本次系列的内容如下:
Android启动流程——1 序言、bootloader引导与Linux启动
Android系统启动——2 init进程
Android系统启动——3 init.rc解析
Android系统启动——4 zyogte进程
Android系统启动——5 zyogte进程(Java篇)
Android系统启动——6 SystemServer启动
Android系统启动——7 附录1:Android属性系统
Android系统启动——8 附录2:相关守护进程简介
本篇文章的主要内容如下:
- 1、SystemServer的启动
- 2、初始化系统上下文——createSystemContext()方法解析
- 3、创建SystemServiceManager
- 4、启动各种服务
SystemServer是Android系统的核心之一,大部分Android提供的服务都运行在这个进程里,SystemServer中运行的服务总共有60多种。为了防止应用进程对系统造成破坏,Android的应用进程没有权限直接访问设备的底层资源,只能通过SystemService中的代理访问。通过Binder,用户进程在使用SystemService中的服务并没有太多不便变之处。
一、SystemServer的启动
前面的文章讲解到ZygoteInit中handleSystemServerProcess函数的最后一步,会调用SystemServer的静态函数main方法,那我们就来看下SystemServer的main函数的具体执行。
代码在SystemServer.java
164 /**
165 * The main entry point from zygote.
166 */
167 public static void main(String[] args) {
168 new SystemServer().run();
169 }
代码很简单,主要就是先new一个SystemServer对象,然后调用run方法
那我们先来下SystemServer的无参构造函数
(一)SystemServer的无参构造函数
代码在SystemServer.java
171 public SystemServer() {
172 // Check for factory test mode.
173 mFactoryTestMode = FactoryTest.getMode();
174 }
我们看到SystemServer的无参构造函数什么也没做,就是调用FactoryTest的静态方法getMode()来获取相应的工厂测试模式。
(二)SystemServer的run方法实现
代码在SystemServer.java
176 private void run() {
177 // If a device's clock is before 1970 (before 0), a lot of
178 // APIs crash dealing with negative numbers, notably
179 // java.io.File#setLastModified, so instead we fake it and
180 // hope that time from cell towers or NTP fixes it shortly.
// 计算时间 如果当前系统时间比1970年更早,就设置当前系统时间为1970年
181 if (System.currentTimeMillis() < EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME) {
182 Slog.w(TAG, "System clock is before 1970; setting to 1970.");
183 SystemClock.setCurrentTimeMillis(EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME);
184 }
185
186 // If the system has "persist.sys.language" and friends set, replace them with
187 // "persist.sys.locale". Note that the default locale at this point is calculated
188 // using the "-Duser.locale" command line flag. That flag is usually populated by
189 // AndroidRuntime using the same set of system properties, but only the system_server
190 // and system apps are allowed to set them.
191 //
192 // NOTE: Most changes made here will need an equivalent change to
193 // core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
// 如果没有设置 语言,则设置当地的语言
194 if (!SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.language").isEmpty()) {
195 final String languageTag = Locale.getDefault().toLanguageTag();
196
197 SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.locale", languageTag);
198 SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.language", "");
199 SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.country", "");
200 SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.localevar", "");
201 }
202
203 // Here we go!
204 Slog.i(TAG, "Entered the Android system server!");
205 EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_SYSTEM_RUN, SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
206
207 // In case the runtime switched since last boot (such as when
208 // the old runtime was removed in an OTA), set the system
209 // property so that it is in sync. We can't do this in
210 // libnativehelper's JniInvocation::Init code where we already
211 // had to fallback to a different runtime because it is
212 // running as root and we need to be the system user to set
213 // the property. http://b/11463182
// 设置虚拟机库文件路径,5.0以后是libart.so
214 SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.dalvik.vm.lib.2", VMRuntime.getRuntime().vmLibrary());
215
216 // Enable the sampling profiler.
// 如果开启了性能分析标志,则开启性能分析
217 if (SamplingProfilerIntegration.isEnabled()) {
218 SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
219 mProfilerSnapshotTimer = new Timer();
220 mProfilerSnapshotTimer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
221 @Override
222 public void run() {
223 SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeSnapshot("system_server", null);
224 }
225 }, SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL, SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL);
226 }
227
228 // Mmmmmm... more memory!
// 清楚VM内存增长上线,由于启动过程需要较多的虚拟机内存空间
229 VMRuntime.getRuntime().clearGrowthLimit();
230
231 // The system server has to run all of the time, so it needs to be
232 // as efficient as possible with its memory usage.
// 设置内存可能有效使用率为0.8
233 VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.8f);
234
235 // Some devices rely on runtime fingerprint generation, so make sure
236 // we've defined it before booting further.
// 针对部分设备依赖运行时就产生指纹信息,因此需要在开机完成前已经定义
237 Build.ensureFingerprintProperty();
238
239 // Within the system server, it is an error to access Environment paths without
240 // explicitly specifying a user.
// 设置访问环境变量的条件,即需要明确指定用户
241 Environment.setUserRequired(true);
242
243 // Ensure binder calls into the system always run at foreground priority.
//确保当前系统进程的binder调用,总是运行在前台优先级(foreground)
244 BinderInternal.disableBackgroundScheduling(true);
245
246 // Prepare the main looper thread (this thread).
247 android.os.Process.setThreadPriority(
248 android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND);
249 android.os.Process.setCanSelfBackground(false);
// 主线程Looper就在当前线程运行
250 Looper.prepareMainLooper();
251
// 加载“android_servers.so”库,该库包含源码在frameworks/base/services/目录下
252 // Initialize native services.
253 System.loadLibrary("android_servers");
254
255 // Check whether we failed to shut down last time we tried.
256 // This call may not return.
//检查上次关键是否失败了,可能没有返回值
257 performPendingShutdown();
258
259 // Initialize the system context.
// 初始化系统上下文
260 createSystemContext();
261
262 // Create the system service manager.
// 创建SystemServiceManager 用于后面的binder机制
263 mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext);
264 LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);
265
266 // Start services.
//启动各种系统服务
267 try {
268 startBootstrapServices();
269 startCoreServices();
270 startOtherServices();
271 } catch (Throwable ex) {
272 Slog.e("System", "******************************************");
273 Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting system services", ex);
274 throw ex;
275 }
276
277 // For debug builds, log event loop stalls to dropbox for analysis.
// 如果是debug版本,为了方便分析,将log事件不断循环地输出到dropbox
278 if (StrictMode.conditionallyEnableDebugLogging()) {
279 Slog.i(TAG, "Enabled StrictMode for system server main thread.");
280 }
281
282 // Loop forever.
// 主进程的looper开启死循环
283 Looper.loop();
284 throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
285 }
main()方法的主要工作如下:
- 1、调整时间,如果系统时间比1970还早,调整到1970
- 2、如果没有设置语言,则设置相应的语言
- 3、设置属性persist.sys.dalvik.vm.lib.2的值为当前虚拟机运行库路径
- 4、是否开启性能分析
- 5、调整虚拟机堆的内存。设定虚拟机堆使用率为0.8,当实际的使用率偏离设定的比率时,虚拟机在垃圾回收的时候将调整堆的大小,使实际使用率接近设定的百分比
- 6、装载库libandroid_servers.so。
- 7、创建SystemServiceManager的对象mSystemServiceManager。这个对象负责系统Service的启动
- 8、调用startBootstrapServices()、startCoreServices()和 startOtherServices()创建并运行所有Java服务
- 9、调用Loop.loop(),进入处理消息的循环
这里面的重点是
- 调用createSystemContext()来创建系统上下文
- 创建SystemServiceManager
- 启动各种服务
那我们就来挨个介绍下
二、初始化系统上下文——createSystemContext()方法解析
代码在SystemServer.java
09 private void createSystemContext() {
// 获取ActivityThread对象
310 ActivityThread activityThread = ActivityThread.systemMain();
// 获取系统的Context
311 mSystemContext = activityThread.getSystemContext();
// 设置主题
312 mSystemContext.setTheme(android.R.style.Theme_DeviceDefault_Light_DarkActionBar);
313 }
代码很简单,就是调用ActivityThread的静态方法systemMain()来获取activityThread对象,然后activityThread的getSystemContext()方法来获取系统上下文,最后设置主题。
未来大家更好的理解,我们先讲解getSystemContext()
(一)、获取系统Context,即getSystemContext()
代码在ActivityThread.java中
1886 public ContextImpl getSystemContext() {
1887 synchronized (this) {
1888 if (mSystemContext == null) {
1889 mSystemContext = ContextImpl.createSystemContext(this);
1890 }
1891 return mSystemContext;
1892 }
1893 }
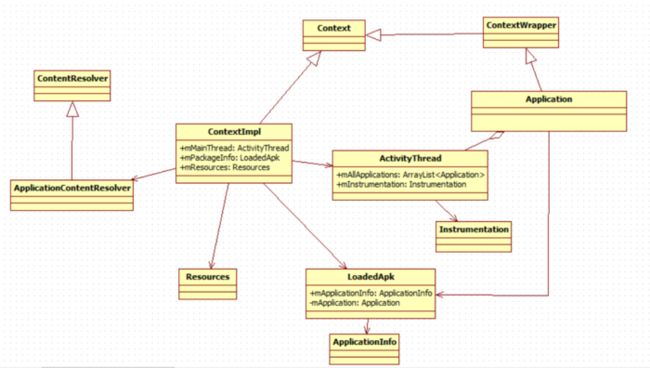
我们看到在ActivityThread存在了一个mSystemContext,如果是第一次,则调用ContextImpl.createSystemContext(this)来创建mSystemContext,那我们来看下ContextImpl里面的createSystemContext(ActivityThread)是怎么实现的
代码在ContextImpl.java
1774 static ContextImpl createSystemContext(ActivityThread mainThread) {
1775 LoadedApk packageInfo = new LoadedApk(mainThread);
1776 ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl(null, mainThread,
1777 packageInfo, null, null, false, null, null, Display.INVALID_DISPLAY);
1778 context.mResources.updateConfiguration(context.mResourcesManager.getConfiguration(),
1779 context.mResourcesManager.getDisplayMetricsLocked());
1780 return context;
1781 }
我们看到createSystemContext()方法中创建了LoadApk对象,参数是ActivityThread。然后直接new了ContextImpl对象。最后返回了该ContextImpl对象
然我们来看下LoadApk对象的实例化过程
1、LoadApk对象的实例化
LoadedApk有两个构造函数,一个是多参数的,用来给新应用;还有一个是单个参数,即给系统进程调用的。我们这个就是单参数的
178 /**
179 * Create information about the system package.
180 * Must call {@link #installSystemApplicationInfo} later.
