForTrust:challenge.protectionSpace.serverTrust];
} else {
NSLog(@"----client verify server----");
SecIdentityRef identity = NULL;
SecTrustRef trust = NULL;
NSString *p12 = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"client" ofType:@"p12"];
NSFileManager *fileManager = [NSFileManager defaultManager];
if (![fileManager fileExistsAtPath:p12]) {
NSLog(@"client.p12 file not exist!");
}else{
NSData *pkcs12Data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:p12];
if ([[self class] extractIdentity:&identity andTrust:&trust fromPKCS12Data:pkcs12Data]) {
SecCertificateRef certificate = NULL;
SecIdentityCopyCertificate(identity, &certificate);
const void *certs[] = {certificate};
CFArrayRef certArray = CFArrayCreate(kCFAllocatorDefault, certs, 1, NULL);
credential = [NSURLCredential credentialWithIdentity:identity certificates:(__bridge NSArray *)certArray persistence:NSURLCredentialPersistencePermanent];
}
}
}
[challenge.sender useCredential:credential forAuthenticationChallenge:challenge];
}
```
```
+ (BOOL)extractIdentity:(SecIdentityRef *)outIdentity andTrust:(SecTrustRef *)outTrust fromPKCS12Data:(NSData *)inPKCS12Data {
OSStatus securityErr = errSecSuccess;
//client certificate password
NSDictionary *optionsDic = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithObject:@"111111" forKey:(__bridge id)kSecImportExportPassphrase];
CFArrayRef items = CFArrayCreate(NULL, 0, 0, NULL);
securityErr = SecPKCS12Import((__bridge CFDataRef)inPKCS12Data, (__bridge CFDictionaryRef)optionsDic, &items);
if (securityErr == errSecSuccess) {
CFDictionaryRef mineIdentAndTrust = CFArrayGetValueAtIndex(items, 0);
const void *tmpIdentity = NULL;
tmpIdentity = CFDictionaryGetValue(mineIdentAndTrust, kSecImportItemIdentity);
*outIdentity = (SecIdentityRef)tmpIdentity;
const void *tmpTrust = NULL;
tmpTrust = CFDictionaryGetValue(mineIdentAndTrust, kSecImportItemTrust);
*outTrust = (SecTrustRef)tmpTrust;
}else{
return false;
}
return true;
}
```
```
-(void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didReceiveResponse:(NSURLResponse *)pResponse {
_Authenticated = YES;
//webview 重新加载请求。
[localWebView loadRequest:originRequest];
[connection cancel];
}
```
还值得注意的是:在https方式加载html的时候,我查到大量的资料中,都是在
```
- (void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didReceiveData:(NSData *)data;
- (void)connectionDidFinishLoading:(NSURLConnection *)connection;
- (void)loadHTMLString:(NSString *)string baseURL:(nullable NSURL *)baseURL;
```
这三个方法去处理的,方式是:将收到的data拼成一个全局的变量,在连接完成时将data转换成字符串,用加载本地html的方式进行加载。
这个方法不可行,在加载非本地html的时候。
在html前端页面中,会有大量的外部资源引用。当将html页面元素当做字符串去加载的时候,就会存在html依赖的外部资源无法加载,html页面会出现图片找不到或者布局混乱的现象。当使用loadHTMLString中的baseURL作为相对路径的指导时,在加载本地资源时,使用的是bundle,但是加载远程资源时,就会触发https证书验证的方法,无限次的循环,整个app高消耗内存和cpu,关键是还加载不到。
因此,在收到pResponse的时候,直接断掉connection,重新加载该页面就ok。这个时候,客户端和服务器都是相互信任的,ssl通道已经建立起来,大家可以愉快的进行操作了。
ajax https请求
这个其实是个伪问题,在https方法加载的页面当中,已经建立起来ssl通道的web环境,直接就可以进行https请求。因此是不需要进行像客户端那样配置。
但是,如果是http方式加载的页面中,进行https请求,那么久存在跨域的问题。这个在下篇中再进行解释。
因此,在html页面是以https方法加载的情况下,不用考虑证书的问题,直接把请求方式改成https,完事。