I、集合
1.1 数组转化为集合
使用java Util类的Array.asList(name)方法将数组转化为集合:
package collections;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Array2CollectionEmp {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
int n = 5;
String[] name = new String[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
name[i] = String.valueOf(i);
}
List list = Arrays.asList(name);
//System.out.println();
for (String li : list) {
String str = li;
System.out.print(str + " ");
}
}
}
1.2 集合比较
将字符串转换为集合并使用Collection类的Collection.min()和Collection.max()来比较集合中的元素:
package collections;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class CompareCollectionEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] coins = { "Penny", "nickel", "dime", "Quarter", "dollar" };
Set set = new TreeSet();
for (int i = 0; i < coins.length; i++) {
set.add(coins[i]);
}
System.out.println(Collections.min(set));
System.out.println(Collections.min(set, String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER));
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++) {
System.out.print("-");
}
System.out.println("");
System.out.println(Collections.max(set));
System.out.println(Collections.max(set, String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER));
}
}
1.3 HashMap遍历
使用Collection类的iterator()方法来遍历集合:
package collections;
import java.util.*;
public class HashMapIterEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap hMap = new HashMap();
hMap.put("1", "1st");
hMap.put("2", "2nd");
hMap.put("3", "3rd");
Collection cl = hMap.values();
Iterator itr = cl.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
}
1.4 集合长度
使用Collections类的collection.add()来添加数据,并使用collection.size()来计算集合的长度:
package collections;
import java.util.*;
public class CollectionSizeEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int size;
HashSet collection = new HashSet();
String str1 = "Yellow", str2 = "White",
str3 = "Green", str4 = "Blue";
Iterator iterator;
collection.add(str1);
collection.add(str2);
collection.add(str3);
collection.add(str4);
System.out.print("集合数据:");
iterator = collection.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iterator.next() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
size = collection.size();
if (collection.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("collection is empty!");
}
else {
System.out.print("collection's size is " + size + "\n");
}
}
}
1.5 HashMap遍历
使用Collection类的iterator()方法来遍历集合:
package collections;
import java.util.*;
public class HashMapIteratorEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap hMap = new HashMap();
hMap.put("1", "1st");
hMap.put("2", "2nd");
hMap.put("3", "3rd");
Collection cl = hMap.values();
Iterator itr = cl.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
}
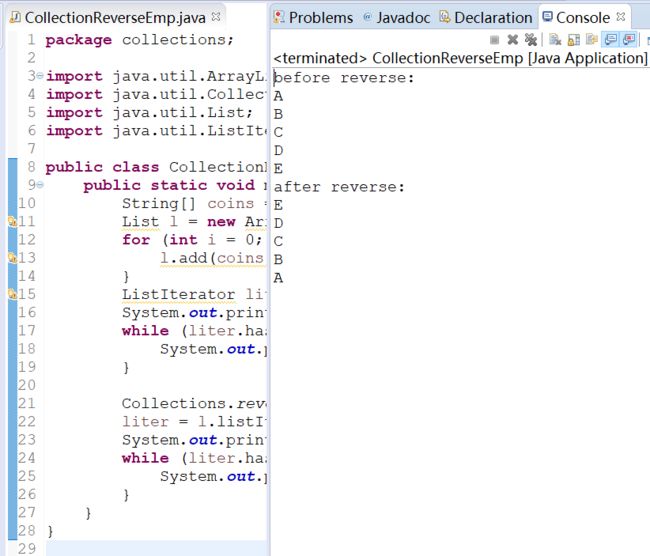
1.6 集合反转
使用Collection和Listiterator类的listIterator()和collection.reverse()方法来反转集合中的元素:
package collections;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ListIterator;
public class CollectionReverseEmp {
public static void main(String[] args){
String[] coins = { "A", "B", "C", "D", "E" };
List l = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < coins.length; i++) {
l.add(coins[i]);
}
ListIterator liter = l.listIterator();
System.out.println("before reverse:");
while (liter.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(liter.next());
}
Collections.reverse(l);
liter = l.listIterator();