181 */
182 LoadedApk(ActivityThread activityThread) {
183 mActivityThread = activityThread;
184 mApplicationInfo = new ApplicationInfo();
// packageName为"android",这个APK为framework-res.apk
185 mApplicationInfo.packageName = "android";
186 mPackageName = "android";
187 mAppDir = null;
188 mResDir = null;
189 mSplitAppDirs = null;
190 mSplitResDirs = null;
191 mOverlayDirs = null;
192 mSharedLibraries = null;
193 mDataDir = null;
194 mDataDirFile = null;
195 mLibDir = null;
196 mBaseClassLoader = null;
197 mSecurityViolation = false;
198 mIncludeCode = true;
199 mRegisterPackage = false;
200 mClassLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
201 mResources = Resources.getSystem();
202 }
LoadApk对象用来保存一个apk信息,这个构造方法中会将使用的包名指定为"android"。
而framework-res.apk的包名为"android"。因此,getSystemServer()方法返回mSystemContext对象所对应的apk文件即是framework-res.apk
那我们再来看下ContextImpl对象的创建
2、ContextImpl对象的实例化
1796 private ContextImpl(ContextImpl container, ActivityThread mainThread,
1797 LoadedApk packageInfo, IBinder activityToken, UserHandle user, boolean restricted,
1798 Display display, Configuration overrideConfiguration, int createDisplayWithId) {
// ContextImpl 对象
1799 mOuterContext = this;
1800
// ActivityThread赋值
1801 mMainThread = mainThread;
1802 mActivityToken = activityToken;
1803 mRestricted = restricted;
1804
1805 if (user == null) {
1806 user = Process.myUserHandle();
1807 }
1808 mUser = user;
1809
// LoadedApk赋值
1810 mPackageInfo = packageInfo;
// 单利模式获取ResourcesManager对象
1811 mResourcesManager = ResourcesManager.getInstance();
1812
1813 final int displayId = (createDisplayWithId != Display.INVALID_DISPLAY)
1814 ? createDisplayWithId
1815 : (display != null) ? display.getDisplayId() : Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY;
1816
1817 CompatibilityInfo compatInfo = null;
1818 if (container != null) {
1819 compatInfo = container.getDisplayAdjustments(displayId).getCompatibilityInfo();
1820 }
1821 if (compatInfo == null) {
1822 compatInfo = (displayId == Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY)
1823 ? packageInfo.getCompatibilityInfo()
1824 : CompatibilityInfo.DEFAULT_COMPATIBILITY_INFO;
1825 }
1826 mDisplayAdjustments.setCompatibilityInfo(compatInfo);
1827 mDisplayAdjustments.setConfiguration(overrideConfiguration);
1828
1829 mDisplay = (createDisplayWithId == Display.INVALID_DISPLAY) ? display
1830 : ResourcesManager.getInstance().getAdjustedDisplay(displayId, mDisplayAdjustments);
1831
// 从LoadApk中创建Resource实例
// 由于packageInfo对于一个APP来说,只有一个,所以说resources只有一个
1832 Resources resources = packageInfo.getResources(mainThread);
1833 if (resources != null) {
1834 if (displayId != Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY
1835 || overrideConfiguration != null
1836 || (compatInfo != null && compatInfo.applicationScale
1837 != resources.getCompatibilityInfo().applicationScale)) {
// 由于mResourcesManager是单例,所以resources是同一份
1838 resources = mResourcesManager.getTopLevelResources(packageInfo.getResDir(),
1839 packageInfo.getSplitResDirs(), packageInfo.getOverlayDirs(),
1840 packageInfo.getApplicationInfo().sharedLibraryFiles, displayId,
1841 overrideConfiguration, compatInfo);
1842 }
1843 }
// resources赋值
1844 mResources = resources;
1845
1846 if (container != null) {
1847 mBasePackageName = container.mBasePackageName;
1848 mOpPackageName = container.mOpPackageName;
1849 } else {
1850 mBasePackageName = packageInfo.mPackageName;
1851 ApplicationInfo ainfo = packageInfo.getApplicationInfo();
1852 if (ainfo.uid == Process.SYSTEM_UID && ainfo.uid != Process.myUid()) {
1853 // Special case: system components allow themselves to be loaded in to other
1854 // processes. For purposes of app ops, we must then consider the context as
1855 // belonging to the package of this process, not the system itself, otherwise
1856 // the package+uid verifications in app ops will fail.
1857 mOpPackageName = ActivityThread.currentPackageName();
1858 } else {
1859 mOpPackageName = mBasePackageName;
1860 }
1861 }
1862
1863 mContentResolver = new ApplicationContentResolver(this, mainThread, user);
1864 }
通过上面代码,我们知道在ContextImpl的构造方法中会初始化该进程的各个字段,例如资源、包信息、屏幕配置等。
关于一些类的关系,如下图:
至此getSystemContext()方法分析完毕,我们知道首次执行getSystemContext,会创建LoadedApk和contextImpl对象,接下来利用刚创建的LoadedApk对象来创建新的ContextImpl对象。
(二)、创建activityThread对象——ActivityThread.systemMain()方法研究
代码在ActivityThread.java
5318 public static ActivityThread systemMain() {
5319 // The system process on low-memory devices do not get to use hardware
5320 // accelerated drawing, since this can add too much overhead to the
5321 // process.
5322 if (!ActivityManager.isHighEndGfx()) {
// 关闭硬件渲染
5323 HardwareRenderer.disable(true);
5324 } else {
5325 HardwareRenderer.enableForegroundTrimming();
5326 }
// 创建ActivityThread对象
5327 ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
// 调用attach(true)来初始化
5328 thread.attach(true);
5329 return thread;
5330 }
我们看到systemMain方法中,创建了了一个ActivityThread对象。然后调用attach(boolean)方法来进行初始化,ActivityThread是一个Application的主线程类,(记住,它不是Thread,因为它既没有继承Thread,也没有实现Runnable)。
PS:由于SystemServer不是一个应用程序,但是这里为什么还要创建ActivityThread?因为SystemServer不仅仅是一个后台进程,同时它还是一个运行着组件的Service进程,很多系统的对话框就是从SystemServer中显示出来的,因此,SystemServer本身也需要一个和APK应用类似的上下文环境。
下面我们就依次来看下创建ActivityThread实例与attach方法的实现
1、 创建ActivityThread实例
现在看他它的无参构造构造函数
代码在ActivityThread.java
1851 ActivityThread() {
1852 mResourcesManager = ResourcesManager.getInstance();
1853 }
代码很简单,我们看到他的无参构造函数就是获取了一个mResourcesManager对象。
我们知道在实例一个类的对象时候,是自动初始化其的属性,而ActivityThread赋值的字段如下:
153 private static final android.graphics.Bitmap.Config THUMBNAIL_FORMAT = Bitmap.Config.RGB_565;
154 static final boolean localLOGV = false;
155 static final boolean DEBUG_MESSAGES = false;
156 /** @hide */
157 public static final boolean DEBUG_BROADCAST = false;
158 private static final boolean DEBUG_RESULTS = false;
159 private static final boolean DEBUG_BACKUP = false;
160 public static final boolean DEBUG_CONFIGURATION = false;
161 private static final boolean DEBUG_SERVICE = false;
162 private static final boolean DEBUG_MEMORY_TRIM = false;
163 private static final boolean DEBUG_PROVIDER = false;
164 private static final long MIN_TIME_BETWEEN_GCS = 5*1000;
165 private static final int SQLITE_MEM_RELEASED_EVENT_LOG_TAG = 75003;
166 private static final int LOG_AM_ON_PAUSE_CALLED = 30021;
167 private static final int LOG_AM_ON_RESUME_CALLED = 30022;
170 public static final int SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON = 0;
171 /** Type for IActivityManager.serviceDoneExecuting: done with an onStart call */
172 public static final int SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_START = 1;
173 /** Type for IActivityManager.serviceDoneExecuting: done stopping (destroying) service */
174 public static final int SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_STOP = 2;
176 private ContextImpl mSystemContext;
180 final ApplicationThread mAppThread = new ApplicationThread();
181 final Looper mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
182 final H mH = new H();
183 final ArrayMap mActivities = new ArrayMap<>();
184 // List of new activities (via ActivityRecord.nextIdle) that should
185 // be reported when next we idle.
186 ActivityClientRecord mNewActivities = null;
187 // Number of activities that are currently visible on-screen.
188 int mNumVisibleActivities = 0;
189 WeakReference mLastAssistStructure;
190 final ArrayMap mServices = new ArrayMap<>();
198 final ArrayList mAllApplications
199 = new ArrayList();
200 // set of instantiated backup agents, keyed by package name
201 final ArrayMap mBackupAgents = new ArrayMap();
205 String mInstrumentationPackageName = null;
206 String mInstrumentationAppDir = null;
207 String[] mInstrumentationSplitAppDirs = null;
208 String mInstrumentationLibDir = null;
209 String mInstrumentedAppDir = null;
210 String[] mInstrumentedSplitAppDirs = null;
211 String mInstrumentedLibDir = null;
212 boolean mSystemThread = false;
213 boolean mJitEnabled = false;
214 boolean mSomeActivitiesChanged = false;
215
216 // These can be accessed by multiple threads; mPackages is the lock.
217 // XXX For now we keep around information about all packages we have
218 // seen, not removing entries from this map.
219 // NOTE: The activity and window managers need to call in to
220 // ActivityThread to do things like update resource configurations,
221 // which means this lock gets held while the activity and window managers
222 // holds their own lock. Thus you MUST NEVER call back into the activity manager
223 // or window manager or anything that depends on them while holding this lock.
224 // These LoadedApk are only valid for the userId that we're running as.
225 final ArrayMap> mPackages
226 = new ArrayMap>();
227 final ArrayMap> mResourcePackages
228 = new ArrayMap>();
229 final ArrayList mRelaunchingActivities
230 = new ArrayList();
231 Configuration mPendingConfiguration = null;
233 private final ResourcesManager mResourcesManager;
这里重点说几个
- 1、创建ApplicationThread对象。用于基于的BinderIPC通信
- 2、创建H对象mH,以及主线的Looper对象mLooper
PS:其中说一个字段,即mSystemThread,这个字段用来标识是否是system继承。默认为false。即不是系统进程。
说完ActivityThread实例的创建过程,那我们来看下其attach(boolean)方法。
2、 ActivityThread的attach(boolean)方法的解析
代码在ActivityThread.java中
5230 private void attach(boolean system) {
// 将sCurrentActivityThread指向自己
5231 sCurrentActivityThread = this;
// 上面传递进来的是否system为true,即该进程为系统进程
5232 mSystemThread = system;
// 其他普通应用是,system为false
5233 if (!system) {
// 普通应用进程
// 给ViewRootImpl添加第一个handler回调
5234 ViewRootImpl.addFirstDrawHandler(new Runnable() {
5235 @Override
5236 public void run() {
// 检查jit能否用,6.0即ART,不用jit,
// 不过由于向下兼容,所以这里还有检查jit
5237 ensureJitEnabled();
5238 }
5239 });
// 设置Java Application 在DDM里面的名称
5240 android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("",
5241 UserHandle.myUserId());
// 将mAppThread放到RuntimeInit类中的静态变量mApplicationObject中
5242 RuntimeInit.setApplicationObject(mAppThread.asBinder());
// 获得 IActivityManager的一个实例,IActivityManager其实一个Binder对象,负责和底层的沟通
// IActivityManager extends IInterface
5243 final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
5244 try {
// 将mAppThread 传入到ActivityThreadManager中
5245 mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
5246 } catch (RemoteException ex) {
5247 // Ignore
5248 }
5249 // Watch for getting close to heap limit.
