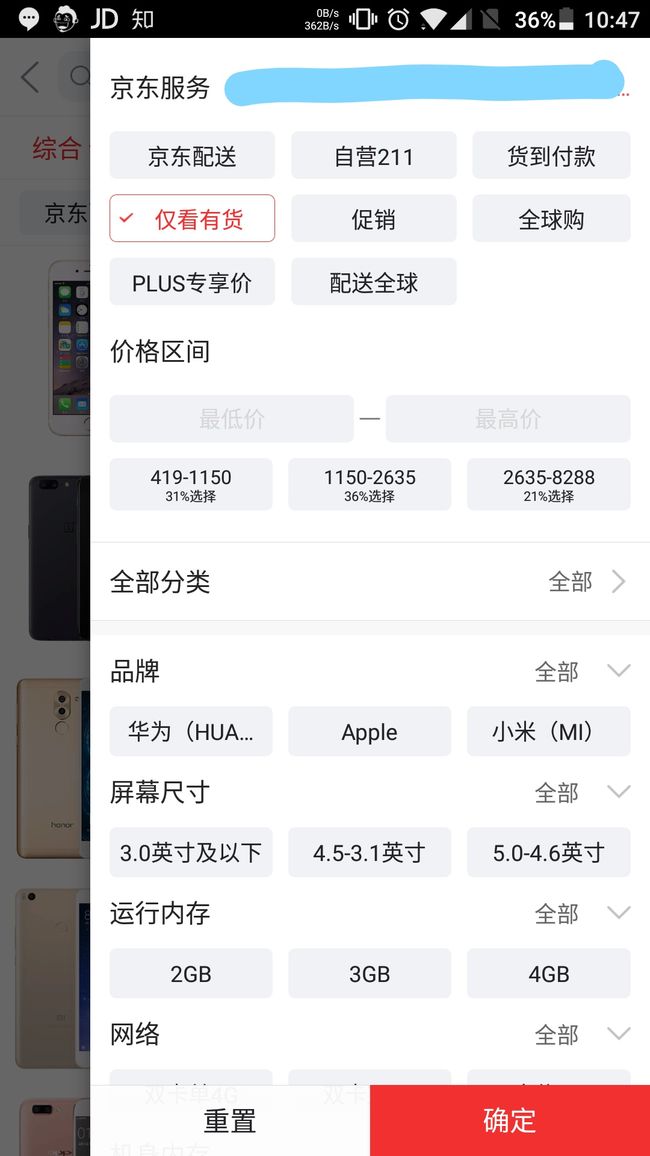
有时候也会需要在前端进行数据筛选,增强交互体验。当数据可用的筛选条件较多时,把逻辑写死会给后期维护带来很大麻烦。下面是我自己写的一个简单的筛选器,筛选条件可以根据数据包含的字段动态设置。
仿照京东的筛选条件,这里就取价格区间和品牌作为测试。
代码
代码中主要使用js的过滤器Array.prototype.filter,该方法会对数组元素进行遍历检查,返回一个符合检查条件的新数组,不会改变原数组。
// filter()
var foo = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9];
var foo1 = foo.filter(
function(item) {
return item >= 5
}
);
console.log(foo1); // [5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
有了这个方法,筛选数据方便了很多,下面先定义一个商品类。
// 定义商品类
function Product(name, brand, price) {
this.name = name; // 名称
this.brand = brand; // 品牌
this.price = price; // 价格
}
创建一个过滤器对象,把所有过滤数据的方法放在里面。为了能自动适配不同的筛选条件,将筛选条件分为两个大类,一个是区间类型rangesFilter ,如:品牌、内存等;一个是选择类型choosesFilter,如:价格、屏幕尺寸等。
不同大类同时筛选时,进行的是与逻辑,每个大类在上一个大类筛选结果上进行筛选。比如我要筛选2000-5000块的华为手机,先调用rangesFilter筛选products并返回结果result1,然后用choosesFilter筛选result1并返回结果resulte2。
当然,如果还有其它大类,不一定是与逻辑,再另行处理。
// 商品筛选器
const ProductFilters = {
/**
* 区间类型筛选
* @param {array} products
* @param {array<{type: String, low: number, high: number}>} ranges
*/
rangesFilter: function (products, ranges) { }
/**
* 选择类型筛选
* @param {array} products
* @param {array<{type: String, value: String}>} chooses
*/
choosesFilter: function (products, chooses) { }
}
区间类型的筛选,代码如下。
// 区间类型条件结构
ranges: [
{
type: 'price', // 筛选类型/字段
low: 3000, // 最小值
high: 6000 // 最大值
}
]
/**
* @param {array} products
* @param {array<{type: String, low: number, high: number}>} ranges
*/
rangesFilter: function (products, ranges) {
if (ranges.length === 0) {
return products;
} else {
/**
* 循环多个区间条件,
* 每种区间类型应该只有一个,
* 比如价格区间不会有1000-2000和4000-6000同时需要的情况
*/
for (let range of ranges) {
// 多个不同类型区间是与逻辑,可以直接赋值给自身
products = products.filter(function (item) {
return item[range.type] >= range.low && item[range.type] <= range.high;
});
}
return products;
}
}
选择类型筛选:
// 选择类型条件结构
chooses: [
{
type: 'brand',
value: '华为'
},
{
type: 'brand',