System.out.println("after reverse:");
while (liter.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(liter.next());
}
}
}
1.7 删除集合中指定元素
使用Collection类的collection.remove()方法来删除集合中的指定元素:
package collections;
import java.util.*;
public class CollectionRemoveEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int size;
HashSet collection = new HashSet();
String str1 = "Yellow", str2 = "White", str3 = "Green", str4 = "Blue";
Iterator iterator;
collection.add(str1);
collection.add(str2);
collection.add(str3);
collection.add(str4);
System.out.println("before remove:");
iterator = collection.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
System.out.println();
collection.remove(str2);
System.out.println("after remove:");
iterator = collection.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
1.8 只读集合
使用Collection类的Collections.unmodifiableList()方法来设置集合为只读:
package collections;
import java.util.*;
public class UnmodifiableListEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
List stuff = Arrays.asList(new String[] {"a","b"});
List list = new ArrayList(stuff);
list = Collections.unmodifiableList(list);
try {
list.set(0, "new value");
} catch (UnsupportedOperationException e) {
System.out.println("为只读");
}
}
}
1.9 集合输出
使用java Util 类的keySet(),values(),firstKey()方法将集合元素输出:
package collections;
import java.util.*;
public class CollectionOutputEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap tMap= new TreeMap();
tMap.put(1, "Sunday");
tMap.put(2, "Monday");
tMap.put(3, "Tuesday");
tMap.put(4, "Wednesday");
tMap.put(5, "Thursday");
tMap.put(6, "Friday");
tMap.put(7, "Saturday");
System.out.println("keys of TreeMap: " + tMap.keySet());
System.out.println("values of TreeMap: " + tMap.values());
System.out.println("key is 5 :" + tMap.get(5));
System.out.println("the first key: " + tMap.firstKey());
System.out.println("the last key: " + tMap.lastKey());
System.out.println("remove the last key: " + tMap.remove(tMap.lastKey()));
System.out.println("now, keys of TreeMap: " + tMap.keySet());
System.out.println("now, values of TreeMap: " + tMap.values());
}
}
1.10 List循环移动元素
使用Collections类的rotate()来循环移动元素,其中第二个参数指定了移动的起始位置:
package collections;
import java.util.*;
public class RotateEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = Arrays.asList("one two three four five size".split(" "));
System.out.println("The List is :" + list);
Collections.rotate(list, 3);
System.out.println("rotate: " + list);
}
}
1.11 遍历HashTable的键值
package collections;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Hashtable;
public class EnumerationEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hashtable ht = new Hashtable();
ht.put("1", "One");
ht.put("2", "Two");
ht.put("3", "Three");
Enumeration e = ht.keys();
while (e.hasMoreElements()) {
System.out.println(e.nextElement());
}
}
}
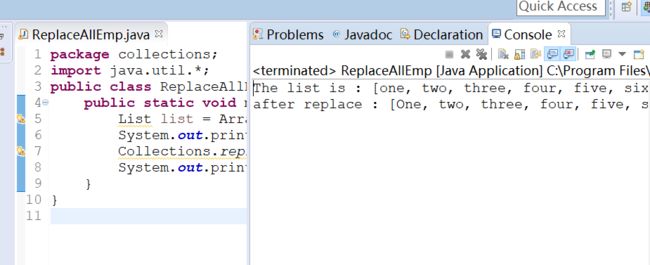
1.12 List元素替换
使用Collections类的replaceAll()方法替换List中的所有指定元素:
package collections;
import java.util.*;
public class ReplaceAllEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = Arrays.asList("one two three four five six one three Four".split(" "));
System.out.println("The list is : " + list);
Collections.replaceAll(list, "one", "One");
System.out.println("after replace : " + list);
}
}
1.13 List 截取
使用Collections类的indexOfSubList()和lastIndexOfSubList()方法来查看子列表是否在列表中,并查看子列表在列表中所在的位置:
package collections;
import java.util.*;