// 添加GC观察者
5250 BinderInternal.addGcWatcher(new Runnable() {
5251 @Override public void run() {
5252 if (!mSomeActivitiesChanged) {
5253 return;
5254 }
5255 Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
5256 long dalvikMax = runtime.maxMemory();
5257 long dalvikUsed = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory();
5258 if (dalvikUsed > ((3*dalvikMax)/4)) {
5259 if (DEBUG_MEMORY_TRIM) Slog.d(TAG, "Dalvik max=" + (dalvikMax/1024)
5260 + " total=" + (runtime.totalMemory()/1024)
5261 + " used=" + (dalvikUsed/1024));
5262 mSomeActivitiesChanged = false;
5263 try {
5264 mgr.releaseSomeActivities(mAppThread);
5265 } catch (RemoteException e) {
5266 }
5267 }
5268 }
5269 });
5270 } else {
// 系统应用进程
5271 // Don't set application object here -- if the system crashes,
5272 // we can't display an alert, we just want to die die die.
// 设置Java Application 在DDM里面的名称 即 system_process
5273 android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("system_process",
5274 UserHandle.myUserId());
// 创建 系统应用的Instrumentation对象
5275 try {
5276 mInstrumentation = new Instrumentation();
// 创建 ContextImpl对象
5277 ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(
5278 this, getSystemContext().mPackageInfo);
// 创建系统进程的Application对象
5279 mInitialApplication = context.mPackageInfo.makeApplication(true, null);
// 调用系统进程的onCreate()方法
5280 mInitialApplication.onCreate();
5281 } catch (Exception e) {
5282 throw new RuntimeException(
5283 "Unable to instantiate Application():" + e.toString(), e);
5284 }
5285 }
5286
5287 // add dropbox logging to libcore
// 添加 dropbox log信息到libcore
5288 DropBox.setReporter(new DropBoxReporter());
5289
// 设置回调方法
5290 ViewRootImpl.addConfigCallback(new ComponentCallbacks2() {
5291 @Override
5292 public void onConfigurationChanged(Configuration newConfig) {
5293 synchronized (mResourcesManager) {
5294 // We need to apply this change to the resources
5295 // immediately, because upon returning the view
5296 // hierarchy will be informed about it.
5297 if (mResourcesManager.applyConfigurationToResourcesLocked(newConfig, null)) {
5298 // This actually changed the resources! Tell
5299 // everyone about it.
5300 if (mPendingConfiguration == null ||
5301 mPendingConfiguration.isOtherSeqNewer(newConfig)) {
5302 mPendingConfiguration = newConfig;
5303
5304 sendMessage(H.CONFIGURATION_CHANGED, newConfig);
5305 }
5306 }
5307 }
5308 }
5309 @Override
5310 public void onLowMemory() {
5311 }
5312 @Override
5313 public void onTrimMemory(int level) {
5314 }
5315 });
5316 }
为了让大家更好地理解,我们先来解释一下里面的几个名词
- DropBox:DropBox是Android在Froyo(API 8)中引用的用来持续化存储系统数据的机制,主要记录Android运行过程中、内核、系统进程、用户进程等出现严重问题时的log,可以认为这是一个可持续存储的系统级别的log
- Instrumentation:一个应用进程,对应一个Instrumentation,这个类的对象,会被优先创建出来,然后通过它来创建其他组件,它也是系统与其他组件交互的桥梁,因此通过它可以监听组件和系统之间的各种交互。
- LoadedApk:在讲解APK安装的时候我们说过,一个应用对应一个LoadedApk对象,里面包含了整个APK的相关信息。其中context.mPackageInf是一个LoadedApk对象
现在我们来总结一下attach方法的主要作用:
- 1、创建Instrumentation对象
- 2、通过调用ContextImpl.createAppContext方法来创建ContextImpl对象
- 3、通过调用context.mPackageInfo.makeApplication创建mInitialApplication对象
- 4、调用mInitialApplication对象的onCreate()
所以我们说attach方法在参数system为true的时候,会创建一个类似的Application的环境。
这里面有两个重要方法即ContextImpl.createAppContext和LoadedApk.makeApplication方法,那我们就来依次解析下
PS:getSystemContext()方法我们前面讲解了会返回一个ContextImpl对象
2.1、 ContextImpl.createAppContext方法的解析
代码在ContextImpl.java
1783 static ContextImpl createAppContext(ActivityThread mainThread, LoadedApk packageInfo) {
1784 if (packageInfo == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("packageInfo");
1785 return new ContextImpl(null, mainThread,
1786 packageInfo, null, null, false, null, null, Display.INVALID_DISPLAY);
1787 }
我们看到,代码很简答, 就是直接new ContextImple
我们上面讲解了创建systemContext的过程,也是直接new ContextImpl对象,我们来对比下
1776 ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl(null, mainThread,
1777 packageInfo, null, null, false, null, null, Display.INVALID_DISPLAY);
// ***上面是创createSystemContext,下面是createAppContext***
1785 return new ContextImpl(null, mainThread,
1786 packageInfo, null, null, false, null, null, Display.INVALID_DISPLAY);
我们发现是一致,没差别
下面我们来看下 LoadedApk.makeApplication的执行
2.2、 LoadedApk.makeApplication方法的解析
代码在LoadedApk.java
//context.mPackageInfo.makeApplication(true, null); 所以forceDefaultAppClass=true,instrumentation=null
554 public Application makeApplication(boolean forceDefaultAppClass,
555 Instrumentation instrumentation) {
// 非空判断,这样可以保证一个LoadApk对象只能创建一个对应的Application对象
556 if (mApplication != null) {
557 return mApplication;
558 }
559
560 Application app = null;
561
562 String appClass = mApplicationInfo.className;
563 if (forceDefaultAppClass || (appClass == null)) {
// forceDefaultAppClass=true,则进入这个if,设置类名
564 appClass = "android.app.Application";
565 }
566
567 try {
//创建ClassLoader对象
568 java.lang.ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader();
// 前面已经介绍了 系统进程的包名就是"android",所以不走这个if
569 if (!mPackageName.equals("android")) {
570 initializeJavaContextClassLoader();
571 }
// 创建ContextImpl
572 ContextImpl appContext = ContextImpl.createAppContext(mActivityThread, this);
// 创建Application对象
573 app = mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.newApplication(
574 cl, appClass, appContext);
575 appContext.setOuterContext(app);
576 } catch (Exception e) {
577 if (!mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.onException(app, e)) {
578 throw new RuntimeException(
579 "Unable to instantiate application " + appClass
580 + ": " + e.toString(), e);
581 }
582 }
// 将app添加早应用列表
583 mActivityThread.mAllApplications.add(app);
// 将刚创建的app赋值给mApplication
584 mApplication = app;
585
586 if (instrumentation != null) {
587 try {
// 利用instrumentation调用Application的onCreate方法
588 instrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
589 } catch (Exception e) {
590 if (!instrumentation.onException(app, e)) {
591 throw new RuntimeException(
592 "Unable to create application " + app.getClass().getName()
593 + ": " + e.toString(), e);
594 }
595 }
596 }
597
598 // Rewrite the R 'constants' for all library apks.
// 重写 所有库apks的R 常量
599 SparseArray packageIdentifiers = getAssets(mActivityThread)
600 .getAssignedPackageIdentifiers();
601 final int N = packageIdentifiers.size();
602 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
603 final int id = packageIdentifiers.keyAt(i);
604 if (id == 0x01 || id == 0x7f) {
605 continue;
606 }
607
608 rewriteRValues(getClassLoader(), packageIdentifiers.valueAt(i), id);
609 }
610
611 return app;
612 }
我们看到这个方法其实就是创建了一个Application对象。
里面有两个方法比较重要getClassLoader()和
getClassLoader().mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.newApplication(cl, appClass, appContext)那我们来看一下
2.2.1、 LoadedApk的getClassLoader()方法的解析
代码在LoadedApk.java中
258 public ClassLoader getClassLoader() {
259 synchronized (this) {
// 如果mClassLoader不为空,则直接返回,保证mClassLoader只赋值一次
260 if (mClassLoader != null) {
261 return mClassLoader;
262 }
263
// 如果不是系统进程
264 if (mIncludeCode && !mPackageName.equals("android")) {
// 普通应用的类加载器的 创建流程
265 // Avoid the binder call when the package is the current application package.
266 // The activity manager will perform ensure that dexopt is performed before
267 // spinning up the process.
268 if (!Objects.equals(mPackageName, ActivityThread.currentPackageName())) {
269 final String isa = VMRuntime.getRuntime().vmInstructionSet();
270 try {
271 ActivityThread.getPackageManager().performDexOptIfNeeded(mPackageName, isa);
272 } catch (RemoteException re) {
273 // Ignored.
274 }
275 }
276
277 final List zipPaths = new ArrayList<>();
278 final List apkPaths = new ArrayList<>();
279 final List libPaths = new ArrayList<>();
280
281 if (mRegisterPackage) {
282 try {
283 ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().addPackageDependency(mPackageName);
284 } catch (RemoteException e) {
285 }
286 }
287
288 zipPaths.add(mAppDir);
289 if (mSplitAppDirs != null) {
290 Collections.addAll(zipPaths, mSplitAppDirs);
291 }
292
293 libPaths.add(mLibDir);
294
295 /*
296 * The following is a bit of a hack to inject
297 * instrumentation into the system: If the app
298 * being started matches one of the instrumentation names,
299 * then we combine both the "instrumentation" and
300 * "instrumented" app into the path, along with the
301 * concatenation of both apps' shared library lists.
302 */
303
304 String instrumentationPackageName = mActivityThread.mInstrumentationPackageName;
305 String instrumentationAppDir = mActivityThread.mInstrumentationAppDir;
306 String[] instrumentationSplitAppDirs = mActivityThread.mInstrumentationSplitAppDirs;
307 String instrumentationLibDir = mActivityThread.mInstrumentationLibDir;
308
309 String instrumentedAppDir = mActivityThread.mInstrumentedAppDir;
310 String[] instrumentedSplitAppDirs = mActivityThread.mInstrumentedSplitAppDirs;
311 String instrumentedLibDir = mActivityThread.mInstrumentedLibDir;
312 String[] instrumentationLibs = null;
313
314 if (mAppDir.equals(instrumentationAppDir)
315 || mAppDir.equals(instrumentedAppDir)) {
316 zipPaths.clear();
317 zipPaths.add(instrumentationAppDir);
318 if (instrumentationSplitAppDirs != null) {
319 Collections.addAll(zipPaths, instrumentationSplitAppDirs);
320 }
321 zipPaths.add(instrumentedAppDir);
322 if (instrumentedSplitAppDirs != null) {
323 Collections.addAll(zipPaths, instrumentedSplitAppDirs);
324 }
325
326 libPaths.clear();
327 libPaths.add(instrumentationLibDir);
328 libPaths.add(instrumentedLibDir);
329
330 if (!instrumentedAppDir.equals(instrumentationAppDir)) {
331 instrumentationLibs = getLibrariesFor(instrumentationPackageName);
332 }
333 }
334
335 apkPaths.addAll(zipPaths);
336
337 if (mSharedLibraries != null) {
338 for (String lib : mSharedLibraries) {
339 if (!zipPaths.contains(lib)) {
340 zipPaths.add(0, lib);
341 }
342 }
343 }
344
345 if (instrumentationLibs != null) {
346 for (String lib : instrumentationLibs) {
347 if (!zipPaths.contains(lib)) {
348 zipPaths.add(0, lib);
349 }
350 }
351 }
352
353 final String zip = TextUtils.join(File.pathSeparator, zipPaths);
354
355 // Add path to libraries in apk for current abi
356 if (mApplicationInfo.primaryCpuAbi != null) {
357 for (String apk : apkPaths) {
358 libPaths.add(apk + "!/lib/" + mApplicationInfo.primaryCpuAbi);
359 }
360 }
361
362 final String lib = TextUtils.join(File.pathSeparator, libPaths);
363
364 /*
365 * With all the combination done (if necessary, actually
366 * create the class loader.
