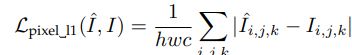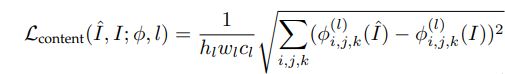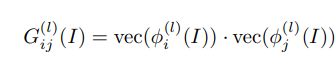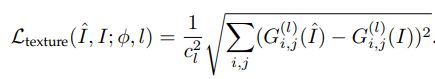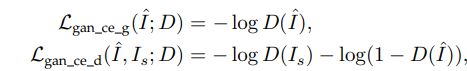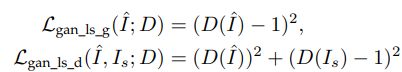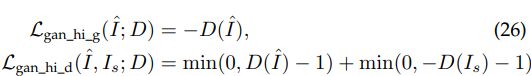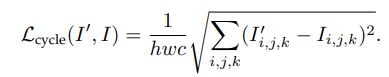原论文:Deep Learning for Image Super-resolution: A Survey
1.Pixel Loss:用来度量生成图片和目标图片的像素级的差异
1.1 L1 loss
1.2 L2 loss
1.3 Charbonnier loss:L1 Loss的变体,最后参数是一个很小常量(e.g., 1e − 3),为了使数值稳定
像素损失是最常见的损失,通常L2损失能够对大的损失进行惩罚,但是在小的损失上无能为力,效果不如L1,像素损失实际上并没有考虑到图像质量(如感知质量,纹理),经常缺乏高频细节,并且产生的纹理过于平滑,难以令人满意
2.Content Loss:如果一个网络,生成的图像足够逼真,那么生成图片的特征(度量特征提取网络中提取的)也应该跟真实图片的足够像,因此通过使特征足够相似,对生成图片质量也有促进作用
l是网络第l层,常用的度量特征提取网络有vgg,resnet。
3.Texture Loss:由于重建后的图像应该与目标图像具有相同的样式(例如,颜色、纹理、对比度),将图像的纹理视为不同特征通道之间的相关性(用矩阵点乘来表示相关性)
最终损失函数是要求相关性相同:
好用是好用,但是需要通过经验(调参)来确定patch的大小,patch太小会造成纹理部分 artefacts(重影),太大会造成整个图片重影。(因为纹理统计是对不同纹理区域求平均值)
4.Adversarial Loss:这就不用多说了,不服就GAN嘛
4.1 loss based on cross entropy
4.2 loss based on least square error
4.3 hinge-format adversarial loss
像素级的判别器会使生成器产生高频噪音,但是特征级的判别器可以很好的捕捉高清图片的潜在属性
其中比较重要的工作有:
“Learning to super-resolve blurry face and text images”合并一个多类GAN,包括单个生成器和特定于类的鉴别器
ESRGAN[101]利用 relativistic GAN[131]来预测真实图像比假图像相对真实的概率,而不是预测输入图像真实或生成的概率。
虽然经过GAN处理后的图片PSNR会低一点(相比pixel loss)但是在感知质量上带来了显著的提高。鉴别器提取了真实图像中一些难以获得的潜在特征,并推动生成的HR图像符合这些模式,从而有助于生成更真实的HR图像
GAN相比其他模型,训练上会比较困难,仍是目前未解决的一个问题
5.Cycle Consistency Loss:
受CycleGAN启发,将HR图像通过另一个CNN网络缩小成I‘,然后跟要处理的小图片做相似性度量
6.Total Variation Loss:
两点作用:1.抑制噪音(主要是噪点),2.提升图像的空间平滑性
7.Prior-Based Loss:基于先验的损失
Super-fan: Integrated facial landmark localization and super-resolution of real-world low resolution faces in arbitrary poses with gans
聚焦于人脸图像的SR,并引入了人脸比对网络(FAN)来约束从原始和生成的图像中检测到的人脸地标的一致性
实践中经常是多个损失函数组合使用,但是权重调节是一个大问题,对结果有决定性的影响,需要各位炼丹师自己去摸索了
2019年11月21日更新
图片超分的方法对视频超分不是很合适,因此又推出了新的度量标准
Video Multimethod Assessment Fusion (VMAF)
https://medium.com/netflix-techblog/toward-a-practical-perceptual-video-quality-metric-653f208b9652
The current version of the VMAF algorithm and model (denoted as VMAF 0.3.1), released as part of the VMAF Development Kit open source software, uses the following elementary metrics fused by Support Vector Machine (SVM) regression [8]:
- Visual Information Fidelity (VIF) [9]. VIF is a well-adopted image quality metric based on the premise that quality is complementary to the measure of information fidelity loss. In its original form, the VIF score is measured as a loss of fidelity combining four scales. In VMAF, we adopt a modified version of VIF where the loss of fidelity in each scale is included as an elementary metric.
- Detail Loss Metric (DLM) [10]. DLM is an image quality metric based on the rationale of separately measuring the loss of details which affects the content visibility, and the redundant impairment which distracts viewer attention. The original metric combines both DLM and additive impairment measure (AIM) to yield a final score. In VMAF, we only adopt the DLM as an elementary metric. Particular care was taken for special cases, such as black frames, where numerical calculations for the original formulation break down.
VIF and DLM are both image quality metrics. We further introduce the following simple feature to account for the temporal characteristics of video:
- Motion. This is a simple measure of the temporal difference between adjacent frames. This is accomplished by calculating the average absolute pixel difference for the luminance component.
9.H. Sheikh and A. Bovik, “Image Information and Visual Quality,” IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 430–444, Feb. 2006.
10.S. Li, F. Zhang, L. Ma, and K. Ngan, “Image Quality Assessment by Separately Evaluating Detail Losses and Additive Impairments,” IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, vol. 13, no. 5, pp. 935–949, Oct. 2011