上篇文章讲到了ant方式进行dex分包《Android Dex分包》,本篇文章再来看一下采用gradle方式进行dex分包的实现。
dex分包的gradle方式实现
我们用同样的demo工程采用gradle进行multidex分包测试。由于本人的AS已经升到2.3.1版本,对应的gradle版本为2.3.1,gradle插件版本升到了3.3,而gradle插件3.3版本要求buildToolsVersion版本为25及以上,而buildTools 25又要求jdk版本大于等于52,即jdk1.8,所以需要将android studio切换到jdk1.8,需要自行下载jdk1.8并配置好环境即可,build.gradle中不需要配置
android studio配置jdk1.8,网上有些教程推荐直接在build.gradle中配置即可,如果是在build.gradle中指定了用jdk1.8来编译
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility 1.8
targetCompatibility 1.8
}
会编译失败,报如下错误
* What went wrong:
A problem occurred configuring project ':app'.
> Jack is required to support java 8 language features. Either enable Jack or remove sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8.
要求使用Jack编译器来支持java8特性,或者移除sourceCompatibility直接编译。
如果要使用Jack编译器,则需要在build.gradle添加如下支持
jackOptions {
enabled true
}
关于Jack编译器,可参考《Android 新一代编译 toolchain Jack & Jill 简介》一文
Jack 是 Java Android Compiler Kit 的缩写,它可以将 Java 代码直接编译为 Dalvik 字节码,并负责 Minification, Obfuscation, Repackaging, Multidexing, Incremental compilation。它试图取代 javac/dx/proguard/jarjar/multidex 库等工具
使用Jack编译器来编译之后,可以正常打包构建,并且也进行了mulitdex处理,但是dexOptions中的参数都未生效,究其原因就是由于采用了Jack编译器来执行编译操作,不同与原来的 javac+dx编译过程,二者区别如下:
//javac+dx编译过程
javac (.java –> .class) –> dx (.class –> .dex)
//jack编译过程
Jack (.java –> .jack –> .dex)
Jack是将java源码编译城.jack文件再转化为.dex文件,不再执行dx操作,所以配置的dexOptions没有生效
本来google推出Jack 编译器是准备取代javac+dx的编译方式,但是由于Jack在支持基本编译功能之外的其他功能上存在一定的局限,所以在今年3月,Google宣布放弃Jack,重新采用javac+dx的方式在Android里支持Java 8。
所以我们这里没有采用这种编译方式,没有在gradler脚本中配置jdk1.8,而是直接在系统变量中更改编译环境为jdk1.8
demo中build.gradle脚本如下
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
android {
compileSdkVersion 23
buildToolsVersion "25.0.0"
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.example.multidextest"
minSdkVersion 14
targetSdkVersion 23
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
testInstrumentationRunner "android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
multiDexEnabled true
//这里不采用jack编译方式
// jackOptions {
// enabled true
// }
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
// compileOptions {
// sourceCompatibility 1.8
// targetCompatibility 1.8
// }
dexOptions {
javaMaxHeapSize "1g"
preDexLibraries = false
additionalParameters = [ //配置multidex参数
'--multi-dex',//多dex分包
'--set-max-idx-number=30000',//每个包内方法数上限
'--main-dex-list='+projectDir+'/main-dex-rule', //打包到主classes.dex的文件列表
'--minimal-main-dex'
]
}
}
dependencies {
compile fileTree(include: ['*.jar'], dir: 'libs')
androidTestCompile('com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:2.2.2', {
exclude group: 'com.android.support', module: 'support-annotations'
})
compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:23.3.0'
compile 'com.android.support.constraint:constraint-layout:1.0.2'
//multidex支持依赖
compile 'com.android.support:multidex:1.0.0'
testCompile 'junit:junit:4.12'
}
main-dex-rule文件内容如下:
com/example/multidextest/MainActivity$1.class
com/example/multidextest/HelperOne.class