367 */
368
369 if (ActivityThread.localLOGV)
370 Slog.v(ActivityThread.TAG, "Class path: " + zip + ", JNI path: " + lib);
371
372 // Temporarily disable logging of disk reads on the Looper thread
373 // as this is early and necessary.
374 StrictMode.ThreadPolicy oldPolicy = StrictMode.allowThreadDiskReads();
375
376 mClassLoader = ApplicationLoaders.getDefault().getClassLoader(zip, lib,
377 mBaseClassLoader);
378
379 StrictMode.setThreadPolicy(oldPolicy);
380 } else {
// 系统进程的类加载器的 创建流程
381 if (mBaseClassLoader == null) {
382 mClassLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
383 } else {
384 mClassLoader = mBaseClassLoader;
385 }
386 }
387 return mClassLoader;
388 }
因为咱们是系统进程,所以直接走else,所以是通过ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader()。来获取系统的类加载器,那我们来看下Instrumentation的newApplication的方法实现
2.2.2、Instrumentation的newApplication(cl, appClass, appContext)方法的解析
代码在Instrumentation.java中
967 /**
968 * Perform instantiation of the process's {@link Application} object. The
969 * default implementation provides the normal system behavior.
970 *
971 * @param cl The ClassLoader with which to instantiate the object.
972 * @param className The name of the class implementing the Application
973 * object.
974 * @param context The context to initialize the application with
975 *
976 * @return The newly instantiated Application object.
977 */
978 public Application newApplication(ClassLoader cl, String className, Context context)
979 throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
980 ClassNotFoundException {
981 return newApplication(cl.loadClass(className), context);
982 }
//*********************************
4 /**
985 * Perform instantiation of the process's {@link Application} object. The
986 * default implementation provides the normal system behavior.
987 *
988 * @param clazz The class used to create an Application object from.
989 * @param context The context to initialize the application with
990 *
991 * @return The newly instantiated Application object.
992 */
993 static public Application newApplication(Class clazz, Context context)
994 throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
995 ClassNotFoundException {
996 Application app = (Application)clazz.newInstance();
997 app.attach(context);
998 return app;
999 }
代码很简单,就是三个参数的newApplication方法直接调用了两个参数的newApplication方法,最后通过反射来创建一个Application的实例,最后调用attach(context)来绑定一个Context。
自此初始化系统上下文——createSystemContext()方法解析讲解完毕
三、创建SystemServiceManager
我们来看下SystemServiceManager的构造函数
代码在SystemServiceManager.java
43 public SystemServiceManager(Context context) {
44 mContext = context;
45 }
我们看到什么也没做,那我们接下来看下LocalServices.addService里面的实现。
代码在LocalServices.java
49 /**
50 * Adds a service instance of the specified interface to the global registry of local services.
51 */
52 public static void addService(Class type, T service) {
53 synchronized (sLocalServiceObjects) {
54 if (sLocalServiceObjects.containsKey(type)) {
55 throw new IllegalStateException("Overriding service registration");
56 }
57 sLocalServiceObjects.put(type, service);
58 }
59 }
我们看到,就是把SystemServiceManager放到LocalServicesd的sLocalServiceObjects中,其中sLocalServiceObjects是一个ArrayMap。这样后面在通过类名,就可以找到SystemServiceManager的对象了。
四、启动各种服务
启动各种服务主要分为3大方法即
- startBootstrapServices();
- startCoreServices();
- startOtherServices();
下面我们就依次讲解下
(一) startBootstrapServices()方法解析
代码在SystemServer.java
/**
316 * Starts the small tangle of critical services that are needed to get
317 * the system off the ground. These services have complex mutual dependencies
318 * which is why we initialize them all in one place here. Unless your service
319 * is also entwined in these dependencies, it should be initialized in one of
320 * the other functions.
321 */
322 private void startBootstrapServices() {
323 // Wait for installd to finish starting up so that it has a chance to
324 // create critical directories such as /data/user with the appropriate
325 // permissions. We need this to complete before we initialize other services.
// 阻塞等待与installd建立socket通道
326 Installer installer = mSystemServiceManager.startService(Installer.class);
327
328 // Activity manager runs the show.
//创建AMS(ActivityManagerService),并启动
329 mActivityManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(
330 ActivityManagerService.Lifecycle.class).getService();
331 mActivityManagerService.setSystemServiceManager(mSystemServiceManager);
332 mActivityManagerService.setInstaller(installer);
333
334 // Power manager needs to be started early because other services need it.
335 // Native daemons may be watching for it to be registered so it must be ready
336 // to handle incoming binder calls immediately (including being able to verify
337 // the permissions for those calls).
// 启动电源管理服务,即PowerManagerService
338 mPowerManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(PowerManagerService.class);
339
340 // Now that the power manager has been started, let the activity manager
341 // initialize power management features.
// mActivityManagerService初始化,并在其中初始化PowerManager
342 mActivityManagerService.initPowerManagement();
343
344 // Manages LEDs and display backlight so we need it to bring up the display.
// 开启服务LightsService,即灯光服务
345 mSystemServiceManager.startService(LightsService.class);
346
347 // Display manager is needed to provide display metrics before package manager
348 // starts up.
// 开启服务DisplayManagerService,显示服务
349 mDisplayManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(DisplayManagerService.class);
350
351 // We need the default display before we can initialize the package manager.
// 在初始化package manager之前,需要默认的显示
352 mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(SystemService.PHASE_WAIT_FOR_DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
353
354 // Only run "core" apps if we're encrypting the device.
// 根据加密设备状态,决定mOnlyCore的值
355 String cryptState = SystemProperties.get("vold.decrypt");
356 if (ENCRYPTING_STATE.equals(cryptState)) {
357 Slog.w(TAG, "Detected encryption in progress - only parsing core apps");
358 mOnlyCore = true;
359 } else if (ENCRYPTED_STATE.equals(cryptState)) {
360 Slog.w(TAG, "Device encrypted - only parsing core apps");
361 mOnlyCore = true;
362 }
363
364 // Start the package manager.
365 Slog.i(TAG, "Package Manager");
// 启动服务PackageManagerService 即包管理
366 mPackageManagerService = PackageManagerService.main(mSystemContext, installer,
367 mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_OFF, mOnlyCore);
368 mFirstBoot = mPackageManagerService.isFirstBoot();
369 mPackageManager = mSystemContext.getPackageManager();
370
371 Slog.i(TAG, "User Service");
// 启动UserManagerService,即用户服务,新建目录“/data/user/”
372 ServiceManager.addService(Context.USER_SERVICE, UserManagerService.getInstance());
373
374 // Initialize attribute cache used to cache resources from packages.
375 AttributeCache.init(mSystemContext);
376
377 // Set up the Application instance for the system process and get started.
// 设置AMS,这样SystemServer进程可以加入到AMS中,冰杯它管理。
378 mActivityManagerService.setSystemProcess();
379
380 // The sensor service needs access to package manager service, app ops
381 // service, and permissions service, therefore we start it after them.
//启动传感器服务
//开启传感器服务
382 startSensorService();
383 }
先看一下注释
开启小而关键的引导服务,因为这些服务是基础服务。由于这些服务相互依赖,并且十分负载,所以这就是我们将它们全部初始化的原因。除非你的service也依赖这些服务,否则,应该放到其他方法里面去初始化。
代码很简答, 主要就是创建一些服务,比如
- ActivityManagerService
- PowerManagerService
- LightsService
- DisplayManagerService
- PackageManagerService
- UserManagerService
- sensor服务
该方法所创建的服务:ActivityManagerService, PowerManagerService, LightsService, DisplayManagerService, PackageManagerService, UserManagerService, sensor服务
这里说一下352行的mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(SystemService.PHASE_WAIT_FOR_DEFAULT_DISPLAY),我们会在后面的内容中详细讲解下。
我们看到代码很简单,就是相应的系统服务:ActivityManagerService, PowerManagerService, LightsService, DisplayManagerService, PackageManagerService, UserManagerService, sensor服务.
(二) startCoreServices()方法解析
代码在SystemServer.java
385 /**
386 * Starts some essential services that are not tangled up in the bootstrap process.
387 */
388 private void startCoreServices() {
389 // Tracks the battery level. Requires LightService.
// 启动服务BatteryService,用于统计电池量量
390 mSystemServiceManager.startService(BatteryService.class);
391
392 // Tracks application usage stats.
// 启动服务UsageStatsService,用于统计应用使用情况
393 mSystemServiceManager.startService(UsageStatsService.class);
394 mActivityManagerService.setUsageStatsManager(
395 LocalServices.getService(UsageStatsManagerInternal.class));
396 // Update after UsageStatsService is available, needed before performBootDexOpt.
397 mPackageManagerService.getUsageStatsIfNoPackageUsageInfo();
398
399 // Tracks whether the updatable WebView is in a ready state and watches for update installs.
//启动服务WebViewUpdateService
400 mSystemServiceManager.startService(WebViewUpdateService.class);
401 }
先看下注释
启动一些在引导阶段不相互依赖的系统服务
主要就是启动服务BatteryService,UsageStatsService,WebViewUpdateService。
(三)startOtherServices()方法解析
403 /**
404 * Starts a miscellaneous grab bag of stuff that has yet to be refactored
405 * and organized.
