DMCplus控制器主要包含两种类型的变量。对一被控过程,自变量是指过程的输入变量,而因变量是过程的输出变量。
过程输入变量是指当其发生变化时,会引起过程发生相应变化的变量。过程输出变量是指当其发生变化时,不会影响过程。
比如说,过程进料速率、再沸器蒸汽流量设定值和环境温度等都是过程输入变量(自变量)。因上述任一变量的变化都会使过程发生改变。过程输入变量既可能是操作员设定,也可能是不断变化的干扰。
塔顶温度、产品杂质在线分析器等则是过程输出变量(因变量)。尽管都可以由操作员所改变,但它们都受到自变量的影响。
自变量进一步分为操作变量(MVs)和干扰变量(DVs)(也被称作前馈(FF)变量)。MVs是DMCplus控制器所操作的自变量。可能包括流量控制器设定点,温度控制器设定点,压力控制器设定点等。
DVs(也被称为前馈(FF)变量)是DMCplus控制器不能操作的但会显著影响过程的自变量。可能包括冷却水温度,进料组成及环境空气温度等。
因变量也被称为控制变量(CVs)。这些变量由DMCplus控制器控制。可能包括产物流质量、温度、压力、压差、阀位或其它过程输出。
尽管CV可以控制在一个固定的设定点,但通常它们被控制在上下限之间。这样DMCplus控制器将有更多空间优化过程。同时还能允许控制器中CVs数量大于MVs。
几乎所有实际过程中,CVs数都超过MVs。然而,其中大部分CVs在任意时刻都是不必受约束的。
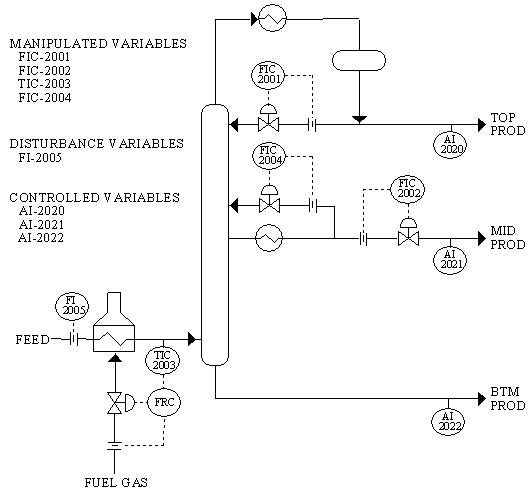
图3:复杂精馏过程
图3给出一个复杂精馏过程例子。这一例子有4个MVs,1个DV和3个CVs,如下所列:
MVs
FIC-2001 塔顶回流量.SP
FIC-2002 塔中产品采出流量.SP
TIC-2003 进料温度.SP
FIC-2004 塔中回流量.SP
DV (FF)
FI-2005 塔进料流量
CVs
AI-2020 塔顶采出产品杂质含量
AI-2021 塔中采出产品杂质含量
AI-2022 塔釜采出产品杂质含量
该系统是一个强耦合系统。改变任何一个MV都会影响到3个CVs。改变DV(进料流率)也会影响3个CVs。所有5个自变量都是过程输入,3个CVs是过程输出。
附原文:
There are two major types ofvariables in a DMCplus controller. Given a process to be controlled, the independent variables are inputs to the process and the dependent variables are those which are outputs from the process.
Process inputs are thosevariables that when changed, cause a corresponding change in the process.Process outputs are those variables that indicate a change in the process, butcannot affect the process.
Examples of process inputs(independent variables) are feed rate to the process, reboiler steam flow setpoint, and ambient temperature. A change in any of these causes the process tochange as well. Process inputs can either be changed by the operator or theymay be disturbances which change continuously.
Examples of process outputs (dependent variables) are a tower toptemperature and a product impurity analyzer. Neither of these can be changeddirectly by the operator, but both are affected by changes in independentvariables.
The independent variables are further classified as eithermanipulated
variables(MVs) ordisturbance variables(DVs), alsocalled Feed forward (FF) variables. Manipulated variables are those independentvariables which are manipulated by the DMCplus controller. These might includeflow controller set points, temperature controller set points, pressurecontroller set points, etc.
The disturbance variables, also known as feedforward variables, areindependent variables that significantly affect the process, but cannot be manipulatedby the DMCplus controller. These might include the cooling water supplytemperature, feed composition, ambient air temperature, etc.
Dependent variables are also known ascontrolled variables(CVs). These are the variables controlled by the DMCplus controller. Thesemight include product stream properties, temperatures, pressures, differentialpressures, valve positions, or other outputs from the process.
While controlled variables may be controlled to a fixed set point,normally they are controlled between upper and lower limits. This allows theDMCplus controller more room to optimize the process. It also allows acontroller to have significantly more controlled variables than it hasmanipulated variables.
In an actual process, it is nearly always the case that the number ofcontrolled variables exceeds the number of manipulated variables. However, atany given time, most of these controlled variables are not constrained.
The figure above shows an example of a process consisting of a ComplexFractionator. This example has four manipulated, one disturbance, and threecontrolled variables, as listed below:
Manipulated Variables
FIC-2001 Top Reflux Flow Controller Set Point
FIC-2002 Middle Product Flow Controller Set Point
TIC-2003 Feed Temperature Controller Set Point
FIC-2004 Middle Reflux Flow Controller Set Point
Disturbance Variables (Feed forward)
FI-2005 Tower Feed Flow
Controlled Variables
AI-2020 Top Product Impurity
AI-2021
Middle Product Impurity
AI-2022 Bottoms Product Impurity
This system is a highly interactive system. Changing any of the four manipulated variables affects all three dependent (controlled) variables.Changes in the disturbance variable (Feed Flow Rate) also affects all three controlled variables. All five independent variables are inputs to the process and all three controlled variables are outputs from the process.
2015.9.9