com/example/multidextest/MainActivity.class
com/example/multidextest/ApplicationLoader.class
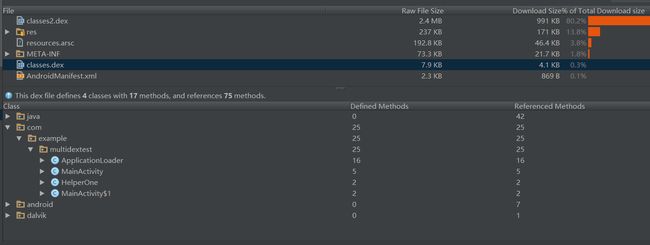
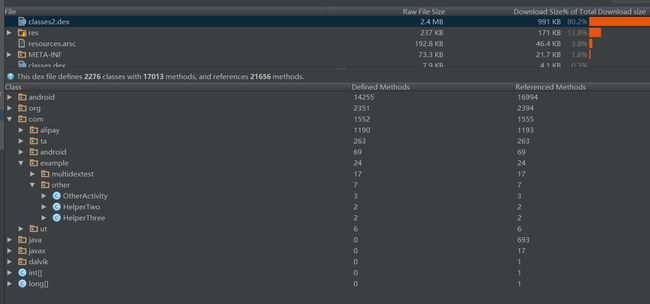
执行gradle命令后,得到构建出的apk文件,通过as可以看到已经包含了多个dex
主dex中包含指定的类文件
从dex中包含其他的未打到主dex中的类和其他依赖的jar包等
关于main-dex-rule文件的自动生成方式,可以参考
可参考 《Android傻瓜式分包插件》或者 《android multidex异步加载》
dex文件的加载
上篇文章已经提到,apk初次安装启动的时候只会对主dex进行优化加载操作,而从dex文件需要在app启动时手动加载,AS中可以通过引入multidex包来支持从dex的加载,有三种方式,如下:
1.manifest文件中指定Application为MultiDexApplication,对于一般不需要在application中执行初始化操作的app可以采用这种
……>
2.自定义Application并继承MultiDexApplication
public class MyApplication extends MultiDexApplication{
……
}
3.重写Application的attachBaseContext方法
public class MyApplication extends Application{
@Override
protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) {
super.attachBaseContext(base);
MultiDex.install(this);
}
}
方式一二相同,先来看方式二的实现只需要将ApplicationLoader类由原先继承自Application类修改为继承MultiDexApplication即可,无需在onCreate中添加其他加载dex的代码。所以可以猜想,MultiDexApplication中肯定是执行了加载从dex的相关操作。下面来看MultiDexApplication的源码
public class MultiDexApplication extends Application {
public MultiDexApplication() {
}
protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) {
super.attachBaseContext(base);
MultiDex.install(this);
}
}
可以看到MultiDexApplication 继承Application, 并在attachBaseContext()中调用了MultiDex.install(this),所以上述几种方式本质是相同的。
MultiDex.install()方法如下:
/**
* Patches the application context class loader by appending extra dex files
* loaded from the application apk. This method should be called in the
* attachBaseContext of your {@link Application}, see
* {@link MultiDexApplication} for more explanation and an example.
*
* @param context application context.
* @throws RuntimeException if an error occurred preventing the classloader
* extension.
*/
public static void install(Context context) {
//省略若干代码...
try {
ApplicationInfo applicationInfo = getApplicationInfo(context);
if (applicationInfo == null) {
// Looks like running on a test Context, so just return without patching.
return;
}
synchronized (installedApk) {
String apkPath = applicationInfo.sourceDir;
//installedApk 为set集合,防止dex重复加载
if (installedApk.contains(apkPath)) {
return;
}
installedApk.add(apkPath);
//省略若干代码...
ClassLoader loader;
try {
//此处获取到的是PathClassLoader
loader = context.getClassLoader();
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
//...
return;
}
//...
try {
clearOldDexDir(context);
} catch (Throwable t) {
Log.w(TAG, "Something went wrong when trying to clear old MultiDex extraction, "
+ "continuing without cleaning.", t);
}
//data/data//code_cache/secondary-dexes" 即从dex优化后的缓存的路径
File dexDir = new File(applicationInfo.dataDir, SECONDARY_FOLDER_NAME);
//从apk中抽取dex文件并存到缓存目录下,保存为zip文件
List files = MultiDexExtractor.load(context, applicationInfo, dexDir, false);
if (checkValidZipFiles(files)) {
//
installSecondaryDexes(loader, dexDir, files);
} else {
Log.w(TAG, "Files were not valid zip files. Forcing a reload.");
// Try again, but this time force a reload of the zip file.