public class ListSubListEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = Arrays.asList("one two three four five six one three four".split(" "));
System.out.println("List is : " + list);
List sublist = Arrays.asList("three four".split(" "));
System.out.println("sublist is : " + sublist);
System.out.println("indexOfSubList: " + Collections.indexOfSubList(list, sublist));
System.out.println("lastIndexOfSubList: " + Collections.lastIndexOfSubList(list, sublist));
}
}
II、网络实例
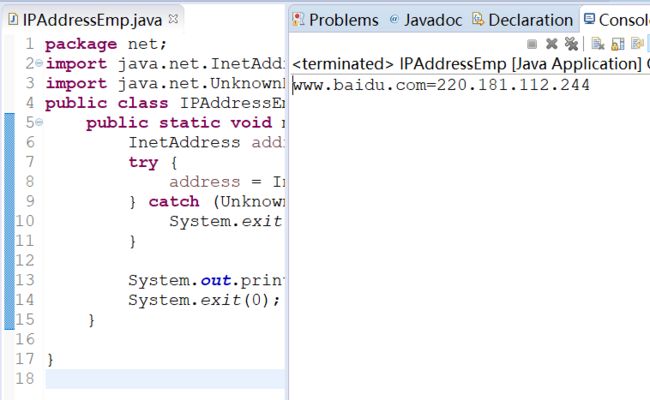
2.1 查看指定主机的IP地址
使用InetAddress类的InetAddress.getByName()方法来获取指定主机的IP地址:
package net;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
public class IPAddressEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InetAddress address = null;
try {
address = InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com");
} catch (UnknownHostException e){
System.exit(2);
}
System.out.println(address.getHostName() + "=" + address.getHostAddress());
System.exit(0);
}
}
2.2 查看端口是否使用
package net;
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class PostEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Socket Skt;
String host = "localhost";
if (args.length > 0) {
host = args[0];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 1024; i++) {
try {
System.out.println("查看 "+ i);
Skt = new Socket(host, i);
System.out.println("端口 " + i + " 已被使用");
}
catch (UnknownHostException e) {
System.out.println("Exception occured"+ e);
break;
}
catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
}
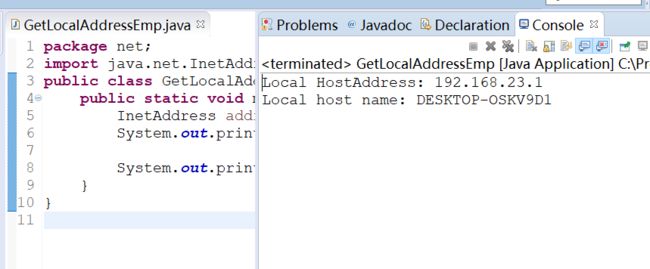
2.3 获取本机ip地址及主机名
使用InetAddress类的getLocalAddress()方法获取本机ip地址及主机名:
package net;
import java.net.InetAddress;
public class GetLocalAddressEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
InetAddress addr = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
System.out.println("Local HostAddress: " + addr.getHostAddress());
System.out.println("Local host name: " + addr.getHostName());
}
}
2.4 获取远程文件大小
package net;
import java.net.URL;
import java.net.URLConnection;
public class FileSizeEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int size;
URL url = new URL("https://upload-images.jianshu.io/upload_images/10118224-762b98d6db641801.png?imageMogr2/auto-orient/strip%7CimageView2/2/w/669/format/webp");
URLConnection conn = url.openConnection();
size = conn.getContentLength();
if (size < 0)
System.out.println("cannot get the size");
else
System.out.println("the size is : " + size + " bytes");
conn.getInputStream().close();
}
}
2.5 Socket实现多线程服务器程序
使用Socket类的accept()方法和ServerSocket类的MultiThreadServer(socketname)方法来实现多线程服务器程序:
package net;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class MultiThreadServerEmp implements Runnable {
Socket csocket;
MultiThreadServerEmp(Socket csocket) {
this.csocket = csocket;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ServerSocket ssock = new ServerSocket(1234);
System.out.println("Listening");
while (true) {
Socket sock = ssock.accept();
System.out.println("Connected");
new Thread(new MultiThreadServerEmp(sock)).start();
}
}
public void run() {
try {
PrintStream pstream = new PrintStream(csocket.getOutputStream());
for (int i = 100; i >= 0; i--) {
pstream.println(i + "bottles of beer on the wall");
}
pstream.close();
csocket.close();
}
catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
使用实现Runnable接口的方式来实现线程,需要重写run方法。
2.6 使用Socket连接到指定主机
使用net.Socket类的getInetAddress()方法来连接到指定主机(类似于ping):
