Ray Tracing实际上是一种渲染框架,通过迭代计算,得到镜面反射效果和折射效果,在上一篇文章中,我使用了最基本的方法,当光线和物体相交时,根据交点和法线方向计算唯一的反射光线和折射光线,进而迭代处理。但是现实情况往往并非如此,反射光线方向不一定是唯一的,因此Path Tracing作为Ray Tracing的一个具体实现,可以实现更加真实的效果。Path Tracing使用了蒙特卡洛方法,利用BRDF随机跟踪多条反射光线,随后根据这些光线的贡献计算该点的颜色值。因此,可想而知,Path Tracing相比于上一篇文章的结果,非常耗时,但是结果也更加真实。当然BRDF里有很多模型,目标也是解决不同场景下出现的问题,因此这是一个深坑,我也没有爬出来orz。
当然某些同学还会遇到一类渲染方法叫做Ray Casting,事实上这个渲染方法就是Ray Tracing的第一步,发射光线,与物体相交,这个方法可以实现阴影的效果,但是没有包括后续的反射效果和折射效果的计算。
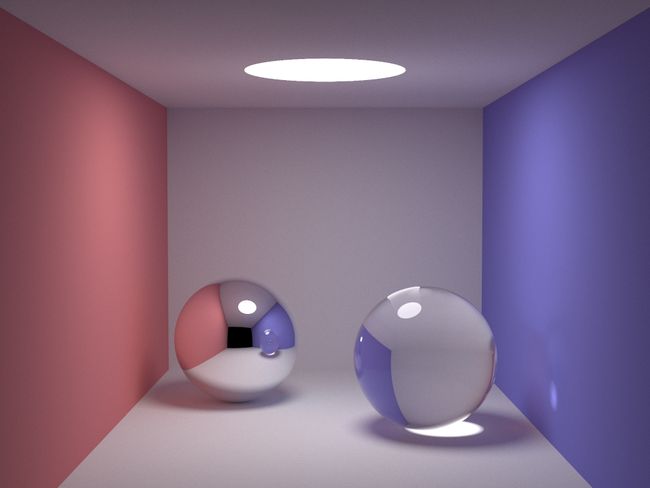
上面这张图片是Path Tracing的一个渲染例子,可以看到效果确实很不错,但是代价是渲染速度非常慢,另外在这里需要强调的一点是,右边的球是透明的,因此具有折射属性,所以可以看到,光源的光线穿过了球体,在下面形成了圆形,还有折射和镜面反射是密不可分的,存在折射就会存在镜面反射,这也是为什么右边的球存在镜面反射。
以下是代码部分:
#include // cl -o pathtracing.exe pathtracing.cpp under windows
#include // g++ -o pathtracing.out pathtracing.cpp under mac
#include
#define M_PI 3.141592653589793
unsigned RAND48_SEED_0 (0x330e);
unsigned RAND48_SEED_1 (0xabcd);
unsigned RAND48_SEED_2 (0x1234);
unsigned RAND48_MULT_0 (0xe66d);
unsigned RAND48_MULT_1 (0xdeec);
unsigned RAND48_MULT_2 (0x0005);
unsigned RAND48_ADD (0x000b);
//Generate random number using seed.