406 */
407 private void startOtherServices() {
408 final Context context = mSystemContext;
409 AccountManagerService accountManager = null;
410 ContentService contentService = null;
411 VibratorService vibrator = null;
412 IAlarmManager alarm = null;
413 IMountService mountService = null;
414 NetworkManagementService networkManagement = null;
415 NetworkStatsService networkStats = null;
416 NetworkPolicyManagerService networkPolicy = null;
417 ConnectivityService connectivity = null;
418 NetworkScoreService networkScore = null;
419 NsdService serviceDiscovery= null;
420 WindowManagerService wm = null;
421 UsbService usb = null;
422 SerialService serial = null;
423 NetworkTimeUpdateService networkTimeUpdater = null;
424 CommonTimeManagementService commonTimeMgmtService = null;
425 InputManagerService inputManager = null;
426 TelephonyRegistry telephonyRegistry = null;
427 ConsumerIrService consumerIr = null;
428 AudioService audioService = null;
429 MmsServiceBroker mmsService = null;
430 EntropyMixer entropyMixer = null;
431 CameraService cameraService = null;
432
// 获取相应的属性
433 boolean disableStorage = SystemProperties.getBoolean("config.disable_storage", false);
434 boolean disableBluetooth = SystemProperties.getBoolean("config.disable_bluetooth", false);
435 boolean disableLocation = SystemProperties.getBoolean("config.disable_location", false);
436 boolean disableSystemUI = SystemProperties.getBoolean("config.disable_systemui", false);
437 boolean disableNonCoreServices = SystemProperties.getBoolean("config.disable_noncore", false);
438 boolean disableNetwork = SystemProperties.getBoolean("config.disable_network", false);
439 boolean disableNetworkTime = SystemProperties.getBoolean("config.disable_networktime", false);
440 boolean isEmulator = SystemProperties.get("ro.kernel.qemu").equals("1");
441
442 try {
443 Slog.i(TAG, "Reading configuration...");
444 SystemConfig.getInstance();
445
446 Slog.i(TAG, "Scheduling Policy");
// 添加调度策略服务
447 ServiceManager.addService("scheduling_policy", new SchedulingPolicyService());
448
//开启通话逻辑控制服务,用于加载Telecom
449 mSystemServiceManager.startService(TelecomLoaderService.class);
450
451 Slog.i(TAG, "Telephony Registry");
// 启动telephony注册服务,用于监听telephony状态的接口
452 telephonyRegistry = new TelephonyRegistry(context);
453 ServiceManager.addService("telephony.registry", telephonyRegistry);
454
455 Slog.i(TAG, "Entropy Mixer");
// 随机数管理器,就是以前的EntropyService,生成随机数的一个东西。随机数一般与密码,加密等相关。
456 entropyMixer = new EntropyMixer(context);
457
// 获取ContentResolver对象
458 mContentResolver = context.getContentResolver();
459
460 Slog.i(TAG, "Camera Service");
// 启动相机服务
461 mSystemServiceManager.startService(CameraService.class);
462
463 // The AccountManager must come before the ContentService
464 try {
465 // TODO: seems like this should be disable-able, but req'd by ContentService
466 Slog.i(TAG, "Account Manager");
// 创建账户服务,并注册到ServiceManager中
467 accountManager = new AccountManagerService(context);
468 ServiceManager.addService(Context.ACCOUNT_SERVICE, accountManager);
469 } catch (Throwable e) {
470 Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting Account Manager", e);
471 }
472
473 Slog.i(TAG, "Content Manager");
474 contentService = ContentService.main(context,
475 mFactoryTestMode == FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL);
476
477 Slog.i(TAG, "System Content Providers");
// 将SettingProvider放到SystemServer进程中来运行
478 mActivityManagerService.installSystemProviders();
479
480 Slog.i(TAG, "Vibrator Service");
// 创建震动服务,并且添加到ServiceManager
481 vibrator = new VibratorService(context);
482 ServiceManager.addService("vibrator", vibrator);
483
// 创建并注册 远程控制服务,主要指通过红外线等控制周围的设备
484 Slog.i(TAG, "Consumer IR Service");
485 consumerIr = new ConsumerIrService(context);
486 ServiceManager.addService(Context.CONSUMER_IR_SERVICE, consumerIr);
487
// 开启闹铃服务
488 mSystemServiceManager.startService(AlarmManagerService.class);
489 alarm = IAlarmManager.Stub.asInterface(
490 ServiceManager.getService(Context.ALARM_SERVICE));
491
492 Slog.i(TAG, "Init Watchdog");
// 获取watch对象
493 final Watchdog watchdog = Watchdog.getInstance();
494 watchdog.init(context, mActivityManagerService);
495
496 Slog.i(TAG, "Input Manager");
//输入服务
497 inputManager = new InputManagerService(context);
498
499 Slog.i(TAG, "Window Manager");
// 启动 WindowManagerService
500 wm = WindowManagerService.main(context, inputManager,
501 mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL,
502 !mFirstBoot, mOnlyCore);
503 ServiceManager.addService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE, wm);
504 ServiceManager.addService(Context.INPUT_SERVICE, inputManager);
505
// 在AMS的内部保存WindowManagerService(WMS)
506 mActivityManagerService.setWindowManager(wm);
507
508 inputManager.setWindowManagerCallbacks(wm.getInputMonitor());
509 inputManager.start();
510
511 // TODO: Use service dependencies instead.
// 调用WindowManagerService重新刷新UI
512 mDisplayManagerService.windowManagerAndInputReady();
513
514 // Skip Bluetooth if we have an emulator kernel
515 // TODO: Use a more reliable check to see if this product should
516 // support Bluetooth - see bug 988521
// 是否启动蓝牙
517 if (isEmulator) {
//是模拟器,所以不启动蓝牙
518 Slog.i(TAG, "No Bluetooh Service (emulator)");
519 } else if (mFactoryTestMode == FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
//是测试模式,所以不启动蓝牙
520 Slog.i(TAG, "No Bluetooth Service (factory test)");
521 } else if (!context.getPackageManager().hasSystemFeature
522 (PackageManager.FEATURE_BLUETOOTH)) {
// 如果系统没有包含蓝牙模块,则不启动蓝牙
523 Slog.i(TAG, "No Bluetooth Service (Bluetooth Hardware Not Present)");
524 } else if (disableBluetooth) {
// 不能启动蓝牙,一般是初始化的没有蓝牙的配置
525 Slog.i(TAG, "Bluetooth Service disabled by config");
526 } else {
527 Slog.i(TAG, "Bluetooth Service");
// 启动蓝牙、
528 mSystemServiceManager.startService(BluetoothService.class);
529 }
530 } catch (RuntimeException e) {
531 Slog.e("System", "******************************************");
532 Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting core service", e);
533 }
534
535 StatusBarManagerService statusBar = null;
536 INotificationManager notification = null;
537 InputMethodManagerService imm = null;
538 WallpaperManagerService wallpaper = null;
539 LocationManagerService location = null;
540 CountryDetectorService countryDetector = null;
541 TextServicesManagerService tsms = null;
542 LockSettingsService lockSettings = null;
543 AssetAtlasService atlas = null;
544 MediaRouterService mediaRouter = null;
545
546 // Bring up services needed for UI.
// 如果不是运行工程模式(运行工程模式中很多的service并不需要启动)
547 if (mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
548 try {
549 Slog.i(TAG, "Input Method Service");
// 创建输入法,并注册
550 imm = new InputMethodManagerService(context, wm);
551 ServiceManager.addService(Context.INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE, imm);
552 } catch (Throwable e) {
553 reportWtf("starting Input Manager Service", e);
554 }
555
556 try {
557 Slog.i(TAG, "Accessibility Manager");
// 启动服务管理
558 ServiceManager.addService(Context.ACCESSIBILITY_SERVICE,
559 new AccessibilityManagerService(context));
560 } catch (Throwable e) {
561 reportWtf("starting Accessibility Manager", e);
562 }
563 }
564
565 try {
// 准备显示
566 wm.displayReady();
567 } catch (Throwable e) {
568 reportWtf("making display ready", e);
569 }
570
// 如果不是运行工程模式(运行工程模式中很多的service并不需要启动)
571 if (mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
572 if (!disableStorage &&
573 !"0".equals(SystemProperties.get("system_init.startmountservice"))) {
574 try {
575 /*
576 * NotificationManagerService is dependant on MountService,
577 * (for media / usb notifications) so we must start MountService first.
578 */
// 由于NotificationManagerService依赖MountService
// 所以要先启动MountService
579 mSystemServiceManager.startService(MOUNT_SERVICE_CLASS);
580 mountService = IMountService.Stub.asInterface(
581 ServiceManager.getService("mount"));
582 } catch (Throwable e) {
583 reportWtf("starting Mount Service", e);
584 }
585 }
586 }
587
588 // We start this here so that we update our configuration to set watch or television
589 // as appropriate.
// 启动UI管理模式,即夜间模式和行车模式
590 mSystemServiceManager.startService(UiModeManagerService.class);
591
592 try {
// 进行dex优化
593 mPackageManagerService.performBootDexOpt();
594 } catch (Throwable e) {
595 reportWtf("performing boot dexopt", e);
596 }
597
598 try {
//显示启动界面
599 ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().showBootMessage(
600 context.getResources().getText(
601 com.android.internal.R.string.android_upgrading_starting_apps),
602 false);
603 } catch (RemoteException e) {
604 }
605
// 如果不是运行工程模式(运行工程模式中很多的service并不需要启动)
606 if (mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
607 if (!disableNonCoreServices) {
608 try {
609 Slog.i(TAG, "LockSettingsService");
// 创建锁屏图案密码服务
610 lockSettings = new LockSettingsService(context);
611 ServiceManager.addService("lock_settings", lockSettings);
612 } catch (Throwable e) {
613 reportWtf("starting LockSettingsService service", e);
614 }
615
616 if (!SystemProperties.get(PERSISTENT_DATA_BLOCK_PROP).equals("")) {
// 启动回复出厂设置的数据保存服务
617 mSystemServiceManager.startService(PersistentDataBlockService.class);
618 }
619
// 启动设备空闲控制器,在Android 6.0上power改动比较大
//粗略的看PowerManagerService感觉变动不大,
// 只是在PowerManagerService的改动代码比较少,
// 但是其是指改动比较大,特比增加了这个DeviceIdleController,来控制设备的Idle状态,
// 当设备在idle状态时,它会忽略CPU的wakelock,Alarm等。
620 mSystemServiceManager.startService(DeviceIdleController.class);
621
622 // Always start the Device Policy Manager, so that the API is compatible with
623 // API8.
