CRISPR Cas9(Clustered Regularly Interspaced ShortPalindromic Repeats CRISPR-Associated Proteins 9)是最近几年兴起用于靶向基因特定DNA修饰的重要工具。本文从CRISPR Cas9起源、CRISPER-Cas9系统的组成、CRISPER-Cas9系统的作用机制三方面为您介绍系统CRISPR Cas9技术。此外关于CRISPR Cas9技术的更多专题介绍后续将不断更新。
一、CRISPR Cas9起源
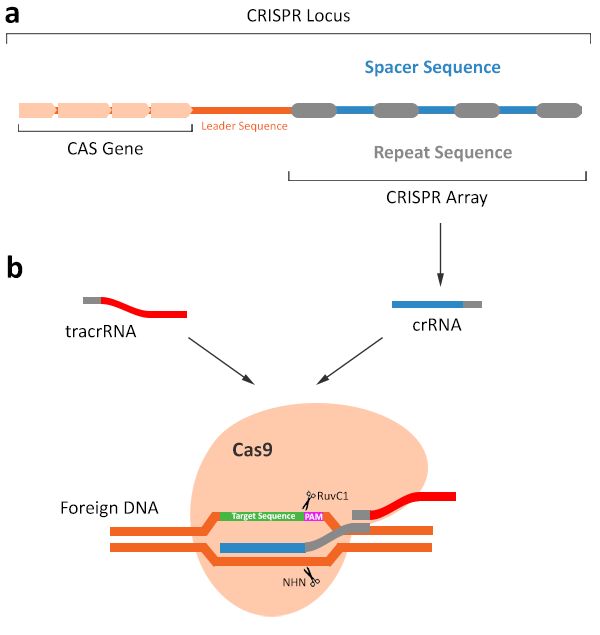
CRISPRCas9系统最初在细菌和古细菌中被发现,是一种细菌应对外来病毒或质粒不断攻击而演化来的获得性免疫防御机制。
当外源DNA首次侵入细菌时,外源DNA被Cas核酸酶切割,并以间隔序列形式整合到CRISPR基因座中。当外源DNA再次入侵时,细菌会以间隔序列作为模板形成短的CRISPR RNA(crRNA),crRNA与反式激活crRNA(tracrRNA)形成复合RNA:该复合RNA作为引导链指导Cas9核酸酶结合到互补的外源DNA。
一旦结合,Cas9蛋白通过其NHN和RuvC1样核酸酶结构域分别切割外源DNA的两条链,使外源DNA降解。
Figure 1 : TheCRISPR Locus and its use as an adaptive immune system. a) Invading DNA arecleaved by the CAS gene products and incorporated into the CRISPR Locus asspacer sequences. Different spacer sequences are separated by conserved repeatsequences. b) Once the same invading DNA is detected in the cell, the spacerDNA is expressed in the form of crRNA. The crRNA then complexes with tracrRNAand guides the Cas endonuclease to the foreign DNA for degradation.
迄今为止,已经发现了45种不同的Cas蛋白家族,每种家族在crRNA的合成、间隔序列的整合以及外源DNA的切割方式上有明显的不同。
根据Cas9蛋白的序列和结构不同,CRISPER-Cas9分为三类:I型,II型和III型。目前常用于基因组编辑的CRISPRCas9系统是改良自酿脓链球菌(Streptococcuspyogenes)的II型CRISPRCas系统。
二、CRISPER-Cas9系统的组成
CRISPRCas9靶向基因组编辑系统有两个组成部分:内切核酸酶-Cas9 和指导RNA-gRNA。
内切核酸酶是来自酿脓链球菌的Cas9核酸酶蛋白。 Cas9核酸酶具有切割双链DNA的活性结构域(RuvC1和HNH样核酸酶结构域),使得双链DNA断裂。
gRNA是由起支架功能的tracrRNA与特异性的crRNA结合形成的嵌合RNA。后来,人们将这两段RNA拼接成一条短RNA,称为sgRNA。
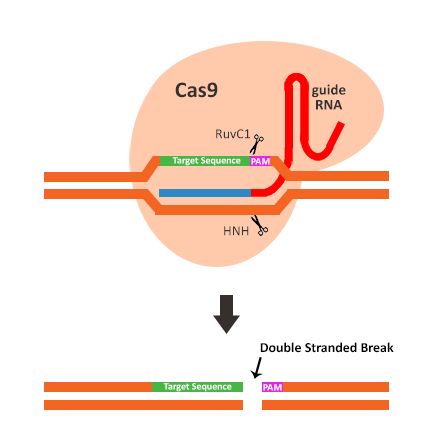
gRNA 5'末端的20bp是特异性的结合序列-寻靶装置,通过RNA-DNA碱基配对将Cas9 / gRNA复合物募集到特异的DNA靶点。
特异性结合序列相邻的是PAM(Protospacer Adjacent Motif)基序。PAM基序是内切核酸酶Cas9的识别位点,Cas9的PAM基序为5'-NGG。Cas9核酸酶在PAM基序上游第3个碱基处切割双链DNA。
