一、实验环境
| master-masql | 192.168.83.132 |
| slave-mysql | 192.168.83.133 |
| mysql-proxy |
192.168.83.134 |
二、安装mysql
1、安装包所需环境
yum -y groupinstall "Development tools" "Server Platform Development"
yum -y install libxml2-devel ncurses-devel openssl*
2、创建mysql用户
# mkdir -pv /mydata/data
# mkdir -pv /mydata/binlogs (master上创建)
# mkdir -pv /mydata/realylogs (slave上创建)
# groupadd -r mysql
# useradd -g mysql -r -s /sbin/nologin -M -d /mydata/data mysql
# chown -R mysql:mysql /mydata/data
3、安装mysql
# tar xf mysql-5.5.33-linux2.6-i686.tar.gz -C /usr/local
# cd /usr/local/
# ln -sv mysql-5.5.33-linux2.6-i686 mysql
# cd mysql
# chown -R mysql:mysql ./*
# scripts/mysql_install_db --user=mysql --datadir=/mydata/data
# chown -R root ./*
4、为mysql提供主配置文件:
# cd /usr/local/mysql
# cp support-files/my-large.cnf /etc/my.cnf
5、修改配置文件
vim /etc/my.cnf (master服务器)
datadir = /mydata/data ##添加
log-bin=/mydata/binlogs/master-bin ##修改日志路径
vim /etc/my.cnf (slave服务器)
datadir = /mydata/data
relay-log = /mydata/realylogs/relay-log ##开启中继日志
#log-bin=mysql-bin ##禁用二进制日志
#binlog_format=mixed
server-id = 10
6、为mysql提供sysv服务脚本:
# cd /usr/local/mysql
# cp support-files/mysql.server /etc/rc.d/init.d/mysqld
# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/init.d/mysqld
7、添加至服务列表:
# chkconfig --add mysqld
# chkconfig mysqld on
8、输出mysql的库文件给系统库查找路径:
# echo '/usr/local/mysql/lib' > /etc/ld.so.conf.d/mysql.conf
9、修改PATH环境变量,让系统可以直接使用mysql的相关命令。具体实现过程这里不再给出。
vim /etc/profile.d/mysqld.sh
export PATH=/usr/local/mysql/bin:$PATH
]# source /etc/profile.d/mysqld.sh
# ldconfig
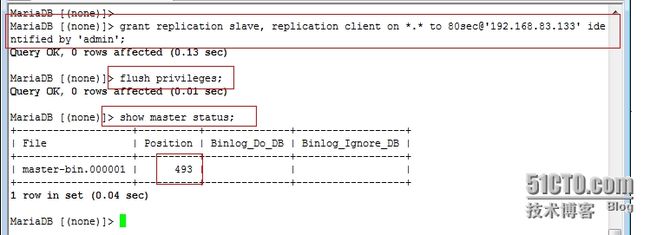
10、在master上创建具有复制权限的slave帐号并查看二进制日志起点
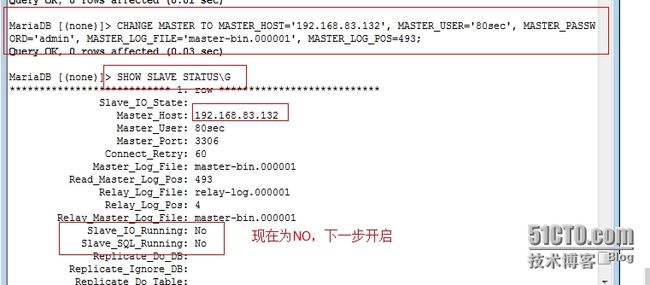
11、配置slave服务器
连接master:
MariaDB [(none)]> HELP CHANGE MASTER TO
Name: 'CHANGE MASTER TO'
Syntax:
CHANGE MASTER TO option [, option] ...
option:
MASTER_BIND = 'interface_name'
| MASTER_HOST = 'host_name' # 指明要连接的主节点,值类型字串
| MASTER_USER = 'user_name' # 具有复制权限的账号,值类型为字串
| MASTER_PASSWORD = 'password' # 上述用户的密码,值类型为字串
| MASTER_PORT = port_num
| MASTER_CONNECT_RETRY = interval
| MASTER_HEARTBEAT_PERIOD = interval
| MASTER_LOG_FILE = 'master_log_name' # 复制起点,主节点上二进制日志,值类型为字串
| MASTER_LOG_POS = master_log_pos # 复制起点,主节点上二进制日志中起始事件的位置,值类型为数值
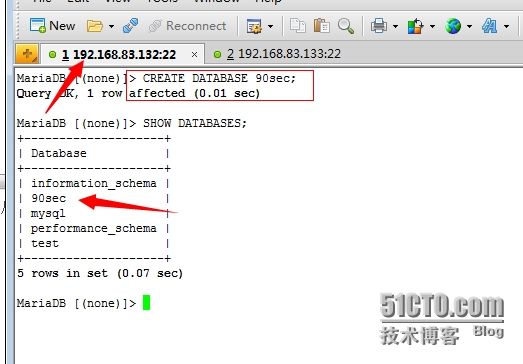
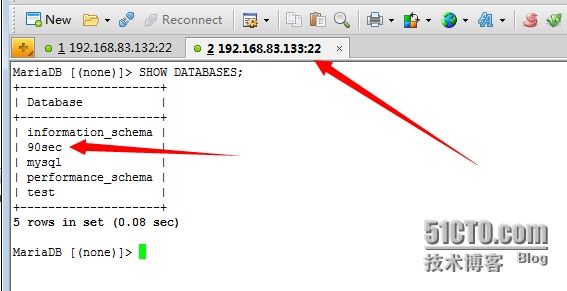
12、测试主从复制是否成功
三、配置读写分离
1、创建用户并安装
[root@70sec /]# yum -y install mysql (只需安装客户端即可,无需启动)
[root@70sec src]# useradd mysql-proxy
[root@70sec src]# tar xf mysql-proxy-0.8.3-linux-glibc2.3-x86-64bit.tar.gz -C /usr/local/
[root@70sec src]# cd /usr/local/
[root@70sec local]# ln -sv mysql-proxy-0.8.3-linux-glibc2.3-x86-64bit/ mysql-proxy
`mysql-proxy' -> `mysql-proxy-0.8.3-linux-glibc2.3-x86-64bit/'
2、为mysql-proxy提供SysV服务脚本,并设置环境变量
[root@70sec local]# vim /etc/rc.d/init.d/mysql-proxy
#!/bin/bash
# mysql-proxy This script starts and stops the mysql-proxy daemon
#
# Source function library.
. /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions
prog="/usr/local/mysql-proxy/bin/mysql-proxy"
# Source networking configuration.
if [ -f /etc/sysconfig/network ]; then
. /etc/sysconfig/network
fi
# Check that networking is up.
[ ${NETWORKING} = "no" ] && exit 0
# Set default mysql-proxy configuration.
ADMIN_USER="admin"
ADMIN_PASSWD="admin"
ADMIN_LUA_SCRIPT="/usr/local/mysql-proxy/share/doc/mysql-proxy/admin.lua"
PROXY_OPTIONS="--daemon"
PROXY_PID=/var/run/mysql-proxy.pid
PROXY_USER="mysql-proxy"
# Source mysql-proxy configuration.
if [ -f /etc/sysconfig/mysql-proxy ]; then
. /etc/sysconfig/mysql-proxy
fi
RETVAL=0
start() {
echo -n $"Starting $prog: "
RETVAL=$?
echo
if [ $RETVAL -eq 0 ]; then
touch /var/lock/subsys/mysql-proxy
fi
}
stop() {
echo -n $"Stopping $prog: "
killproc -p $PROXY_PID -d 3 $prog
RETVAL=$?
echo
if [ $RETVAL -eq 0 ]; then
rm -f /var/lock/subsys/mysql-proxy
rm -f $PROXY_PID
fi
}
# See how we were called.
case "$1" in
start)
start
;;
stop)
stop
;;
restart)
stop
start
;;
condrestart|try-restart)
if status -p $PROXY_PIDFILE $prog >&/dev/null; then
stop
start
fi
;;
status)
status -p $PROXY_PID $prog
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart|reload|status|condrestart|try-restart}"
RETVAL=1
;;
esac
exit $RETVAL
[root@70sec local]# chkconfig --add mysql-proxy
[root@70sec local]# chkconfig mysql-proxy on
3、为服务脚本提供配置文件/etc/sysconfig/mysql-proxy
[root@70sec mysql-proxy]# vim share/doc/mysql-proxy/admin.lua
# Options for mysql-proxy
ADMIN_USER="admin"
ADMIN_PASSWORD="admin"
ADMIN_ADDRESS=""
ADMIN_LUA_SCRIPT="/usr/local/mysql-proxy/share/doc/mysql-proxy/admin.lua"
PROXY_ADDRESS=""
PROXY_USER="mysql-proxy"
PROXY_OPTIONS="--daemon --log-level=info --log-use-syslog --plugins=proxy --plugins=admin --proxy-backend-addresses=192.168.83.132:3306 --proxy-read-only-backend-addresses=192.168.83.133:3306 --proxy-lua-script=/usr/local/mysql-proxy/share/doc/mysql-proxy/rw-splitting.lua"
4、创建admin管理脚本
[root@70sec local]# vim share/doc/mysql-proxy/admin.lua
--[[ $%BEGINLICENSE%$
Copyright (c) 2007, 2012, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as
published by the Free Software Foundation; version 2 of the
License.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software
Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA
02110-1301 USA
$%ENDLICENSE%$ --]]
function set_error(errmsg)
proxy.response = {
type = proxy.MYSQLD_PACKET_ERR,
errmsg = errmsg or "error"
}
end
function read_query(packet)
if packet:byte() ~= proxy.COM_QUERY then
set_error("[admin] we only handle text-based queries (COM_QUERY)")
return proxy.PROXY_SEND_RESULT
end
local query = packet:sub(2)
local rows = { }
local fields = { }
if query:lower() == "select * from backends" then
fields = {
{ name = "backend_ndx",
type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_LONG },
{ name = "address",
type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_STRING },
{ name = "state",
type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_STRING },
{ name = "type",
type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_STRING },
{ name = "uuid",
type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_STRING },
{ name = "connected_clients",
type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_LONG },
}
for i = 1, #proxy.global.backends do
local states = {
"unknown",
"up",
"down"
}
local types = {
"unknown",
"rw",
"ro"
}
local b = proxy.global.backends[i]
rows[#rows + 1] = {
i,
b.dst.name, -- configured backend address
states[b.state + 1], -- the C-id is pushed down starting at 0
types[b.type + 1], -- the C-id is pushed down starting at 0
b.uuid, -- the MySQL Server's UUID if it is managed
b.connected_clients -- currently connected clients
}
end
elseif query:lower() == "select * from help" then
fields = {
{ name = "command",
type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_STRING },
{ name = "description",
type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_STRING },
}
rows[#rows + 1] = { "SELECT * FROM help", "shows this help" }
rows[#rows + 1] = { "SELECT * FROM backends", "lists the backends and their state" }
else
set_error("use 'SELECT * FROM help' to see the supported commands")
return proxy.PROXY_SEND_RESULT
end
proxy.response = {
type = proxy.MYSQLD_PACKET_OK,
resultset = {
fields = fields,
rows = rows
}
}
return proxy.PROXY_SEND_RESULT
end
5、启动服务并查看
[root@70sec mysql-proxy]# service mysql-proxy start
Starting /usr/local/mysql-proxy/bin/mysql-proxy: [ OK ]
[root@70sec mysql-proxy]# ss -anlpt
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port :::*
LISTEN 0 128 *:4041 *:* users:(("mysql-proxy",27609,11))
LISTEN 0 128 *:3306 *:* users:(("mysql-proxy",27609,10))
6、管理功能测试
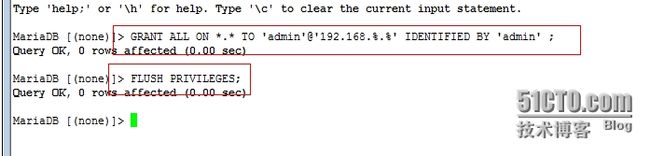
7、在master上创建远程帐号
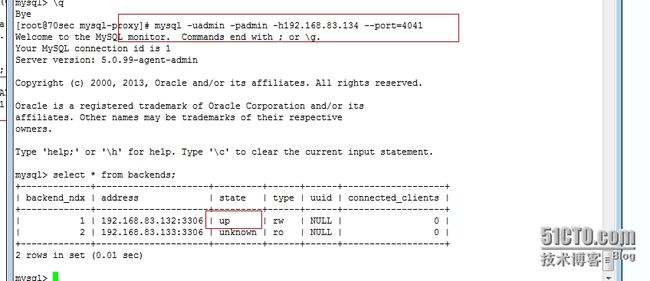
8、在mysql-proxy上测试
9、查看被谁写入
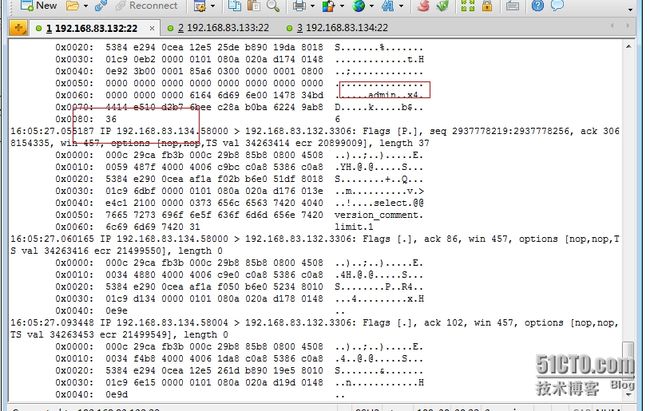
10、也可以通过抓包测试
[root@90sec mydata]# tcpdump -i eth0 -nn -XX dst host 192.168.83.132 and tcp dst port 3306
[root@90sec mydata]# tcpdump -i eth0 -nn -XX dst host 192.168.83.133 and tcp dst port 3306
mysql-proxy的配置选项大致可分为帮助选项、管理选项、代理选项及应用程序选项几类,下面一起去介绍它们。
--help
--help-admin
--help-proxy
--help-all ———— 以上四个选项均用于获取帮助信息;
--proxy-address=host:port ———— 代理服务监听的地址和端口;
--admin-address=host:port ———— 管理模块监听的地址和端口;
--proxy-backend-addresses=host:port ———— 后端mysql服务器的地址和端口;
--proxy-read-only-backend-addresses=host:port ———— 后端只读mysql服务器的地址和端口;
--proxy-lua-script=file_name ———— 完成mysql代理功能的Lua脚本;
--daemon ———— 以守护进程模式启动mysql-proxy;
--keepalive ———— 在mysql-proxy崩溃时尝试重启之;
--log-file=/path/to/log_file_name ———— 日志文件名称;
--log-level=level ———— 日志级别;
--log-use-syslog ———— 基于syslog记录日志;
--plugins=plugin,.. ———— 在mysql-proxy启动时加载的插件;
--user=user_name ———— 运行mysql-proxy进程的用户;
--defaults-file=/path/to/conf_file_name ———— 默认使用的配置文件路径;其配置段使用[mysql-proxy]标识;
--proxy-skip-profiling ———— 禁用profile;
--pid-file=/path/to/pid_file_name ———— 进程文件名;