// 开启 设备配置管理服务
624 mSystemServiceManager.startService(DevicePolicyManagerService.Lifecycle.class);
625 }
626
627 if (!disableSystemUI) {
628 try {
629 Slog.i(TAG, "Status Bar");
// 创建并注册 状态栏服务
630 statusBar = new StatusBarManagerService(context, wm);
631 ServiceManager.addService(Context.STATUS_BAR_SERVICE, statusBar);
632 } catch (Throwable e) {
633 reportWtf("starting StatusBarManagerService", e);
634 }
635 }
636
637 if (!disableNonCoreServices) {
638 try {
639 Slog.i(TAG, "Clipboard Service");
// 创建并注册 剪切板服务
640 ServiceManager.addService(Context.CLIPBOARD_SERVICE,
641 new ClipboardService(context));
642 } catch (Throwable e) {
643 reportWtf("starting Clipboard Service", e);
644 }
645 }
646
647 if (!disableNetwork) {
648 try {
649 Slog.i(TAG, "NetworkManagement Service");
// 创建并注册 网络物理接口管理服务
650 networkManagement = NetworkManagementService.create(context);
651 ServiceManager.addService(Context.NETWORKMANAGEMENT_SERVICE, networkManagement);
652 } catch (Throwable e) {
653 reportWtf("starting NetworkManagement Service", e);
654 }
655 }
656
657 if (!disableNonCoreServices) {
658 try {
659 Slog.i(TAG, "Text Service Manager Service");
// 创建并注册 提供拼写和检查的文本服务
660 tsms = new TextServicesManagerService(context);
661 ServiceManager.addService(Context.TEXT_SERVICES_MANAGER_SERVICE, tsms);
662 } catch (Throwable e) {
663 reportWtf("starting Text Service Manager Service", e);
664 }
665 }
666
667 if (!disableNetwork) {
668 try {
669 Slog.i(TAG, "Network Score Service");
// 创建并注册 网络通信记录服务
670 networkScore = new NetworkScoreService(context);
671 ServiceManager.addService(Context.NETWORK_SCORE_SERVICE, networkScore);
672 } catch (Throwable e) {
673 reportWtf("starting Network Score Service", e);
674 }
675
676 try {
677 Slog.i(TAG, "NetworkStats Service");
// 创建并注册 网络连接状态服务
678 networkStats = new NetworkStatsService(context, networkManagement, alarm);
679 ServiceManager.addService(Context.NETWORK_STATS_SERVICE, networkStats);
680 } catch (Throwable e) {
681 reportWtf("starting NetworkStats Service", e);
682 }
683
684 try {
685 Slog.i(TAG, "NetworkPolicy Service");
// 创建并注册 网络策略管理服务
686 networkPolicy = new NetworkPolicyManagerService(
687 context, mActivityManagerService,
688 (IPowerManager)ServiceManager.getService(Context.POWER_SERVICE),
689 networkStats, networkManagement);
690 ServiceManager.addService(Context.NETWORK_POLICY_SERVICE, networkPolicy);
691 } catch (Throwable e) {
692 reportWtf("starting NetworkPolicy Service", e);
693 }
694
// 开启wifi相关服务
695 mSystemServiceManager.startService(WIFI_P2P_SERVICE_CLASS);
696 mSystemServiceManager.startService(WIFI_SERVICE_CLASS);
697 mSystemServiceManager.startService(
698 "com.android.server.wifi.WifiScanningService");
699
700 mSystemServiceManager.startService("com.android.server.wifi.RttService");
701
// 启动以太网服务
702 if (mPackageManager.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_ETHERNET) ||
703 mPackageManager.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_USB_HOST)) {
704 mSystemServiceManager.startService(ETHERNET_SERVICE_CLASS);
705 }
706
707 try {
708 Slog.i(TAG, "Connectivity Service");
// 创建并注册 网络连接管理服务
709 connectivity = new ConnectivityService(
710 context, networkManagement, networkStats, networkPolicy);
711 ServiceManager.addService(Context.CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE, connectivity);
712 networkStats.bindConnectivityManager(connectivity);
713 networkPolicy.bindConnectivityManager(connectivity);
714 } catch (Throwable e) {
715 reportWtf("starting Connectivity Service", e);
716 }
717
// 创建并注册NsdService服务,它是基于苹果的Bonjour服务发现协议,提供远程服务的发现和零配置功能的服务
718 try {
719 Slog.i(TAG, "Network Service Discovery Service");
720 serviceDiscovery = NsdService.create(context);
721 ServiceManager.addService(
722 Context.NSD_SERVICE, serviceDiscovery);
723 } catch (Throwable e) {
724 reportWtf("starting Service Discovery Service", e);
725 }
726 }
727
728 if (!disableNonCoreServices) {
729 try {
730 Slog.i(TAG, "UpdateLock Service");
// 创建并注册 UpdateLockService 更新锁服务
731 ServiceManager.addService(Context.UPDATE_LOCK_SERVICE,
732 new UpdateLockService(context));
733 } catch (Throwable e) {
734 reportWtf("starting UpdateLockService", e);
735 }
736 }
737
738 /*
739 * MountService has a few dependencies: Notification Manager and
740 * AppWidget Provider. Make sure MountService is completely started
741 * first before continuing.
742 */
// 由于MountService有一些依赖项目:Notification Manager和AppWidget Provider。
// 所以在启动MountService前要确保Notification Manager和AppWidget Provider。
743 if (mountService != null && !mOnlyCore) {
744 try {
745 mountService.waitForAsecScan();
746 } catch (RemoteException ignored) {
747 }
748 }
749
750 try {
// accountManager 准备就绪
751 if (accountManager != null)
752 accountManager.systemReady();
753 } catch (Throwable e) {
754 reportWtf("making Account Manager Service ready", e);
755 }
756
757 try {
// contentService 准备就绪
758 if (contentService != null)
759 contentService.systemReady();
760 } catch (Throwable e) {
761 reportWtf("making Content Service ready", e);
762 }
763
//开启,并注册NotificationManagerService
764 mSystemServiceManager.startService(NotificationManagerService.class);
765 notification = INotificationManager.Stub.asInterface(
766 ServiceManager.getService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE));
767 networkPolicy.bindNotificationManager(notification);
768
// 启动DeviceStorageMonitorService,即磁盘空间状态检测服务
769 mSystemServiceManager.startService(DeviceStorageMonitorService.class);
770
771 if (!disableLocation) {
772 try {
773 Slog.i(TAG, "Location Manager");
// 开启,并注册LocationManagerService,即定位服务
774 location = new LocationManagerService(context);
775 ServiceManager.addService(Context.LOCATION_SERVICE, location);
776 } catch (Throwable e) {
777 reportWtf("starting Location Manager", e);
778 }
779
780 try {
781 Slog.i(TAG, "Country Detector");
// 开启,并注册CountryDetectorService,用于检测用户国家
782 countryDetector = new CountryDetectorService(context);
783 ServiceManager.addService(Context.COUNTRY_DETECTOR, countryDetector);
784 } catch (Throwable e) {
785 reportWtf("starting Country Detector", e);
786 }
787 }
788
789 if (!disableNonCoreServices) {
790 try {
791 Slog.i(TAG, "Search Service");
// 开启,并注册SearchManagerService,用于搜索管理服务
792 ServiceManager.addService(Context.SEARCH_SERVICE,
793 new SearchManagerService(context));
794 } catch (Throwable e) {
795 reportWtf("starting Search Service", e);
796 }
797 }
798
799 try {
800 Slog.i(TAG, "DropBox Service");
// 开启,并注册DropBoxManagerService,用于系统运行时日志的存储与管理
801 ServiceManager.addService(Context.DROPBOX_SERVICE,
802 new DropBoxManagerService(context, new File("/data/system/dropbox")));
803 } catch (Throwable e) {
804 reportWtf("starting DropBoxManagerService", e);
805 }
806
807 if (!disableNonCoreServices && context.getResources().getBoolean(
808 R.bool.config_enableWallpaperService)) {
809 try {
810 Slog.i(TAG, "Wallpaper Service");
// 开启,并注册WallpaperManagerService,用于壁纸管理服务
811 wallpaper = new WallpaperManagerService(context);
812 ServiceManager.addService(Context.WALLPAPER_SERVICE, wallpaper);
813 } catch (Throwable e) {
814 reportWtf("starting Wallpaper Service", e);
815 }
816 }
817
818 try {
819 Slog.i(TAG, "Audio Service");
// 开启,并注册AudioService,用于AudioFlinger的上层管理封装,主要是音量、音效及铃声等的管理开启
820 audioService = new AudioService(context);
821 ServiceManager.addService(Context.AUDIO_SERVICE, audioService);
822 } catch (Throwable e) {
823 reportWtf("starting Audio Service", e);
824 }
825
// 开启DockObserver,如果设备有一个座子,管理当手机装上或者拔出这个座子的状态
826 if (!disableNonCoreServices) {
827 mSystemServiceManager.startService(DockObserver.class);
828 }
829
830 try {
// 开启WiredAccessoryManager,用于检测手机的耳机
831 Slog.i(TAG, "Wired Accessory Manager");
832 // Listen for wired headset changes
833 inputManager.setWiredAccessoryCallbacks(
834 new WiredAccessoryManager(context, inputManager));
835 } catch (Throwable e) {
836 reportWtf("starting WiredAccessoryManager", e);
837 }
838
839 if (!disableNonCoreServices) {
// 开启MIDI服务,MIDI(Musical Instrument Digital Interface)乐器数字接口
840 if (mPackageManager.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_MIDI)) {
841 // Start MIDI Manager service
842 mSystemServiceManager.startService(MIDI_SERVICE_CLASS);
843 }
844
// 开启USB服务
845 if (mPackageManager.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_USB_HOST)
846 || mPackageManager.hasSystemFeature(
847 PackageManager.FEATURE_USB_ACCESSORY)) {
848 // Manage USB host and device support
849 mSystemServiceManager.startService(USB_SERVICE_CLASS);
850 }
851
// 开启并注册SerialService(串口服务)
852 try {
853 Slog.i(TAG, "Serial Service");
854 // Serial port support
855 serial = new SerialService(context);
856 ServiceManager.addService(Context.SERIAL_SERVICE, serial);
857 } catch (Throwable e) {
858 Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting SerialService", e);
859 }
860 }
861
// 开启TwilightService,用来检测用户所在位置是否为晚上,被UiModeManager等用来调整夜间模式
862 mSystemServiceManager.startService(TwilightService.class);
863
// 开启JobSchedulerService
864 mSystemServiceManager.startService(JobSchedulerService.class);
865
866 if (!disableNonCoreServices) {
//如果系统要求有备份,则开启备份服务BackupManagerService$Lifecycle
867 if (mPackageManager.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_BACKUP)) {
868 mSystemServiceManager.startService(BACKUP_MANAGER_SERVICE_CLASS);
869 }
870
//如果系统要求有appwidget,则开启AppWidgetService,提供Widget的管理和相关服务
871 if (mPackageManager.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_APP_WIDGETS)) {
872 mSystemServiceManager.startService(APPWIDGET_SERVICE_CLASS);
873 }
874
//如果系统要求有语音识别,则开启语音识别服务VoiceInteractionManagerService
875 if (mPackageManager.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_VOICE_RECOGNIZERS)) {
876 mSystemServiceManager.startService(VOICE_RECOGNITION_MANAGER_SERVICE_CLASS);
877 }
878
//如果系统要求手势启动,则开启语手势启动GestureLauncherService
879 if (GestureLauncherService.isGestureLauncherEnabled(context.getResources())) {
880 Slog.i(TAG, "Gesture Launcher Service");
881 mSystemServiceManager.startService(GestureLauncherService.class);
882 }
883 }
884
//开启DiskStatsService,即磁盘状态服务,主要用于磁盘统计服务,供dumpsys使用
885 try {
886 Slog.i(TAG, "DiskStats Service");
887 ServiceManager.addService("diskstats", new DiskStatsService(context));
888 } catch (Throwable e) {
889 reportWtf("starting DiskStats Service", e);
890 }
891
892 try {
893 // need to add this service even if SamplingProfilerIntegration.isEnabled()
894 // is false, because it is this service that detects system property change and
895 // turns on SamplingProfilerIntegration. Plus, when sampling profiler doesn't work,
896 // there is little overhead for running this service.