files = MultiDexExtractor.load(context, applicationInfo, dexDir, true);
if (checkValidZipFiles(files)) {
installSecondaryDexes(loader, dexDir, files);
} else {
// Second time didn't work, give up
throw new RuntimeException("Zip files were not valid.");
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Multidex installation failure", e);
throw new RuntimeException("Multi dex installation failed (" + e.getMessage() + ").");
}
Log.i(TAG, "install done");
}
重点关注MultiDexExtractor.load(context, applicationInfo, dexDir, false) 从apk中抽取出从dex,
该方法有四个参数
context 上下文
applicationInfo 应用信息,用于获取apk文件
dexDir dex文件优化后的缓存路径
forceReload 是否强制重新从apk文件中抽取dex
/**
* Extracts application secondary dexes into files in the application data
* directory.
*
* @return a list of files that were created. The list may be empty if there
* are no secondary dex files.
* @throws IOException if encounters a problem while reading or writing
* secondary dex files
*/
static List load(Context context, ApplicationInfo applicationInfo, File dexDir,
boolean forceReload) throws IOException {
Log.i(TAG, "MultiDexExtractor.load(" + applicationInfo.sourceDir + ", " + forceReload + ")");
final File sourceApk = new File(applicationInfo.sourceDir);
//首先进行crc校验
long currentCrc = getZipCrc(sourceApk);
List files;
if (!forceReload && !isModified(context, sourceApk, currentCrc)) {
try {
//已经从apk中抽取出dex文件并存到缓存目录中,则直接返回zip文件list
files = loadExistingExtractions(context, sourceApk, dexDir);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to reload existing extracted secondary dex files,"
+ " falling back to fresh extraction", ioe);
files = performExtractions(sourceApk, dexDir);
putStoredApkInfo(context, getTimeStamp(sourceApk), currentCrc, files.size() + 1);
}
} else {
Log.i(TAG, "Detected that extraction must be performed.");
//从apk中复制dex文件到缓存目录
files = performExtractions(sourceApk, dexDir);
//保存时间戳、crc、dex数量等信息到sp
putStoredApkInfo(context, getTimeStamp(sourceApk), currentCrc, files.size() + 1);
}
Log.i(TAG, "load found " + files.size() + " secondary dex files");
return files;
}
forceReload为false并且已经从apk中抽取过dex文件则直接调用loadExistingExtractions 返回dex文件的zip列表
private static List loadExistingExtractions(Context context, File sourceApk, File dexDir)
throws IOException {
Log.i(TAG, "loading existing secondary dex files");
//dex文件的前缀 ,即data/data/packageName/code_cache/secondary-dexes/data/data/apkName.apk.classes
final String extractedFilePrefix = sourceApk.getName() + EXTRACTED_NAME_EXT;
//获取dex数目
int totalDexNumber = getMultiDexPreferences(context).getInt(KEY_DEX_NUMBER, 1);
final List files = new ArrayList(totalDexNumber);
//遍历除主dex外的其他dex
for (int secondaryNumber = 2; secondaryNumber <= totalDexNumber; secondaryNumber++) {
//文件名为 data/data/packageName/code_cache/secondary-dexes/data/data/apkName.apk.classes*.zip
String fileName = extractedFilePrefix + secondaryNumber + EXTRACTED_SUFFIX;
//以zip文件形式返回
File extractedFile = new File(dexDir, fileName);
if (extractedFile.isFile()) {
//添加到list中并返回
files.add(extractedFile);
if (!verifyZipFile(extractedFile)) {
Log.i(TAG, "Invalid zip file: " + extractedFile);
throw new IOException("Invalid ZIP file.");
}
} else {
throw new IOException("Missing extracted secondary dex file '" +
extractedFile.getPath() + "'");
}
}
return files;
}
否则调用performExtractions()方法从apk中抽取dex文件
private static List performExtractions(File sourceApk, File dexDir)
throws IOException {
final String extractedFilePrefix = sourceApk.getName() + EXTRACTED_NAME_EXT;
// Ensure that whatever deletions happen in prepareDexDir only happen if the zip that
// contains a secondary dex file in there is not consistent with the latest apk. Otherwise,
// multi-process race conditions can cause a crash loop where one process deletes the zip
// while another had created it.