unsigned short _rand48_seed[3] = {
RAND48_SEED_0,
RAND48_SEED_1,
RAND48_SEED_2
};
unsigned short _rand48_mult[3] = {
RAND48_MULT_0,
RAND48_MULT_1,
RAND48_MULT_2
};
void dorand48(unsigned short xseed[3])
{
unsigned accu;
unsigned short temp[2];
accu = RAND48_MULT_0 * xseed[0] + RAND48_ADD;
temp[0] = (unsigned short) accu;
accu >>= 16;
accu += RAND48_MULT_0 * xseed[1] + RAND48_MULT_1 * xseed[0];
temp[1] = (unsigned short) accu;
accu >>= 16;
accu += RAND48_MULT_0 * xseed[2] + RAND48_MULT_1 * xseed[1] + RAND48_MULT_2 * xseed[0];
xseed[0] = temp[0];
xseed[1] = temp[1];
xseed[2] = (unsigned short) accu;
}
double erand48(unsigned short xseed[3])
{
dorand48(xseed);
return ldexp((double) xseed[0], -48) +
ldexp((double) xseed[1], -32) +
ldexp((double) xseed[2], -16);
}
float erand24(unsigned short xseed[3])
{
dorand48(xseed);
return ldexp((float) xseed[1], -32) + ldexp((float) xseed[2], -16);
}
//Define the struct vec
struct Vec
{
float x, y, z;
/*Vec(float x_ = 0)
{
x = x_;
y = y_;
z = z_;
}*/
Vec(float x_ = 0, float y_ = 0, float z_ = 0)
{
x = x_;
y = y_;
z = z_;
}
Vec operator+(const Vec &b) const
{
return Vec(x + b.x, y + b.y, z + b.z);
}
Vec operator-(const Vec &b) const
{
return Vec(x - b.x, y - b.y, z - b.z);
}
Vec operator-() const
{
return Vec(-x, -y, -z);
}
Vec operator*(float b) const
{
return Vec(x * b, y * b, z * b);
}
Vec mult(const Vec &b) const
{
return Vec(x * b.x, y * b.y, z * b.z);
}
Vec& norm()
{
return *this = *this * (1 / sqrt(x * x + y * y + z * z));
}
float dot(const Vec &b) const
{
return x * b.x + y * b.y + z * b.z;
}
Vec operator%(Vec&b)
{
return Vec(y * b.z - z * b.y, z * b.x - x * b.z, x * b.y - y * b.x);
}
};
//Define the struct Ray, including start and orientation P(t) = O + tD
struct Ray
{
Vec o, d;
Ray(Vec o_, Vec d_) : o(o_), d(d_) {}
};
// three material types, diffuse, specular and refractive
enum Refl_t { DIFF, SPEC, REFR };
struct Sphere
{
float rad; // radius of sphere
Vec p, e, c; // position, emission, color
Refl_t refl; // reflection type including diffuse, specular and refractive
Sphere(float rad_, Vec p_, Vec e_, Vec c_, Refl_t refl_) : rad(rad_), p(p_), e(e_), c(c_), refl(refl_) { }
float intersect(const Ray &r) const // returns distance, 0 if nohit
{
Vec op = p - r.o; // Solve t^2*d.d + 2*t*(o-p).d + (o-p).(o-p)-R^2 = 0
double t, eps = 1e-4, b = op.dot(r.d), det = b * b - op.dot(op) + rad * rad;
if (det < 0) return 0;
else det = sqrt(det);
return (t = b - det) > eps ? t : ((t = b + det) > eps ? t : 0);
/*Vec l = p - r.o;
double eps = 1e-4;
double tca = l.dot(r.d);
if(tca < 1e-4) return 0;
double dist = l.dot(l) - tca*tca;
double rad2 = rad * rad;
if (dist > rad2) return 0;
double thc = sqrt(rad2 - dist);
double t0 = tca - thc;
double t1 = tca - thc;
return (t0) > eps ? t0 : (t1 > eps ? t1: 0);*/
}
};
Sphere spheres[] = {//Scene: radius, position, emission, color, material
Sphere(1e5, Vec( 1e5 + 1, 40.8, 81.6), Vec(), Vec(.75, .25, .25), DIFF), //Left
Sphere(1e5, Vec(-1e5 + 99, 40.8, 81.6), Vec(), Vec(.25, .25, .75), DIFF), //Rght
Sphere(1e5, Vec(50, 40.8, 1e5), Vec(), Vec(.75, .75, .75), DIFF), //Back
Sphere(1e5, Vec(50, 40.8, -1e5 + 170), Vec(), Vec(), DIFF), //Frnt
Sphere(1e5, Vec(50, 1e5, 81.6), Vec(), Vec(.75, .75, .75), DIFF), //Botm
Sphere(1e5, Vec(50, -1e5 + 81.6, 81.6), Vec(), Vec(.75, .75, .75), DIFF), //Top
Sphere(16.5, Vec(27, 16.5, 47), Vec(), Vec(1, 1, 1)*.999, SPEC), //Mirr