897 Slog.i(TAG, "SamplingProfiler Service");
// 创建 并注册 耗时统计服务SamplingProfilerService
898 ServiceManager.addService("samplingprofiler",
899 new SamplingProfilerService(context));
900 } catch (Throwable e) {
901 reportWtf("starting SamplingProfiler Service", e);
902 }
903
904 if (!disableNetwork && !disableNetworkTime) {
905 try {
906 Slog.i(TAG, "NetworkTimeUpdateService");
// 创建NetworkTimeUpdateService,用于件事网络时间,当网络时间变化时更新本地时间。
907 networkTimeUpdater = new NetworkTimeUpdateService(context);
908 } catch (Throwable e) {
909 reportWtf("starting NetworkTimeUpdate service", e);
910 }
911 }
912
913 try {
914 Slog.i(TAG, "CommonTimeManagementService");
// 创建 并注册commonTimeMgmtService,用于管理本地常见的时间服务的配置,在网络配置变化时重新配置本地服务
915 commonTimeMgmtService = new CommonTimeManagementService(context);
916 ServiceManager.addService("commontime_management", commonTimeMgmtService);
917 } catch (Throwable e) {
918 reportWtf("starting CommonTimeManagementService service", e);
919 }
920
921 if (!disableNetwork) {
922 try {
923 Slog.i(TAG, "CertBlacklister");
// 创建 CertBlacklister,CertBlacklister提供了一个简单的机制来更新SSL证书公钥和序列号的平台黑名单
924 CertBlacklister blacklister = new CertBlacklister(context);
925 } catch (Throwable e) {
926 reportWtf("starting CertBlacklister", e);
927 }
928 }
929
930 if (!disableNonCoreServices) {
931 // Dreams (interactive idle-time views, a/k/a screen savers, and doze mode)
// 创建 DreamManagerService,用于屏幕保护
932 mSystemServiceManager.startService(DreamManagerService.class);
933 }
934
935 if (!disableNonCoreServices) {
936 try {
937 Slog.i(TAG, "Assets Atlas Service");
// 创建 并注册 AssetAtlasService,用于将预加载bitmap组装成纹理贴图可以用来被跨进程使用,以减少内存。
938 atlas = new AssetAtlasService(context);
939 ServiceManager.addService(AssetAtlasService.ASSET_ATLAS_SERVICE, atlas);
940 } catch (Throwable e) {
941 reportWtf("starting AssetAtlasService", e);
942 }
943 }
944
945 if (!disableNonCoreServices) {
// 创建 并注册 GraphicsStatsService,负责收集汇总Android系统的渲染剖面数据(profile data)
// 主要途径是通过允许渲染线程请求匿名共享存储缓冲(ashmem buffer)来存放它们统计信息来实现的。
946 ServiceManager.addService(GraphicsStatsService.GRAPHICS_STATS_SERVICE,
947 new GraphicsStatsService(context));
948 }
949
950 if (mPackageManager.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_PRINTING)) {
// 开启打印服务
951 mSystemServiceManager.startService(PRINT_MANAGER_SERVICE_CLASS);
952 }
953
// 开启RestrictionsManagerService,负责查询管理用户限制的机制。因为APP可以向远程设备管理员发送权限请求。
954 mSystemServiceManager.startService(RestrictionsManagerService.class);
955
// 开启MediaSessionService,是MediaSession框架的管理服务
956 mSystemServiceManager.startService(MediaSessionService.class);
957
958 if (mPackageManager.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_HDMI_CEC)) {
// 开启HdmiControlService,负责HDMI
959 mSystemServiceManager.startService(HdmiControlService.class);
960 }
961
962 if (mPackageManager.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_LIVE_TV)) {
// 开启TvInputManagerService,负责android TV
963 mSystemServiceManager.startService(TvInputManagerService.class);
964 }
965
966 if (!disableNonCoreServices) {
967 try {
968 Slog.i(TAG, "Media Router Service");
// 开启 并注册MediaRouterService,负责多媒体路由(因为多媒体可能既有有限,也有无线等)
969 mediaRouter = new MediaRouterService(context);
970 ServiceManager.addService(Context.MEDIA_ROUTER_SERVICE, mediaRouter);
971 } catch (Throwable e) {
972 reportWtf("starting MediaRouterService", e);
973 }
974
// 开启TrustManagerService,负责管理信任证书
975 mSystemServiceManager.startService(TrustManagerService.class);
976
// 开启FingerprintService,负责指纹识别
977 mSystemServiceManager.startService(FingerprintService.class);
978
979 try {
980 Slog.i(TAG, "BackgroundDexOptService");
// 启动JobSchedule 后台延Dex优化
981 BackgroundDexOptService.schedule(context, 0);
982 } catch (Throwable e) {
983 reportWtf("starting BackgroundDexOptService", e);
984 }
985
986 }
987
// 启动LauncherAppsService,负责管理Launcher的请求和回调
988 mSystemServiceManager.startService(LauncherAppsService.class);
989 }
990
991 if (!disableNonCoreServices) {
//管理媒体投影会话
992 mSystemServiceManager.startService(MediaProjectionManagerService.class);
993 }
994
995 // Before things start rolling, be sure we have decided whether
996 // we are in safe mode.
// 安全模式
997 final boolean safeMode = wm.detectSafeMode();
998 if (safeMode) {
999 mActivityManagerService.enterSafeMode();
1000 // Disable the JIT for the system_server process
1001 VMRuntime.getRuntime().disableJitCompilation();
1002 } else {
1003 // Enable the JIT for the system_server process
1004 VMRuntime.getRuntime().startJitCompilation();
1005 }
1006
1007 // MMS service broker
// MmsService 的代理,因为MmsService运行在电话进程中,可能随时crash,它会通过一个connection与MmsService 建立一个桥梁,MmsService实现了公开的 SMS/MMS 的API。
1008 mmsService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(MmsServiceBroker.class);
1009
1010 // It is now time to start up the app processes...
1011
1012 try {
// 震动 已经准备完毕
1013 vibrator.systemReady();
1014 } catch (Throwable e) {
1015 reportWtf("making Vibrator Service ready", e);
1016 }
1017
1018 if (lockSettings != null) {
1019 try {
1020 lockSettings.systemReady();
1021 } catch (Throwable e) {
1022 reportWtf("making Lock Settings Service ready", e);
1023 }
1024 }
1025
1026 // Needed by DevicePolicyManager for initialization
1027 mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(SystemService.PHASE_LOCK_SETTINGS_READY);
1028
1029 mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(SystemService.PHASE_SYSTEM_SERVICES_READY);
1030
1031 try {
1032 wm.systemReady();
1033 } catch (Throwable e) {
1034 reportWtf("making Window Manager Service ready", e);
1035 }
1036
1037 if (safeMode) {
1038 mActivityManagerService.showSafeModeOverlay();
1039 }
1040
1041 // Update the configuration for this context by hand, because we're going
1042 // to start using it before the config change done in wm.systemReady() will
1043 // propagate to it.
1044 Configuration config = wm.computeNewConfiguration();
1045 DisplayMetrics metrics = new DisplayMetrics();
1046 WindowManager w = (WindowManager)context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
1047 w.getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(metrics);
1048 context.getResources().updateConfiguration(config, metrics);
1049
1050 try {
1051 // TODO: use boot phase
1052 mPowerManagerService.systemReady(mActivityManagerService.getAppOpsService());
1053 } catch (Throwable e) {
1054 reportWtf("making Power Manager Service ready", e);
1055 }
1056
1057 try {
1058 mPackageManagerService.systemReady();
1059 } catch (Throwable e) {
1060 reportWtf("making Package Manager Service ready", e);
1061 }
1062
1063 try {
1064 // TODO: use boot phase and communicate these flags some other way
1065 mDisplayManagerService.systemReady(safeMode, mOnlyCore);
1066 } catch (Throwable e) {
1067 reportWtf("making Display Manager Service ready", e);
1068 }
1069
1070 // These are needed to propagate to the runnable below.
1071 final NetworkManagementService networkManagementF = networkManagement;
1072 final NetworkStatsService networkStatsF = networkStats;
1073 final NetworkPolicyManagerService networkPolicyF = networkPolicy;
1074 final ConnectivityService connectivityF = connectivity;
1075 final NetworkScoreService networkScoreF = networkScore;
1076 final WallpaperManagerService wallpaperF = wallpaper;
1077 final InputMethodManagerService immF = imm;
1078 final LocationManagerService locationF = location;
1079 final CountryDetectorService countryDetectorF = countryDetector;
1080 final NetworkTimeUpdateService networkTimeUpdaterF = networkTimeUpdater;
1081 final CommonTimeManagementService commonTimeMgmtServiceF = commonTimeMgmtService;
1082 final TextServicesManagerService textServiceManagerServiceF = tsms;
1083 final StatusBarManagerService statusBarF = statusBar;
1084 final AssetAtlasService atlasF = atlas;
1085 final InputManagerService inputManagerF = inputManager;
1086 final TelephonyRegistry telephonyRegistryF = telephonyRegistry;
1087 final MediaRouterService mediaRouterF = mediaRouter;
1088 final AudioService audioServiceF = audioService;
1089 final MmsServiceBroker mmsServiceF = mmsService;
1090
1091 // We now tell the activity manager it is okay to run third party
1092 // code. It will call back into us once it has gotten to the state
1093 // where third party code can really run (but before it has actually
1094 // started launching the initial applications), for us to complete our
1095 // initialization.
1096 mActivityManagerService.systemReady(new Runnable() {
1097 @Override
1098 public void run() {
1099 Slog.i(TAG, "Making services ready");
1100 mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(
1101 SystemService.PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY);
1102
1103 try {
1104 mActivityManagerService.startObservingNativeCrashes();
1105 } catch (Throwable e) {
1106 reportWtf("observing native crashes", e);
1107 }
1108
1109 Slog.i(TAG, "WebViewFactory preparation");
1110 WebViewFactory.prepareWebViewInSystemServer();
1111
1112 try {
1113 startSystemUi(context);
1114 } catch (Throwable e) {
1115 reportWtf("starting System UI", e);
1116 }
1117 try {
1118 if (networkScoreF != null) networkScoreF.systemReady();
1119 } catch (Throwable e) {
1120 reportWtf("making Network Score Service ready", e);
1121 }
1122 try {
1123 if (networkManagementF != null) networkManagementF.systemReady();
1124 } catch (Throwable e) {
1125 reportWtf("making Network Managment Service ready", e);
1126 }
1127 try {
1128 if (networkStatsF != null) networkStatsF.systemReady();
1129 } catch (Throwable e) {
1130 reportWtf("making Network Stats Service ready", e);
1131 }
1132 try {
1133 if (networkPolicyF != null) networkPolicyF.systemReady();
1134 } catch (Throwable e) {
1135 reportWtf("making Network Policy Service ready", e);
1136 }
1137 try {
1138 if (connectivityF != null) connectivityF.systemReady();
1139 } catch (Throwable e) {
1140 reportWtf("making Connectivity Service ready", e);
1141 }
1142 try {
1143 if (audioServiceF != null) audioServiceF.systemReady();
1144 } catch (Throwable e) {
1145 reportWtf("Notifying AudioService running", e);
1146 }
1147 Watchdog.getInstance().start();
1148
1149 // It is now okay to let the various system services start their
1150 // third party code...
