此篇博客所有源码均来自JDK 1.8
信号量Semaphore是一个控制访问多个共享资源的计数器,和CountDownLatch一样,其本质上是一个“共享锁”。
Semaphore,在API是这么介绍的:
一个计数信号量。从概念上讲,信号量维护了一个许可集。如有必要,在许可可用前会阻塞每一个 acquire(),然后再获取该许可。每个 release() 添加一个许可,从而可能释放一个正在阻塞的获取者。但是,不使用实际的许可对象,Semaphore 只对可用许可的号码进行计数,并采取相应的行动。
Semaphore 通常用于限制可以访问某些资源(物理或逻辑的)的线程数目。
下面我们就一个停车场的简单例子来阐述Semaphore:
为了简单起见我们假设停车场仅有5个停车位,一开始停车场没有车辆所有车位全部空着,然后先后到来三辆车,停车场车位够,安排进去停车,然后又来三辆,这个时候由于只有两个停车位,所有只能停两辆,其余一辆必须在外面候着,直到停车场有空车位,当然以后每来一辆都需要在外面候着。当停车场有车开出去,里面有空位了,则安排一辆车进去(至于是哪辆 要看选择的机制是公平还是非公平)。
从程序角度看,停车场就相当于信号量Semaphore,其中许可数为5,车辆就相对线程。当来一辆车时,许可数就会减 1 ,当停车场没有车位了(许可书 == 0 ),其他来的车辆需要在外面等候着。如果有一辆车开出停车场,许可数 + 1,然后放进来一辆车。
号量Semaphore是一个非负整数(>=1)。当一个线程想要访问某个共享资源时,它必须要先获取Semaphore,当Semaphore >0时,获取该资源并使Semaphore – 1。如果Semaphore值 = 0,则表示全部的共享资源已经被其他线程全部占用,线程必须要等待其他线程释放资源。当线程释放资源时,Semaphore则+1
实现分析
Semaphore结构如下:
[图片上传中。。。(1)]
从上图可以看出Semaphore内部包含公平锁(FairSync)和非公平锁(NonfairSync),继承内部类Sync,其中Sync继承AQS(再一次阐述AQS的重要性)。
Semaphore提供了两个构造函数:
- Semaphore(int permits) :创建具有给定的许可数和非公平的公平设置的 Semaphore。 2. Semaphore(int permits, boolean fair) :创建具有给定的许可数和给定的公平设置的 Semaphore。
实现如下:
public Semaphore(int permits) {
sync = new NonfairSync(permits);
}
public Semaphore(int permits, boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync(permits) : new NonfairSync(permits);
}
Semaphore默认选择非公平锁。
当信号量Semaphore = 1 时,它可以当作互斥锁使用。其中0、1就相当于它的状态,当=1时表示其他线程可以获取,当=0时,排他,即其他线程必须要等待。
信号量获取
Semaphore提供了acquire()方法来获取一个许可。
public void acquire() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);
}
内部调用AQS的acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg),该方法以共享模式获取同步状态:
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}
在acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)中,tryAcquireShared(int arg)由子类来实现,对于Semaphore而言,如果我们选择非公平模式,则调用NonfairSync的tryAcquireShared(int arg)方法,否则调用FairSync的tryAcquireShared(int arg)方法。
公平
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
for (;;) {
//判断该线程是否位于CLH队列的列头
if (hasQueuedPredecessors())
return -1;
//获取当前的信号量许可
int available = getState();
//设置“获得acquires个信号量许可之后,剩余的信号量许可数”
int remaining = available - acquires;
//CAS设置信号量
if (remaining < 0 ||
compareAndSetState(available, remaining))
return remaining;
}
}
非公平
对于非公平而言,因为它不需要判断当前线程是否位于CLH同步队列列头,所以相对而言会简单些。
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquireShared(acquires);
}
final int nonfairTryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
for (;;) {
int available = getState();
int remaining = available - acquires;
if (remaining < 0 ||
compareAndSetState(available, remaining))
return remaining;
}
}
信号量释放
获取了许可,当用完之后就需要释放,Semaphore提供release()来释放许可。
public void release() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
内部调用AQS的releaseShared(int arg):
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
releaseShared(int arg)调用Semaphore内部类Sync的tryReleaseShared(int arg):
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
for (;;) {
int current = getState();
//信号量的许可数 = 当前信号许可数 + 待释放的信号许可数
int next = current + releases;
if (next < current) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum permit count exceeded");
//设置可获取的信号许可数为next
if (compareAndSetState(current, next))
return true;
}
}
对于信号量的获取释放详细过程,请参考如下博客:
- 【死磕Java并发】-----J.U.C之AQS:CLH同步队列
- 【死磕Java并发】-----J.U.C之AQS:同步状态的获取与释放
- 【死磕Java并发】-----J.U.C之AQS:阻塞和唤醒线程
- 【死磕Java并发】-----J.U.C之重入锁:ReentrantLock
应用示例
我们已停车为示例:
public class SemaphoreTest {
static class Parking{
//信号量
private Semaphore semaphore;
Parking(int count){
semaphore = new Semaphore(count);
}
public void park(){
try {
//获取信号量
semaphore.acquire();
long time = (long) (Math.random() * 10);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "进入停车场,停车" + time + "秒..." );
Thread.sleep(time);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "开出停车场...");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
semaphore.release();
}
}
}
static class Car extends Thread {
Parking parking ;
Car(Parking parking){
this.parking = parking;
}
@Override
public void run() {
parking.park(); //进入停车场
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Parking parking = new Parking(3);
for(int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++){
new Car(parking).start();
}
}
}
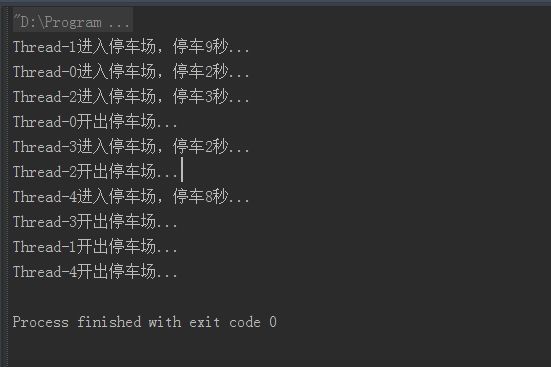
运行结果如下: