之前一篇介绍了《Activity 启动流程分析》,本篇继续学习 Android中Service的启动流程。
Service的启动方式
有两种,分别是startService(),bindService(),经历的生命周期也不太一样。
通过
startService()
onCreate()->onStartCommand()->onDestroy()
建议不要在onStartCommand()做耗时操作通过
bindService()
onCreate()->onbind()->onUnbind()->onDestroy()
Service的所有生命周期方法都是在主线程进行的,即ActivityThread启动的线程
onStartCommand()返回值种类:
- START_NOT_STICKY
- START_STRCKY
- START_REDELIVER_INTENT
Service以及四大组件多进程?
android的四大组件都可以开启多进程,通过manifest文件设置process属性
可以同时startService()和bindService()时?如何退出?
答案是可以的,参考 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_22804827/article/details/78609636
- service的onCreate只会执行一次,onBind也只会执行一次,onStartCommand可以执行多次
- 无论多少个Activity绑定了Service,onBind()和onUnBind()只会执行一次
- 多个Activity绑定Service,只有所有的Activity与Service绑定的Contxet失效后,Service才会执行onUnbind(),最后onDestory()进行销毁
- 多个Activity绑定Service,只有所有的Activity调用stopService(),或者在Service内部调用stopSelf(),最后才会停止服务。
- 同时startService()和bindService(),只有stopService() 加上unBindService()让context失效,最后才会停止服务。
涉及的类
- ContextImpl:Context的具体实现
- ActivityManagerService:四大组件的服务管理,负责分发任务
- ActiveServices:实际负责Service启动绑定等事情
- ApplicationThread:表示APP的主线程,有main函数
- ActivityThread:ActivityThread的内部类,是一个binder对象,是ActivityManagerService向ActivityThread通信的桥梁
- LoadedApk:
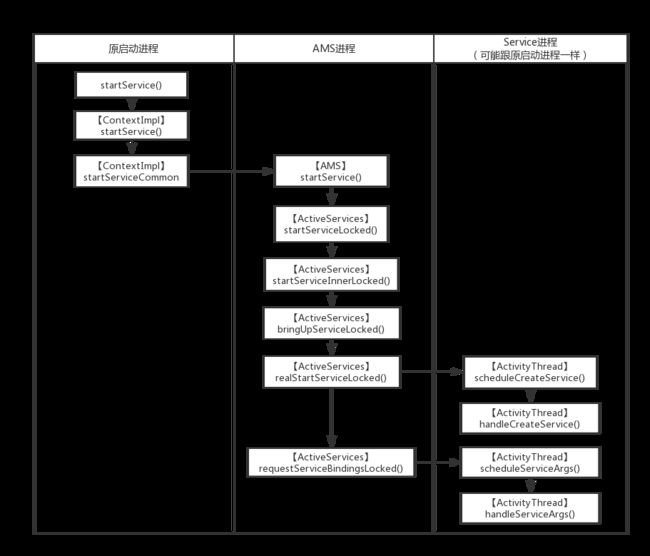
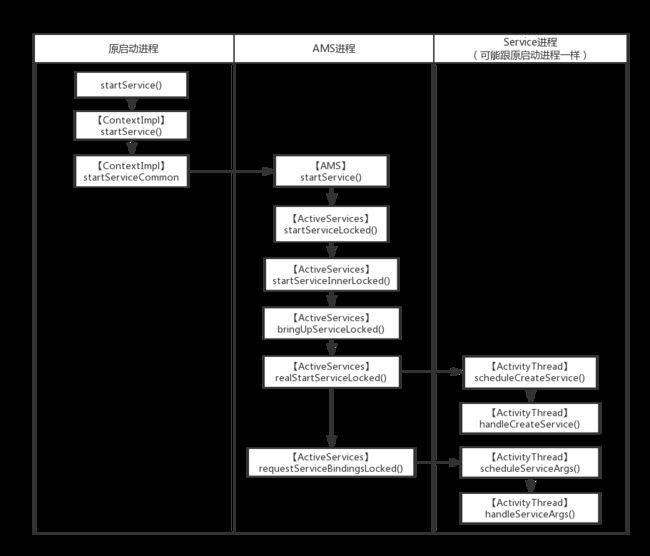
StartService()
//ContextWrapper
public ComponentName startService(Intent service) {
return mBase.startService(service);
}
我们通过Context.startService(),走到ContextWrapper,mBase是一个Context,具体实现在ContextImpl
// ContextImpl
public ComponentName startService(Intent service) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return startServiceCommon(service, false, mUser);
}
private ComponentName startServiceCommon(Intent service, boolean requireForeground,
UserHandle user) {
try {
validateServiceIntent(service);
service.prepareToLeaveProcess(this);
ComponentName cn = ActivityManager.getService().startService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), service, service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(
getContentResolver()), requireForeground,
getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
...
