什么是IPC机制
IPC为Inter-Process Communication的缩写,含义为进程间的通信或者跨进程通信。
为什么使用IPC机制
- 获取到更多的内存
在Android系统中一个应用默认只有一个进程,每个进程都有自己独立的资源和内存空间,其它进程不能任意访问当前进程的内存和资源,系统给每个进程分配的内存会有限制。如果一个进程占用内存超过了这个内存限制,就会报OOM的问题,很多涉及到大图片的频繁操作或者需要读取一大段数据在内存中使用时,很容易报OOM的问题。
- 实现数据的共享
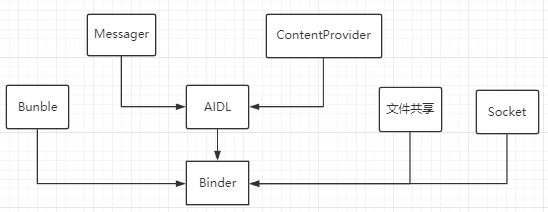
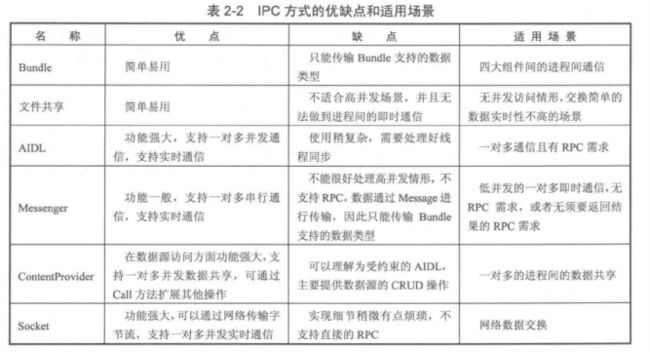
Android中常见的IPC方式
- Bundle:使用Intent传递Bundle数据
- 文件共享:两个进程通过读/写同一个文件来交换数据
- Messager:在不同进程中传递Message对象,将数据存放在Message对象中
- AIDL:一种IDL语言,用于生成Android设备上两个进程之间通信的代码
- ContentProvider:Android中提供的专用于不同应用间进行数据共享的方式
- Socket:通过Socket实现进程之间的通信
如何使用AIDL实现IPC
- 创建AIDL接口:
// IMyAidlInterface.aidl
package com.example.lq.ipcdemo;
interface IMyAidlInterface {
int findFactorialService(int x);
}
- 创建客户端:
private ServiceConnection serviceConnection;
private IMyAidlInterface iMyAidlInterface;
//创建服务连接
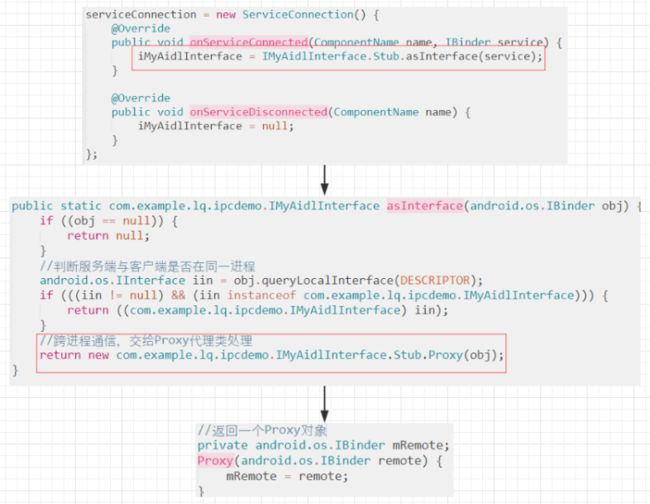
serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
//获取到IMyAidlInterface实例对象
iMyAidlInterface = IMyAidlInterface.Stub.asInterface(service);
//调用iMyAidlInterface中的方法
int result = iMyAidlInterface.findFactorialService(10);
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
iMyAidlInterface = null;
}
};
- 创建服务端:
public class MyService extends Service {
//创建IBinder对象
private IBinder binder = new IMyAidlInterface.Stub(){
@Override
public int findFactorialService(int x) throws RemoteException {
int fact = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= x; i ++){
fact = fact * i;
}
return fact;
}
};
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return binder; //返回IBinder对象
}
}
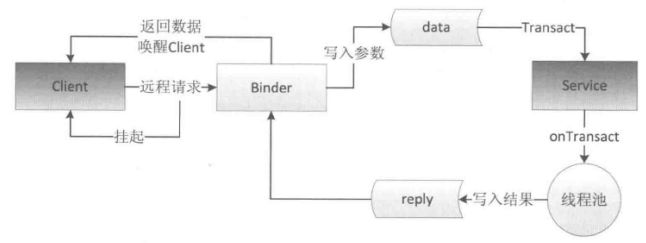
IPC通信方式:Binder机制
简而言之,Binder机制就是Android中的一种跨进程通信方式。
AIDL自动生成的Java文件类
public interface IMyAidlInterface extends android.os.IInterface {
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements com.example.lq.ipcdemo.IMyAidlInterface {
private static final java.lang.String DESCRIPTOR = "com.example.lq.ipcdemo.IMyAidlInterface";
public Stub() {
this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR);
}
public static com.example.lq.ipcdemo.IMyAidlInterface asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj) {
if ((obj == null)) {
return null;
}
//判断服务端与客户端是否在同一进程
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin != null) && (iin instanceof com.example.lq.ipcdemo.IMyAidlInterface))) {
return ((com.example.lq.ipcdemo.IMyAidlInterface) iin);
}
//跨进程通信,交给Proxy代理类处理
return new com.example.lq.ipcdemo.IMyAidlInterface.Stub.Proxy(obj);
}
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder() {
return this;
}
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case INTERFACE_TRANSACTION: {
reply.writeString(DESCRIPTOR);
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_findFactorialService: {
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
int _arg0;
//解析获取参数
_arg0 = data.readInt();
//调用实现方法
int _result = this.findFactorialService(_arg0);
//写入结果到reply中
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeInt(_result);
return true;
}
}
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
}
private static class Proxy implements com.example.lq.ipcdemo.IMyAidlInterface {
//返回一个Proxy对象
private android.os.IBinder mRemote;
Proxy(android.os.IBinder remote) {
mRemote = remote;
}
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder() {
return mRemote;
}