prepareDexDir(dexDir, extractedFilePrefix);
List files = new ArrayList();
final ZipFile apk = new ZipFile(sourceApk);
try {
int secondaryNumber = 2;
//获取classes2.dex
ZipEntry dexFile = apk.getEntry(DEX_PREFIX + secondaryNumber + DEX_SUFFIX);
while (dexFile != null) {
//data/data/packageName/code_cache/secondary-dexes/data/data/apkName.apk.classes*.zip
String fileName = extractedFilePrefix + secondaryNumber + EXTRACTED_SUFFIX;
File extractedFile = new File(dexDir, fileName);
//添加到list列表中
files.add(extractedFile);
Log.i(TAG, "Extraction is needed for file " + extractedFile);
int numAttempts = 0;
boolean isExtractionSuccessful = false;
//最多重试3次
while (numAttempts < MAX_EXTRACT_ATTEMPTS && !isExtractionSuccessful) {
numAttempts++;
// Create a zip file (extractedFile) containing only the secondary dex file
// (dexFile) from the apk.
//从apk中抽取classes*dex文件并重命名为zip文件保存到指定目录
extract(apk, dexFile, extractedFile, extractedFilePrefix);
// Verify that the extracted file is indeed a zip file.
//判断是否抽取成功
isExtractionSuccessful = verifyZipFile(extractedFile);
// Log the sha1 of the extracted zip file
Log.i(TAG, "Extraction " + (isExtractionSuccessful ? "success" : "failed") +
" - length " + extractedFile.getAbsolutePath() + ": " +
extractedFile.length());
if (!isExtractionSuccessful) {
// Delete the extracted file
extractedFile.delete();
if (extractedFile.exists()) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to delete corrupted secondary dex '" +
extractedFile.getPath() + "'");
}
}
}
if (!isExtractionSuccessful) {
throw new IOException("Could not create zip file " +
extractedFile.getAbsolutePath() + " for secondary dex (" +
secondaryNumber + ")");
}
//自增以读取下一个classes*.dex文件
secondaryNumber++;
dexFile = apk.getEntry(DEX_PREFIX + secondaryNumber + DEX_SUFFIX);
}
} finally {
try {
apk.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to close resource", e);
}
}
return files;
}
抽取方法extract()
private static void extract(ZipFile apk, ZipEntry dexFile, File extractTo,
String extractedFilePrefix) throws IOException, FileNotFoundException {
//获取classes*.dex 对应输入流
InputStream in = apk.getInputStream(dexFile);
ZipOutputStream out = null;
//创建临时文件
File tmp = File.createTempFile(extractedFilePrefix, EXTRACTED_SUFFIX,
extractTo.getParentFile());
Log.i(TAG, "Extracting " + tmp.getPath());
try {
//输出为zip文件,zip文件中包含classes.dex
out = new ZipOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(tmp)));
try {
ZipEntry classesDex = new ZipEntry("classes.dex");
// keep zip entry time since it is the criteria used by Dalvik
classesDex.setTime(dexFile.getTime());
out.putNextEntry(classesDex);
byte[] buffer = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE];
int length = in.read(buffer);
while (length != -1) {
out.write(buffer, 0, length);
length = in.read(buffer);
}
out.closeEntry();
} finally {
out.close();
}
Log.i(TAG, "Renaming to " + extractTo.getPath());
if (!tmp.renameTo(extractTo)) {
throw new IOException("Failed to rename \"" + tmp.getAbsolutePath() +
"\" to \"" + extractTo.getAbsolutePath() + "\"");
}
} finally {
closeQuietly(in);
tmp.delete(); // return status ignored
}
}
再回到MultiDex的install()方法中,通过MultiDexExtractor.load()得到dex文件的zip列表后,调用installSecondaryDexes()
private static void installSecondaryDexes(ClassLoader loader, File dexDir, List files)
throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException,
InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, IOException {
if (!files.isEmpty()) {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 19) {
V19.install(loader, files, dexDir);
} else if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 14) {
V14.install(loader, files, dexDir);
} else {
V4.install(loader, files);
}
}
}
根据sdk版本不同,调用对应的方法,V19、V14、V4都是MultiDex的内部类,处理的逻辑也差不多,这里主要看一下V19
/**
* Installer for platform versions 19.