Sphere(16.5, Vec(73, 16.5, 78), Vec(), Vec(1, 1, 1)*.999, SPEC), //Glas
Sphere(600, Vec(50, 681.6 - .27, 81.6), Vec(12, 12, 12), Vec(), DIFF) //Light
};
/*Sphere spheres[] = {//Scene: radius, position, emission, color, material
// center 50 40.8 62
// floor 0
// back 0
// rad pos emis col refl
// Sphere(1e3, Vec(1,1,-2)*1e4, Vec(1,1,1)*5e2, Vec(), DIFF), // moon
// Sphere(3e2, Vec(.6,.2,-2)*1e4, Vec(1,1,1)*5e3, Vec(), DIFF), //
// moon
Sphere(2.5e3, Vec(.82,.92,-2)*1e4, Vec(1,1,1)*.8e2, Vec(), DIFF), // moon
// Sphere(2.5e4, Vec(50, 0, 0), Vec(1,1,1)*1e-3, Vec(.2,.2,1)*0.0075, DIFF), // sky
// Sphere(2.5e4, Vec(50, 0, 0), Vec(0.114, 0.133, 0.212)*1e-2, Vec(.216,.384,1)*0.0007, DIFF), // sky
Sphere(2.5e4, Vec(50, 0, 0), Vec(0.114, 0.133, 0.212)*1e-2, Vec(.216,.384,1)*0.003, DIFF), // sky
Sphere(5e0, Vec(-.2,0.16,-1)*1e4, Vec(1.00, 0.843, 0.698)*1e2, Vec(), DIFF), // star
Sphere(5e0, Vec(0, 0.18,-1)*1e4, Vec(1.00, 0.851, 0.710)*1e2, Vec(), DIFF), // star
Sphere(5e0, Vec(.3, 0.15,-1)*1e4, Vec(0.671, 0.780, 1.00)*1e2, Vec(), DIFF), // star
Sphere(3.5e4, Vec(600,-3.5e4+1, 300), Vec(), Vec(.6,.8,1)*.01, REFR), //pool
Sphere(5e4, Vec(-500,-5e4+0, 0), Vec(), Vec(1,1,1)*.35, DIFF), //hill
Sphere(16.5, Vec(27,0,47), Vec(), Vec(1,1,1)*.33, DIFF), //hut
Sphere(7, Vec(27+8*sqrt(2),0,47+8*sqrt(2)),Vec(), Vec(1,1,1)*.33, DIFF), //door
Sphere(500, Vec(-1e3,-300,-3e3), Vec(), Vec(1,1,1)*.351, DIFF), //mnt
Sphere(830, Vec(0, -500,-3e3), Vec(), Vec(1,1,1)*.354, DIFF), //mnt
Sphere(490, Vec(1e3, -300,-3e3), Vec(), Vec(1,1,1)*.352, DIFF), //mnt
};*/
//Convert unbounded color range to [0,1]
inline float clamp(float x)
{
return x < 0 ? 0 : x > 1 ? 1 : x;
}
//Convert [0,1] to [0,255]
inline int toInt(float x)
{
return int(pow(clamp(x), 1 / 2.2f) * 255 + .5f);
}
//Compute the intersection between ray and objects in scene, and find the closest object
bool intersect(const Ray& r, double& t, int& id)
{
double n = sizeof(spheres) / sizeof(Sphere);
double inf = t = 1e20;
for(int i = int(n); i--;)
{
double d = spheres[i].intersect(r);
if (d && d < t) {
t = d;
id = i;
}
}
return t < inf;
}
/*struct RadState
{
Vec e;
Vec f;
};*/
Vec radiance(Ray r, int depth, unsigned short *Xi)
{
Vec resE(0, 0, 0);
Vec resF(1, 1, 1);
for (int depth = 0; depth != 10; ++depth)
{
double t; // distance to intersection
int id = 0; // id of intersected object
if (!intersect(r, t, id))
{
resF = Vec();
continue;
}
const Sphere &obj = spheres[id]; // the hit object
Vec x = r.o + r.d * t;
Vec n = (x - obj.p).norm();
Vec nl = n.dot(r.d) < 0 ? n : -n;
Vec f = obj.c;
double p = f.x > f.y && f.x > f.z ? f.x : f.y > f.z ? f.y : f.z; // max refl
if (obj.refl == DIFF)
{ // Ideal DIFFUSE reflection
double r1 = 2 * M_PI * erand48(Xi), r2 = erand48(Xi), r2s = sqrt(r2);
Vec w = nl, u = ((fabs(w.x) > .1 ? Vec(0, 1) : Vec(1)) % w).norm(), v = w % u;
Vec d = (u * cos(r1) * r2s + v * sin(r1) * r2s + w * sqrt(1 - r2)).norm();
r = Ray(x + d * 0.1, d);
resE = resE + obj.e.mult(resF);
resF = resF.mult(f);
continue;
}
else if (obj.refl == SPEC)
{// Ideal SPECULAR reflection
r = Ray(x, r.d - n * 2 * n.dot(r.d));
resE = resE + obj.e.mult(resF);
resF = resF.mult(f);
continue;
}
else {
resF = Vec();
continue;
}
Ray reflRay(x, r.d - n * 2 * n.dot(r.d)); // Ideal dielectric REFRACTION
bool into = n.dot(nl) > 0; // Ray from outside going in?