public java.lang.String getInterfaceDescriptor() {
return DESCRIPTOR;
}
@Override
public int findFactorialService(int x) throws android.os.RemoteException {
//获取到Parcel对象
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
int _result;
try {
//将描述符和参数写入_data中
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
_data.writeInt(x);
//调用底层的transact方法将结果写入_reply
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_findFactorialService, _data, _reply, 0);
//解析并返回结果
_reply.readException();
_result = _reply.readInt();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
return _result;
}
}
static final int TRANSACTION_findFactorialService = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 0);
}
public int findFactorialService(int x) throws android.os.RemoteException;
}
实际上,其内部主要含有两个核心内部类Stub和Proxy。若客户端和服务端位于同一进程,则返回服务端的Stub对象本身,否则返回的是系统封装后的Stub.Proxy对象。
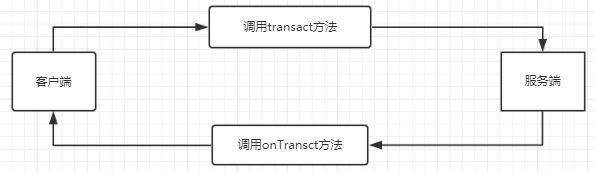
transact:客户端发送跨进程请求,将参数传递进去
onTransact:监听到客户端的请求,服务端会通过系统封装后交由方法处理,传入data参数,获取到reply结果。
transact与onTransact之间的关系:
客户端调用服务端方法流程图:
实现AIDL双向通信:服务端定时向客户端发送消息
- 接口类
interface IServiceCallback {
void notifyClient(String msg);
}
import com.example.lq.ipcdemo.IServiceCallback;
interface IMyAidlInterface {
int findFactorialService(int x);
void registerCallback(IServiceCallback callback);
void unregisterCallback(IServiceCallback callback);
}
- 服务端类
public class MyService extends Service {
//创建RemoteCallbackList列表
private RemoteCallbackList mCallbacks = new RemoteCallbackList<>();
private IBinder binder = new IMyAidlInterface.Stub(){
@Override
public int findFactorialService(int x) throws RemoteException {
int fact = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= x; i ++){
fact = fact * i;
}
return fact;
}
//注册
@Override
public void registerCallback(IServiceCallback callback) throws RemoteException {
mCallbacks.register(callback);
}
//注销
@Override
public void unregisterCallback(IServiceCallback callback) throws RemoteException {
mCallbacks.unregister(callback);
}
};
//通知所有连接服务的客户端
private void notifyMessage(String msg){
final int len = mCallbacks.beginBroadcast();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i ++){
try {
mCallbacks.getBroadcastItem(i).notifyClient(msg);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
mCallbacks.finishBroadcast();
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Timer timer = new Timer();
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
notifyMessage("Hello,Client!");
}
}, 10000, 1000);
}
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return binder;
}
}
- 客户端类
IServiceCallback callback = new IServiceCallback.Stub(){
@Override
public void notifyClient(String msg) throws RemoteException {
showToast(msg);
}
};
serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
iMyAidlInterface = IMyAidlInterface.Stub.asInterface(service);
try {
iMyAidlInterface.registerCallback(callback);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
try {
iMyAidlInterface.unregisterCallback(callback);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
iMyAidlInterface = null;
}
};
ContentProvider的Binder实现
ContentProvider是Android中提供的专门用于不同应用之间进行数据共享的方式,系统预制了许多ContentProvider,比如通信录信息,日程表信息等。
ContentProvider的query操作:
getContentResolver().query(uri, projection, selection, selectionArgs, sortOrder);
对应的transact方法:
public Cursor query(String callingPkg, Uri url, String[] projection, String selection,
String[] selectionArgs, String sortOrder, ICancellationSignal cancellationSignal)
throws RemoteException {
//实例化BulkCursorToCursorAdaptor对象
BulkCursorToCursorAdaptor adaptor = new BulkCursorToCursorAdaptor();
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
try {
data.writeInterfaceToken(IContentProvider.descriptor);
data.writeString(callingPkg);
url.writeToParcel(data, 0);
int length = 0;
if (projection != null) {
length = projection.length;
}
data.writeInt(length);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
data.writeString(projection[i]);
}
data.writeString(selection);
if (selectionArgs != null) {
length = selectionArgs.length;
} else {
length = 0;
}
data.writeInt(length);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
data.writeString(selectionArgs[i]);
}
data.writeString(sortOrder);
data.writeStrongBinder(adaptor.getObserver().asBinder());
data.writeStrongBinder(cancellationSignal != null ? cancellationSignal.asBinder() : null);
//发送给Binder服务端
mRemote.transact(IContentProvider.QUERY_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
DatabaseUtils.readExceptionFromParcel(reply);
if (reply.readInt() != 0) {
BulkCursorDescriptor d = BulkCursorDescriptor.CREATOR.createFromParcel(reply);
adaptor.initialize(d);
} else {
adaptor.close();
adaptor = null;
}
return adaptor;
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
adaptor.close();
throw ex;
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
adaptor.close();
throw ex;
} finally {
data.recycle();
reply.recycle();
}
}
对应的onTranct方法:
public boolean onTransact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags)
throws RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case QUERY_TRANSACTION:{
data.enforceInterface(IContentProvider.descriptor);
String callingPkg = data.readString();
Uri url = Uri.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);
int num = data.readInt();
String[] projection = null;
if (num > 0) {
projection = new String[num];
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
projection[i] = data.readString();
}
}
String selection = data.readString();
num = data.readInt();
String[] selectionArgs = null;
if (num > 0) {
selectionArgs = new String[num];
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
selectionArgs[i] = data.readString();
}
}
String sortOrder = data.readString();
IContentObserver observer = IContentObserver.Stub.asInterface(
data.readStrongBinder());
ICancellationSignal cancellationSignal = ICancellationSignal.Stub.asInterface(
data.readStrongBinder());
//调用服务端实现的query方法
Cursor cursor = query(callingPkg, url, projection, selection, selectionArgs,
sortOrder, cancellationSignal);
if (cursor != null) {
CursorToBulkCursorAdaptor adaptor = null;
try {
//创建CursorToBulkCursorAdaptor对象
adaptor = new CursorToBulkCursorAdaptor(cursor, observer,
getProviderName());
cursor = null;
BulkCursorDescriptor d = adaptor.getBulkCursorDescriptor();
adaptor = null;
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeInt(1);
d.writeToParcel(reply, Parcelable.PARCELABLE_WRITE_RETURN_VALUE);
} finally {
if (adaptor != null) {
adaptor.close();
}
if (cursor != null) {
cursor.close();
}
}
} else {
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeInt(0);
}
return true;
}
...
}
}