*/
private static final class V19 {
private static void install(ClassLoader loader, List additionalClassPathEntries,
File optimizedDirectory)
throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException,
NoSuchFieldException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException {
/* The patched class loader is expected to be a descendant of
* dalvik.system.BaseDexClassLoader. We modify its
* dalvik.system.DexPathList pathList field to append additional DEX
* file entries.
*/
//获取PathClassLoader的pathList成员变量,即DexPathList对象,其成员变量dexElements用于存储dex文件相关信息
Field pathListField = findField(loader, "pathList");
Object dexPathList = pathListField.get(loader);
ArrayList suppressedExceptions = new ArrayList();
//调用makeDexElements方法,内部通过反射调用DexPathList的makeDexElements方法,返回dexElements
//参数为/code_cache/secondary-dexes缓存目录中包含classes.dex的zip文件list以及优化后的dex文件存放目录
//expandFieldArray方法先获取dexPathList对象的现有dexElements变量,然后建其和makeDexElements方法返回
//的dexElements数组合并,然后再将合并之后的结果设置为dexPathList对象的dexElements变量
expandFieldArray(dexPathList, "dexElements", makeDexElements(dexPathList,
new ArrayList(additionalClassPathEntries), optimizedDirectory,
suppressedExceptions));
if (suppressedExceptions.size() > 0) {
for (IOException e : suppressedExceptions) {
Log.w(TAG, "Exception in makeDexElement", e);
}
Field suppressedExceptionsField =
findField(loader, "dexElementsSuppressedExceptions");
IOException[] dexElementsSuppressedExceptions =
(IOException[]) suppressedExceptionsField.get(loader);
if (dexElementsSuppressedExceptions == null) {
dexElementsSuppressedExceptions =
suppressedExceptions.toArray(
new IOException[suppressedExceptions.size()]);
} else {
IOException[] combined =
new IOException[suppressedExceptions.size() +
dexElementsSuppressedExceptions.length];
suppressedExceptions.toArray(combined);
System.arraycopy(dexElementsSuppressedExceptions, 0, combined,
suppressedExceptions.size(), dexElementsSuppressedExceptions.length);
dexElementsSuppressedExceptions = combined;
}
suppressedExceptionsField.set(loader, dexElementsSuppressedExceptions);
}
}
/**
* A wrapper around
* {@code private static final dalvik.system.DexPathList#makeDexElements}.
*/
private static Object[] makeDexElements(
Object dexPathList, ArrayList files, File optimizedDirectory,
ArrayList suppressedExceptions)
throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException,
NoSuchMethodException {
Method makeDexElements =
findMethod(dexPathList, "makeDexElements", ArrayList.class, File.class,
ArrayList.class);
return (Object[]) makeDexElements.invoke(dexPathList, files, optimizedDirectory,
suppressedExceptions);
}
}
makeDexElements()其实就是通过反射方式调用dexPathList对象的makeDexElements方法,将从dex添加到其dexElements属性中,具体的过程在前面的文章中已经介绍过—《android Dex文件的加载》,这里不再赘述。
private static void expandFieldArray(Object instance, String fieldName,
Object[] extraElements) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalArgumentException,
IllegalAccessException {
Field jlrField = findField(instance, fieldName);
Object[] original = (Object[]) jlrField.get(instance);
Object[] combined = (Object[]) Array.newInstance(
original.getClass().getComponentType(), original.length + extraElements.length);
System.arraycopy(original, 0, combined, 0, original.length);
System.arraycopy(extraElements, 0, combined, original.length, extraElements.length);
jlrField.set(instance, combined);
}
到这里MultiDex.install(this)方法的逻辑就分析完了,可以看到其中的处理步骤和上篇文章ant方式中我们手动加载从dex的方式基本上是一致的,所以这两种方式并没有本质上的区别。