return cn;
}
}
-
validateServiceIntent()是验证Intent是否合法 - AMS运行在单独的进程,是一个binder,ActivityManager.getService() 获取得到是IActivityManager,它是binder引用,供外部跨进程调用。
// ContextImpl
private void validateServiceIntent(Intent service) {
if (service.getComponent() == null && service.getPackage() == null) {
if (getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
IllegalArgumentException ex = new IllegalArgumentException(
"Service Intent must be explicit: " + service);
throw ex;
} else {
Log.w(TAG, "Implicit intents with startService are not safe: " + service
+ " " + Debug.getCallers(2, 3));
}
}
}
从上面可以看出,service.getComponent() == null && service.getPackage() == null 说明是隐式启动,5.0以后不支持隐式启动。
接着看AMS如何启动service
// ActivityManagerService
public ComponentName startService(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service,
String resolvedType, boolean requireForeground, String callingPackage, int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...
synchronized(this) {
final int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
ComponentName res;
try {
res = mServices.startServiceLocked(caller, service,
resolvedType, callingPid, callingUid,
requireForeground, callingPackage, userId);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
return res;
}
}
其中 mServices 是 ActiveServices,他负责管理Service的活动,其实AMS就像一个桥梁,由他接收消息,分派任务给指定的类负责,比如Activity启动就分发给ActivityStarter,Service的启动就分发ActiveServices。
// ActiveServices
ComponentName startServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service, String resolvedType,
int callingPid, int callingUid, boolean fgRequired, String callingPackage, final int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
ServiceLookupResult res =
retrieveServiceLocked(service, resolvedType, callingPackage,
callingPid, callingUid, userId, true, callerFg, false, false);
// retrieveServiceLocked()获取或者新建一个ServiceRecord
final boolean bgLaunch = !mAm.isUidActiveLocked(r.appInfo.uid);
// 调用了startServiceInnerLocked
ComponentName cmp = startServiceInnerLocked(smap, service, r, callerFg, addToStarting);
}
ComponentName startServiceInnerLocked(ServiceMap smap, Intent service, ServiceRecord r,
boolean callerFg, boolean addToStarting) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
ServiceState stracker = r.getTracker();
if (stracker != null) {
stracker.setStarted(true, mAm.mProcessStats.getMemFactorLocked(), r.lastActivity);
}
r.callStart = false;
synchronized (r.stats.getBatteryStats()) {
r.stats.startRunningLocked();
}
String error = bringUpServiceLocked(r, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false, false);
return r.name;
}
bringUpServiceLocked()是一个很重要的方法,startService()、bindService()都会走到。
// ActiveServices
private String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg,
boolean whileRestarting, boolean permissionsReviewRequired)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
if (r.app != null && r.app.thread != null) {
// Service在运行
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, false);
return null;
}
ProcessRecord app;// 获取对应的进程ProcessRecord
if (!isolated) {
app = mAm.getProcessRecordLocked(procName, r.appInfo.uid, false);
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
// 将其加入到mPendingServices队列
app.addPackage(r.appInfo.packageName, r.appInfo.longVersionCode, mAm.mProcessStats);
// 真正启动Service
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
}
}
// 如果app进程不存在,则会AMS startProcessLocked()
if (app == null && !permissionsReviewRequired) {
if ((app=mAm.startProcessLocked(procName, r.appInfo, true, intentFlags,
hostingType, r.name, false, isolated, false)) == null) {
bringDownServiceLocked(r);
return msg;
}
if (isolated) {
r.isolatedProc = app;
}
}
}
如果Service目标进程不存在会走AMS startProcessLocked(),跟Activity开启进程一样,Process.start创建一个新的进程,走到ActivityThread的main函数,创建Application等。
// AcitveServices
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);
requestServiceBindingsLocked(r, execInFg);
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, true);
}
app.thread其实就是IApplicationThread,它是一个binder,对应的服务端就是ApplicationThread,它是ActivityThread的内部类,对外提供跟ActivityThread通信的接口。
最后会走到ActivityThread.scheduleCreateService()
requestServiceBindingsLocked()跟bindService()有关,这里先不管
sendServiceArgsLocked()最后会走到onStartCommand()
// ActivityThread
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token,
ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.info = info;
s.compatInfo = compatInfo;
sendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s);
}
sendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s); 就是切换到主线程,因为scheduleCreateService运行在binder线程池中,最后通过H handler处理
// ActivityThread
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
unscheduleGcIdler();
LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);
Service service = null;
try {
// 通过classLoader加载初始化Service
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
service = packageInfo.getAppFactory()
.instantiateService(cl, data.info.name, data.intent);
}
try {
// 创建context
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo);
context.setOuterContext(service);
// 如果Application不存在,会创建Application
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManager.getService());
// 调用service的onCreate()
service.onCreate();
mServices.put(data.token, service);
try {
ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
}
}
handleCreateService()负责实例化service,创建Context、Application等,跟Activity的hanleLaunchActivity()很相似。最后调用Service的onCreate()
再看下onStartCommand()再哪里被调用?
// ActiveService
private final void sendServiceArgsLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean execInFg,
boolean oomAdjusted) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
r.app.thread.scheduleServiceArgs(r, slice);
}
同样利用ApplicationThread到达AcitivityThread所在的进程。
//ActivityThread
public final void scheduleServiceArgs(IBinder token, ParceledListSlice args) {
List list = args.getList();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
ServiceStartArgs ssa = list.get(i);
ServiceArgsData s = new ServiceArgsData();
s.token = token;
s.taskRemoved = ssa.taskRemoved;
s.startId = ssa.startId;
s.flags = ssa.flags;
s.args = ssa.args;
sendMessage(H.SERVICE_ARGS, s);
}
}
private void handleServiceArgs(ServiceArgsData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (s != null) {
try {
...
int res;
if (!data.taskRemoved) {
res = s.onStartCommand(data.args, data.flags, data.startId);
} else {
s.onTaskRemoved(data.args);
res = Service.START_TASK_REMOVED_COMPLETE;
}
}
}
}
最后切换到ActivityThread的主线程,调用onStartCommand()
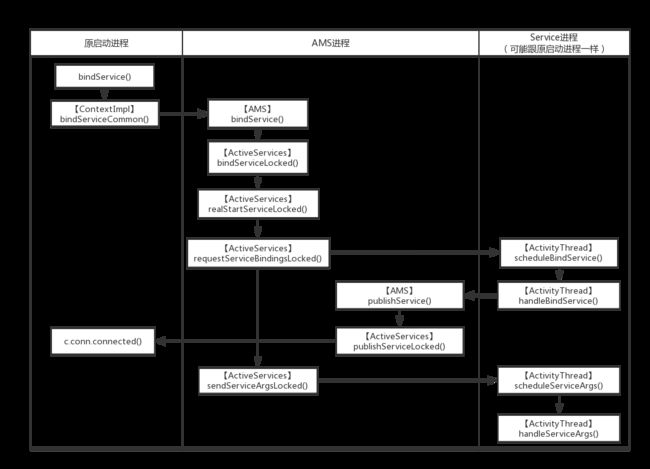
bindService()
Service的bindService()跟startService()的流程很类似,但是他涉及到ServiceConnection的传输,还要通过ServiceConnection返回binder的代理给客户端,通知已经绑定成功
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags) {
return mBase.bindService(service, conn, flags);
}
// ContextImpl
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return bindServiceCommon(service, conn, flags, mMainThread.getHandler(), getUser());
}
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags, Handler
handler, UserHandle user) {
// 转化成IServiceConnection
if (mPackageInfo != null) {
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(), handler, flags);
}
validateServiceIntent(service);
try {
IBinder token = getActivityToken();
...