value: '苹果'
}
]
/**
* @param {array} products
* @param {array<{type: String, value: String}>} chooses
*/
choosesFilter: function (products, chooses) {
let tmpProducts = [];
if (chooses.length === 0) {
tmpProducts = products;
} else {
/**
* 选择类型条件是或逻辑,使用数组连接concat
*/
for (let choice of chooses) {
tmpProducts = tmpProducts.concat(products.filter(function (item) {
return item[choice.type].indexOf(choice.value) !== -1;
}));
}
}
return tmpProducts;
}
定义一个执行函数doFilter()。
function doFilter(products, conditions) {
// 根据条件循环调用筛选器里的方法
for (key in conditions) {
// 判断是否有需要的过滤方法
if (ProductFilters.hasOwnProperty(key + 'Filter') && typeof ProductFilters[key + 'Filter'] === 'function') {
products = ProductFilters[key + 'Filter'](products, Conditions[key]);
}
}
return products;
}
// 将两种大类的筛选条件放在同一个对象里
let Conditions = {
ranges: [
{
type: 'price',
low: 3000,
high: 6000
}
],
chooses: [
{
type: 'brand',
value: '华为'
}
]
}
测试
创建10个商品数据,以及筛选条件
// 商品数组
const products = [
new Product('华为荣耀9', '华为', 2299),
new Product('华为P10', '华为', 3488),
new Product('小米MIX2', '小米', 3599),
new Product('小米6', '小米', 2499),
new Product('小米Note3', '小米', 2499),
new Product('iPhone7 32G', '苹果', 4588),
new Product('iPhone7 Plus 128G', '苹果', 6388),
new Product('iPhone8', '苹果', 5888),
new Product('三星Galaxy S8', '三星', 5688),
new Product('三星Galaxy S7 edge', '三星', 3399),
];
// 筛选条件
let Conditions = {
ranges: [
{
type: 'price',
low: 3000,
high: 6000
}
],
chooses: [
{
type: 'brand',
value: '华为'
},
{
type: 'brand',
value: '苹果'
}
]
}
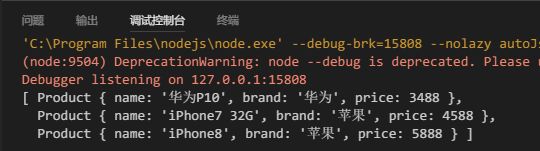
调用函数
let result = doFilter(products, Conditions);
console.log(result);
输出
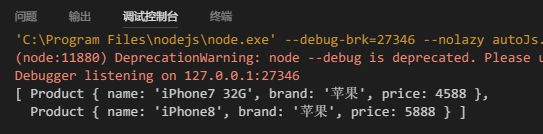
代码的扩展性和可维护性都很好,只要保证筛选条件中的
type字段在商品数据中一致都可以筛选,比如将筛选条件改为
let Conditions = {
ranges: [
{
type: 'price',
low: 3000,
high: 6000
}
],
chooses: [
{
type: 'name',
value: 'iPhone'
}
]
}
输出
搜索匹配等一些地方也需要优化,是否区分大小写、是完全匹配还是模糊匹配等。