一、本课目标(全是重点)
- 掌握使用insert完成增加操作
- 掌握使用update完成修改操作
- 掌握使用@param注解实现多参数入参
- 掌握使用delete完成删除操作
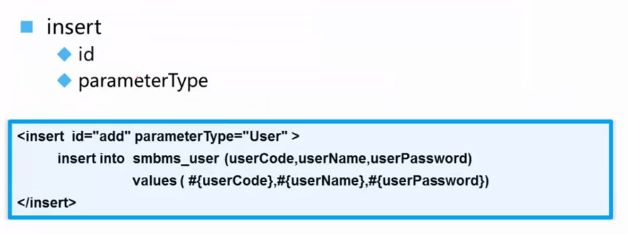
二、insert
完成增加操作需要使用insert元素映射插入语句。insert元素有两个属性:id和parameterType。id和select元素中的id作用是一样的,是作为命名空间中的唯一标识。parameter其实跟select元素里面的parameterType也是一样的,都是参数的数据类型,这里因为插入肯定是有参数传入的,所以这类也有parameteType。
UserMapper.xml配置文件:
insert into smbms_user (userCode,userName,userPassword,
gender,birthday,phone,address,userRole,
createdBy,creationDate) values (
#{userCode},#{userName},#{userPassword},
#{gender},#{birthday},#{phone},
#{address},#{userRole},#{createdBy},
#{creationDate})
接口代码:
public int add(User user);
单元测试代码:
@Test
public void testAdd() {
logger.debug("testAdd-------------------");
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
int count = 0;
sqlSession = MyBatisUtil.createSqlSession();
User user = new User();
try {
user.setUserCode("001");
user.setUserName("测试用户001");
user.setAddress("测试地址");
user.setBirthday(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd").parse("2018-8-25"));
user.setGender(1);
user.setUserPassword("123456");
user.setPhone("13526543651");
user.setUserRole(1);
user.setCreatedBy(1);
user.setCreationDate(new Date());
count = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class).add(user);
sqlSession.commit();
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
MyBatisUtil.closeSqlSession(sqlSession);
}
logger.debug(count);
}
最终运行结果正常。
注:insert、update、delete元素均没有resultType属性。因为这三个最后的返回结果都是影响的行数,所以也不需要resulttype这个属性。
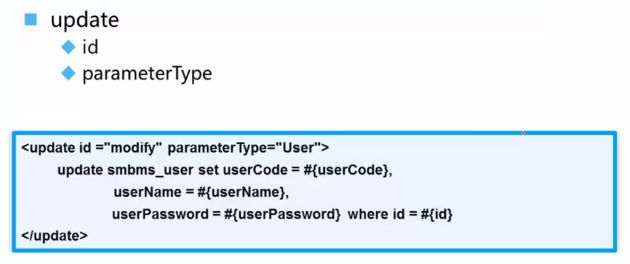
三、update
配置文件;
update smbms_user set userCode=#{userCode},
userName=#{userName},userPassword=#{userPassword},
gender=#{gender},phone=#{phone},address=#{address},
userRole=#{userRole},modifyBy=#{modifyBy},
modifyDate=#{modifyDate} where id=#{id}
接口方法:
public int modify(User user);
测试代码:
@Test
public void testModify() {
logger.debug("testAdd-------------------");
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
int count = 0;
sqlSession = MyBatisUtil.createSqlSession();
User user = new User();
try {
user.setId(16);
user.setUserCode("001_M");
user.setUserName("测试用户001_M");
user.setAddress("测试地址_M");
user.setBirthday(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd").parse("2018-8-25"));
user.setGender(1);
user.setUserPassword("123456");
user.setPhone("13526543651");
user.setUserRole(1);
user.setModifyBy(1);
user.setModifyDate(new Date());
count = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class).modify(user);
sqlSession.commit();
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
MyBatisUtil.closeSqlSession(sqlSession);
}
logger.debug(count);
}
测试结果正常。
注:刚开始没有写
sqlSession.commit();
的时候,进行测试时,在控制台能输出结果,但是数据库中的数据并不会发生改变。
mybatis单独使用时,使用SqlSession来处理事务,打开会话,事务处理开始,增删改操作时要执行commit操作,事物提交后,关闭会话,事物结束。
四、多参数入参
需求说明:实现超市订单管理系统—修改个人密码功能
分析:
- 传入参数(多个):用户id和新密码
- 使用注解@param来传入多个参数
- 映射SQL中的参数:#{注解名称}
配置文件:
update smbms_user set userPassword=#{pwd}
where id=#{id}
接口代码:
public int updatePwd(@Param("id")Integer id, @Param("pwd")String password);
测试代码:
@Test
public void testUpdatePwd() {
logger.debug("testAdd-------------------");
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
int count = 0;
sqlSession = MyBatisUtil.createSqlSession();
try {
count = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class).updatePwd(16, "41312019");
sqlSession.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
MyBatisUtil.closeSqlSession(sqlSession);
}
logger.debug(count);
}
测试结果正常。
注:超过4个以上的参数最好封装成对象入参,参数固定的业务方法最好直接使用多参数入参。
五、delete
配置文件;
delete from smbms_user where id=#{id}
接口代码:
public int deleteUserById(@Param("id")Integer id);
测试代码:
@Test
public void testDeleteUserById() {
logger.debug("testAdd-------------------");
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
int count = 0;
sqlSession = MyBatisUtil.createSqlSession();
try {
count = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class).deleteUserById(16);
sqlSession.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
MyBatisUtil.closeSqlSession(sqlSession);
}
logger.debug(count);
}
测试结果正常。
注:基于良好的编程习惯,只要是没有封装直接传入参数就都使用注解。