int res = ActivityManager.getService().bindService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
return res != 0;
}
}
bindServiceCommon有两个主要的任务,
- 生成一个ServiceConnection的binder服务,这样当Service绑定成功后就可以通过binder引用的接口调用ServiceConnection的onServiceConnected()。
- 将ServiceConnection的对应binder的引用传给AMS,并bindService()
其中binder服务就是LoadApk.ServiceDispatcher,所以mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher()负责创建LoadApk.ServiceDispatcher,并提供binder引用。
其实在同一进程内提供的binder实体,跨进程之后会通过binder驱动转化为binder引用,这里通通叫binder,具体可以看Android的binder知识点
// LoadedApk
public final IServiceConnection getServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection c,
Context context, Handler handler, int flags) {
synchronized (mServices) {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = null;
ArrayMap map = mServices.get(context);
if (map != null) {
sd = map.get(c);
}
if (sd == null) {
sd = new ServiceDispatcher(c, context, handler, flags);
if (map == null) {
map = new ArrayMap<>();
mServices.put(context, map);
}
map.put(c, sd);
} else {
sd.validate(context, handler);
}
return sd.getIServiceConnection();
}
}
getServiceDispatcher()先查询是否已经存在已有的ServiceConnection对应的LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher,如果有就直接复用,不需要再建立LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher,增加多一个binder了。否则就创建ServiceDispatcher。
//AMS
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags, String callingPackage,
int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
synchronized(this) {
return mServices.bindServiceLocked(caller, token, service,
resolvedType, connection, flags, callingPackage, userId);
}
}
终于来到了AMS的bindService(),他还是分发给了ActiveServices负责bindServiceLocked()
// ActiveServices
int bindServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, final IServiceConnection connection, int flags,
String callingPackage, final int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
// 获取或创建一个ServiceRecord
ServiceLookupResult res =
retrieveServiceLocked(service, resolvedType, callingPackage, Binder.getCallingPid(),
Binder.getCallingUid(), userId, true, callerFg, isBindExternal, allowInstant);
if ((flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {
s.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
if (bringUpServiceLocked(s, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false,
permissionsReviewRequired) != null) {
return 0;
}
}
}
// ActiveServices
private String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg,
boolean whileRestarting, boolean permissionsReviewRequired)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
if (r.app != null && r.app.thread != null) {
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, false);
return null;
}
app = mAm.getProcessRecordLocked(procName, r.appInfo.uid, false);
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
app.addPackage(r.appInfo.packageName, r.appInfo.longVersionCode, mAm.mProcessStats);
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
return null;
}
}
}
在ActiveServices的部分流程上跟startService()没有什么大的不同,同样走到realStartServiceLocked()
// AcitveServices
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);
requestServiceBindingsLocked(r, execInFg);
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, true);
}
app.thread.scheduleCreateService()负责创建service,不在分析,这里讲上面没说到的requestServiceBindingsLocked()方法,最后怎么调用到了ServiceConnection的onServiceConnected()
// AcitveServices
private final void requestServiceBindingsLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean execInFg)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
for (int i=r.bindings.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
IntentBindRecord ibr = r.bindings.valueAt(i);
if (!requestServiceBindingLocked(r, ibr, execInFg, false)) {
break;
}
}
}
private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord r, IntentBindRecord i,
boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
r.app.thread.scheduleBindService(r, i.intent.getIntent(), rebind,
r.app.repProcState);
}
利用IApplicationThread切换到ActivityThread,最后切换到主线程,调用handleBindService()。这部分基本上是一样的。
// ActivityThread
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (s != null) {
try {
data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
data.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
try {
if (!data.rebind) {
// 调用了onBind(),返回一个IBinder对象
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
ActivityManager.getService().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
s.onRebind(data.intent);
ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
ensureJitEnabled();
}
}
}
}
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
调用了Service的生命周期onBind(),还返回了一个binder(这里应该是binder实体,因为同一个进程内),本来开始以为这里会利用LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher的binder引用调用ServiceConnection的onServiceConnected(),实际上并没有,而是又跨进程调用AMS的pubishService,由AMS回调ServiceConnection的onServiceConnected()
// AMS
public void publishService(IBinder token, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
synchronized(this) {
mServices.publishServiceLocked((ServiceRecord)token, intent, service);
}
}
这里老规矩,AMS分发任务给ActiveServices
// ActiveServices
void publishServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
if (r != null) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter = new Intent.FilterComparison(intent);
IntentBindRecord b = r.bindings.get(filter);
if (b != null && !b.received) {
b.binder = service;
b.requested = true;
b.received = true;
for (int conni=r.connections.size()-1; conni>=0; conni--) {
ArrayList clist = r.connections.valueAt(conni);
for (int i=0; i 这里知道为什么了ActivityThread没有直接跨进程调用ServiceConnection的onServiceConnected(),原来只有AMS保存了LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher的binder引用,最后调用 c.conn.connected(r.name, service, false);
// LoadApk.InnerConnection
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
final WeakReference mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference(sd);
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service, boolean dead)
throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service, dead);
}
}
}
这里可以看出InnerConnection就是一个binder,他的作用就是让其他进程可以跨进程调用到connected()。
最后在 LoadApk.InnerConnection利用ServiceDispatcher 调用了onServiceConnected()方法。
流程图
总结
(没想好,待补上)