package net;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
public class WebPingEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
InetAddress addr;
Socket sock = new Socket("www.baidu.com", 80);
addr = sock.getInetAddress();
System.out.println("connected " + addr);
sock.close();
}
catch (java.io.IOException e) {
System.out.println("cannot connect " + args[0]);
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
2.7 获取URL相应头的日期信息
使用HttpURLConnection 的 httpCon.getDate()方法来获取URL响应头的日期信息:
package net;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.Date;
public class URLGetDateEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
URL url = new URL("http://www.baidu.com");
HttpURLConnection httpCon = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
long date = httpCon.getDate();
if (date == 0) {
System.out.println("cannot get date");
}
else {
System.out.println("the date is : " + new Date(date));
}
}
}
2.8 获取URL响应头信息
package net;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.net.URLConnection;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class URLGetHeaderEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
URL url = new URL("http://www.baidu.com");
URLConnection conn = url.openConnection();
Map headers = conn.getHeaderFields();
Set keys = headers.keySet();
for (String key : keys) {
String val = conn.getHeaderField(key);
System.out.println(key + " " + val);
}
System.out.println(conn.getLastModified()); //最后一次修改日期
}
}
2.9 解析URL
使用URL类的getProtocol(),getFile()等方法解析URL地址:
package net;
import java.net.URL;
public class URLProcessEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
URL url = new URL("http://www.baidu.com");
System.out.println("URL is " + url.toString());
System.out.println("Protocol " + url.getProtocol());
System.out.println("File " + url.getFile());
System.out.println("Host " + url.getHost());
System.out.println("Path " + url.getPath());
System.out.println("Port " + url.getPort());
System.out.println("Default Port " + url.getDefaultPort());
}
}
2.10 ServerSocket与Socket通信
建立服务器端:
· 服务器建立通信ServerSocket;
· 服务端建立Socket接受客户端连接;
· 建立IO输入流读取客户端发送的数据;
· 建立IO输出流向客户端发送数据消息;
package net;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class ServerEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(8888);
System.out.println("start server...");
Socket s = ss.accept();
System.out.println("client:" + s.getInetAddress().getLocalHost() + "has connected the server");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
String mess = br.readLine();
System.out.println("client: " + mess);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(s.getOutputStream()));
bw.write(mess + "\n");
bw.flush();
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
建立客户端:
· 创建Socket通信,设置通信服务器的IP和Port;
· 建立IO输出流向服务器发送数据消息;
· 建立IO输入流读取服务器发送来的数据消息;
package net;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
public class ClientEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Socket s = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8888);
InputStream is = s.getInputStream();
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(os));
//向服务器端发送一条消息
bw.write("测试客户端和服务端通信,服务器收到后返回到客户端\n");
bw.flush();
//读取服务器返回的消息
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
String mess = br.readLine();
System.out.println("server: " + mess);
}
catch (UnknownHostException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}