Figure 2 : The last 20 base pairs of thegRNA acts as a homing device, recruiting the Cas9 endonuclease to theappropriate target sequence. Once there, the two cleavage domains of the Cas9create a double stranded break 3 or 4 base pairs downstream of the PAMsequence. The DSB is then repaired by either the error-prone non-homologous endjoining repair pathway, or the template-dependent homology directed repair
三、CRISPER-Cas9系统的作用机制
CRISPR Cas9系统产生双链DNA缺口后,生物体内一般通过非同源末端连接(NHEJ)或同源定向修复(HDR)这两种修复方式对断裂的双链DNA进行修复。
修复方式一:非同源末端连接修复途径(NHEJ)
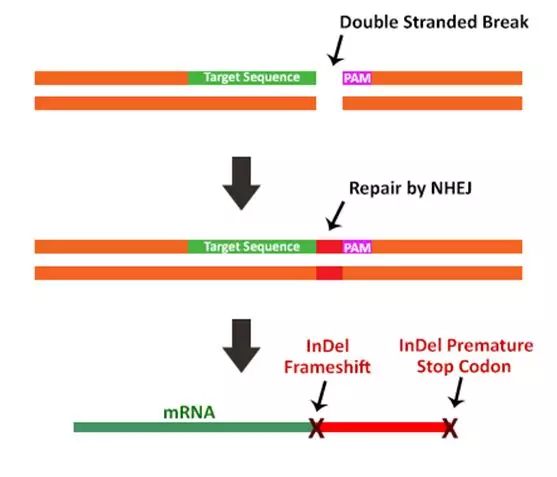
NHEJ修复途径是一种错误倾向修复机制,用于在缺少修复模板的情况下修复断裂的双链DNA。该途径主要用于CRISPR Cas9系统介导的基因沉默。主要用于当DNA发生断裂时,NHEJ修复途径被开启,DNA断裂处插入或缺失几个碱基,然后双链DNA的切割末端连接在一起,这个过程极容易导致切割位点发生移码突变,从而沉默该基因。因此,在沉默编码基因时, gRNA应靶向基因的N端来确保最大程度的基因破坏。
Figure3 :The non-homologous end joining repair mechanism attempts to ligate the endsof the DSB together without the use of a homologous template. This process iserror prone as the loss or addition of a few nucleotides is inevitable withthis mechanism. As a result NHEJ creates InDel mutations which either disruptthe reading frame of the gene or introduce premature stop codons.
修复方式二:同源性定向修复(HDR)
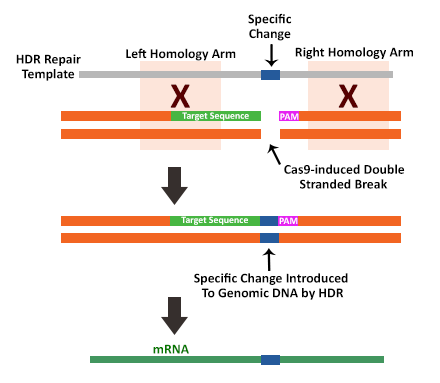
对比NHEJ修复途径,同源性定向修复(HDR)途径是更为精确的修复机制。这种修复机制主要用于CRISPR Cas9系统介导的基因敲入。在该修复路径中,需要将一段与预期编辑位点上下游紧邻序列具有高度同源性的DNA修复模板、特异的gRNA和Cas9核酸酶一起引入细胞中。在高度同源性DNA模板存在的情况下, HDR机制可以通过同源重组将一段DNA插入编辑位点。这种修复方式可以将一段DNA序列精准地插入特定的基因组位点。
Figure 4 : In thepresence of a suitable repair template containing homology arms directlyupstream and downstream of the double stranded break, the recombination-basedhomology directed repair mechanism is used. In this way precise changes—be itadditions or deletion—can be made anywhere in the genome.