double nc = 1, nt = 1.5, nnt = into ? nc / nt : nt / nc, ddn = r.d.dot(nl), cos2t;
if ((cos2t = 1 - nnt * nnt * (1 - ddn * ddn)) < 0 && depth < 5) // Total internal reflection
{
r = reflRay;
resE = resE + obj.e.mult(resF);
resF = resF.mult(f);
continue;
}
Vec tdir = (r.d * nnt - n * ((into ? 1 : -1) * (ddn * nnt + sqrt(cos2t)))).norm();
double a = nt - nc;
double b = nt + nc;
double R0 = a * a / (b * b);
double c = 1 - (into ? -ddn : tdir.dot(n));
double Re = R0 + (1 - R0) * c * c * c * c * c;
double Tr = 1 - Re;
double P = .25 + .5 * Re;
double RP = Re / P;
double TP = Tr / (1 - P);
if (erand48(Xi) < P)
{
r = reflRay;
resE = resE + obj.e.mult(resF) * RP;
resF = resF.mult(f) * RP;
}
else
{
r = Ray(x, tdir);
resE = resE + obj.e.mult(resF) * TP;
resF = resF.mult(f) * TP;
}
}
return resE;
}
/*Vec radiance(const Ray &r, int depth, unsigned short *Xi){
double t; // distance to intersection
int id=0; // id of intersected object
if (!intersect(r, t, id)) return Vec(); // if miss, return black
const Sphere &obj = spheres[id]; // the hit object
Vec x=r.o+r.d*t, n=(x-obj.p).norm(), nl=n.dot(r.d)<0?n:n*-1, f=obj.c;
double p = f.x>f.y && f.x>f.z ? f.x : f.y>f.z ? f.y : f.z; // max refl
if (++depth>5) if (erand48(Xi).1?Vec(0,1):Vec(1))%w).norm(), v=w%u;
Vec d = (u*cos(r1)*r2s + v*sin(r1)*r2s + w*sqrt(1-r2)).norm();
return obj.e + f.mult(radiance(Ray(x,d),depth,Xi));
} else if (obj.refl == SPEC) // Ideal SPECULAR reflection
return obj.e + f.mult(radiance(Ray(x,r.d-n*2*n.dot(r.d)),depth,Xi));
Ray reflRay(x, r.d-n*2*n.dot(r.d)); // Ideal dielectric REFRACTION
bool into = n.dot(nl)>0; // Ray from outside going in?
double nc=1, nt=1.5, nnt=into?nc/nt:nt/nc, ddn=r.d.dot(nl), cos2t;
if ((cos2t=1-nnt*nnt*(1-ddn*ddn))<0) // Total internal reflection
return obj.e + f.mult(radiance(reflRay,depth,Xi));
Vec tdir = (r.d*nnt - n*((into?1:-1)*(ddn*nnt+sqrt(cos2t)))).norm();
double a=nt-nc, b=nt+nc, R0=a*a/(b*b), c = 1-(into?-ddn:tdir.dot(n));
double Re=R0+(1-R0)*c*c*c*c*c,Tr=1-Re,P=.25+.5*Re,RP=Re/P,TP=Tr/(1-P);
return
obj.e + f.mult(
(erand48(Xi)