1151 mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(
1152 SystemService.PHASE_THIRD_PARTY_APPS_CAN_START);
1153
1154 try {
1155 if (wallpaperF != null) wallpaperF.systemRunning();
1156 } catch (Throwable e) {
1157 reportWtf("Notifying WallpaperService running", e);
1158 }
1159 try {
1160 if (immF != null) immF.systemRunning(statusBarF);
1161 } catch (Throwable e) {
1162 reportWtf("Notifying InputMethodService running", e);
1163 }
1164 try {
1165 if (locationF != null) locationF.systemRunning();
1166 } catch (Throwable e) {
1167 reportWtf("Notifying Location Service running", e);
1168 }
1169 try {
1170 if (countryDetectorF != null) countryDetectorF.systemRunning();
1171 } catch (Throwable e) {
1172 reportWtf("Notifying CountryDetectorService running", e);
1173 }
1174 try {
1175 if (networkTimeUpdaterF != null) networkTimeUpdaterF.systemRunning();
1176 } catch (Throwable e) {
1177 reportWtf("Notifying NetworkTimeService running", e);
1178 }
1179 try {
1180 if (commonTimeMgmtServiceF != null) {
1181 commonTimeMgmtServiceF.systemRunning();
1182 }
1183 } catch (Throwable e) {
1184 reportWtf("Notifying CommonTimeManagementService running", e);
1185 }
1186 try {
1187 if (textServiceManagerServiceF != null)
1188 textServiceManagerServiceF.systemRunning();
1189 } catch (Throwable e) {
1190 reportWtf("Notifying TextServicesManagerService running", e);
1191 }
1192 try {
1193 if (atlasF != null) atlasF.systemRunning();
1194 } catch (Throwable e) {
1195 reportWtf("Notifying AssetAtlasService running", e);
1196 }
1197 try {
1198 // TODO(BT) Pass parameter to input manager
1199 if (inputManagerF != null) inputManagerF.systemRunning();
1200 } catch (Throwable e) {
1201 reportWtf("Notifying InputManagerService running", e);
1202 }
1203 try {
1204 if (telephonyRegistryF != null) telephonyRegistryF.systemRunning();
1205 } catch (Throwable e) {
1206 reportWtf("Notifying TelephonyRegistry running", e);
1207 }
1208 try {
1209 if (mediaRouterF != null) mediaRouterF.systemRunning();
1210 } catch (Throwable e) {
1211 reportWtf("Notifying MediaRouterService running", e);
1212 }
1213
1214 try {
1215 if (mmsServiceF != null) mmsServiceF.systemRunning();
1216 } catch (Throwable e) {
1217 reportWtf("Notifying MmsService running", e);
1218 }
1219 }
1220 });
1221 }
我们看到上面代码其实很简单主要就是不断的启动系统级别的服务。这里面我们会经常看看到这样的函数SystemService.onBootPhase()。这是一个什么东西,那我们就来研究下服务启动
(四) 服务启动
下面我们先来了解下一下启动系统服务的两种方式:
- 一种是通过SystemServiceManager的startService(),该方法用于启动继承于SystemService的服务。主要功能:创建serviceClass的对象,将刚创建的对象添加到SystemServiceManager的成员变量mServices,再调用刚创建对象的onStart()方法。对于服务启动到一定阶段,进入相应的Phase时,会调用SystemServiceManager的startBootPhase()回调方法,该方法会循环遍历所有向SystemServiceManager注册过的onBootPhase()方法。
- 另一种是通过ServiceManager的addService(String name,IBinder service),该方法用于初始化继承于IBinder的服务。主要功能将服务向Native层的ServiceManager注册服务。
关于第二种,即通过ServiceManager的addService(String name,IBinder service),我们在讲解Binder机制的时候,就已经讲解了,我们就不说了,下面我们来重点说下上面第一种,说到第一种,就不能不提一个类即SystemService
为了让大家对这个类有一个清晰的认识,我还是把其比较重要的代码粘贴上来
23/**
24 * The base class for services running in the system process. Override and implement
25 * the lifecycle event callback methods as needed.
26 *
27 * The lifecycle of a SystemService:
28 *
29 * - The constructor is called and provided with the system {@link Context}
30 * to initialize the system service.
31 *
- {@link #onStart()} is called to get the service running. The service should
32 * publish its binder interface at this point using
33 * {@link #publishBinderService(String, IBinder)}. It may also publish additional
34 * local interfaces that other services within the system server may use to access
35 * privileged internal functions.
36 *
- Then {@link #onBootPhase(int)} is called as many times as there are boot phases
37 * until {@link #PHASE_BOOT_COMPLETED} is sent, which is the last boot phase. Each phase
38 * is an opportunity to do special work, like acquiring optional service dependencies,
39 * waiting to see if SafeMode is enabled, or registering with a service that gets
40 * started after this one.
41 *
42 * NOTE: All lifecycle methods are called from the system server's main looper thread.
43 *
44 *
45 * {@hide}
46 */
47public abstract class SystemService {
48 /*
49 * Boot Phases
50 */
51 public static final int PHASE_WAIT_FOR_DEFAULT_DISPLAY = 100; // maybe should be a dependency?
52
53 /**
54 * After receiving this boot phase, services can obtain lock settings data.
55 */
56 public static final int PHASE_LOCK_SETTINGS_READY = 480;
57
58 /**
59 * After receiving this boot phase, services can safely call into core system services
60 * such as the PowerManager or PackageManager.
61 */
62 public static final int PHASE_SYSTEM_SERVICES_READY = 500;
63
64 /**
65 * After receiving this boot phase, services can broadcast Intents.
66 */
67 public static final int PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY = 550;
68
69 /**
70 * After receiving this boot phase, services can start/bind to third party apps.
71 * Apps will be able to make Binder calls into services at this point.
72 */
73 public static final int PHASE_THIRD_PARTY_APPS_CAN_START = 600;
74
75 /**
76 * After receiving this boot phase, services can allow user interaction with the device.
77 * This phase occurs when boot has completed and the home application has started.
78 * System services may prefer to listen to this phase rather than registering a
79 * broadcast receiver for ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED to reduce overall latency.
80 */
81 public static final int PHASE_BOOT_COMPLETED = 1000;
.....
120 /**
121 * Called on each phase of the boot process. Phases before the service's start phase
122 * (as defined in the @Service annotation) are never received.
123 *
124 * @param phase The current boot phase.
125 */
126 public void onBootPhase(int phase) {}
....
}
我们先来看下其类的注释
1、类注释翻译
系统进程中运行的服务的基类。可以根据需要覆盖其生命周期事件的回调方法。
SystemService的生命周期的流程
- 1、先调用带有context的构造函数,用于初始化系统的服务。
- 2、调用onStart()方法,来启动服务运行,该服务应该在此处调用publishBinderService(String,IBinder)方法来发布其绑定的接口。当然它也可能发布额外的本地接口,系统服务器内的其他服务可以调用这些本地服务来访问其内部。
- 3、调用onBootPhase(int)的次数很多,直到PHASE_BOOT_COMPLETED被发送,这是最后一次启动阶段的标志。每个阶段都要进行特定的工作。例如获取可选的服务依赖关系、查看是否启动了SafeMode、或者注册一个依赖该服务启动后的服务。
- 注意:所有生命周期的方法都是从系统服务的主循环线程调用的。
2、几个阶段的解释:
下面我们来看下几个PHASE的阶段:
- PHASE_WAIT_FOR_DEFAULT_DISPLAY:等待显示阶段
- PHASE_LOCK_SETTINGS_READY:锁定阶段:
即在启动阶段后,service就可以获得锁定的设置数据。- PHASE_SYSTEM_SERVICES_READY:系统服务准备就绪阶段:
在启动阶段后,就可以安心的调用核心系统服务,比如PowerManager或者PackageManager- PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY:AMS准备就绪阶段:
在启动阶段后,service就可以发送广播了。- PHASE_THIRD_PARTY_APPS_CAN_START:启动第三方应用阶段:
在启动阶段后,服务就可以启动/绑定第三方应用程序App就可以。并在此时调用Binder服务。- PHASE_BOOT_COMPLETED:启动结束阶段
在启动阶段后,此时服务可以运行用户与设备进行交互。当启动完成后Home应用程序会在此阶段启动。系统服务可能会监听这个阶段,而不是注册ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED的广播接收器来减少整体延迟。
3、为什么要这么做:
SystemServer会依次启动许多服务,但服务之间的功能是相互依赖的。因此,每个服务刚被启动的时候,都必须完成最基本的初始化。
所以当系统运动到某个阶段时,调用SystemServiceManager的startBootPhase,这样所有的服务都可以进一步完成换这个阶段可以进行的初始化工作。
通过这个方式,每个服务的初始化过程可以按阶段分为好几个部分,增加了不同阶段的初始化工作的清晰度;同时,每个阶段调用startBootPhase函数,就像一种同步机制一样,让所有服务的初始化进程保持一致的步调。
4、SystemServiceManager的startBootPhase(int)方法解析
代码在SystemServiceManager.java
/**
118 * Starts the specified boot phase for all system services that have been started up to
119 * this point.
120 *
121 * @param phase The boot phase to start.
122 */
123 public void startBootPhase(final int phase) {
124 if (phase <= mCurrentPhase) {
125 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Next phase must be larger than previous");
126 }
127 mCurrentPhase = phase;
128
129 Slog.i(TAG, "Starting phase " + mCurrentPhase);
130
131 final int serviceLen = mServices.size();
132 for (int i = 0; i < serviceLen; i++) {
133 final SystemService service = mServices.get(i);
134 try {
135 service.onBootPhase(mCurrentPhase);
136 } catch (Exception ex) {
137 throw new RuntimeException("Failed to boot service "
138 + service.getClass().getName()
139 + ": onBootPhase threw an exception during phase "
140 + mCurrentPhase, ex);
141 }
142 }
143 }
先翻译一下注释:
确保在这个节点上,开启了特殊的引导阶段的所有系统服务
5、系统服务启动的流程:
SystemServiceManager的startBootPhase()贯穿system_server进程的整个启动过程:
其中PHASE_BOOT_COMPLETED=1000,该阶段是发生在boot完成和home应用启动完毕。系统服务更倾向于监听该阶段,而不是注册广播ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED,从而降低系统延迟。
下面我们就详细每个流程中的具体事情
- 最开始的时候:创建四大引导服务:
- AMS(ActivityManagerService)
- PowerManagerService(这里通常不用PMS表示,通常的PMS表示;PackageManagerService)
- LightsService
- DMS(DisplayManagerService)
- 1 PHASE_WAIT_FOR_DEFAULT_DISPLAY(等待显示阶段):
- 进行回调onBootPhase(PHASE_WAIT_FOR_DEFAULT_DISPLAY)
- DisplayManagerService
- 创建服务
- PackageManagerService类
- WindowManagerService类
- InputManagerService类
- NetworkManagerService类
- FingerprintService类
- LauncherAppsService类
- .....
- 2 PHASE_LOCK_SETTINGS_READY(锁定阶段):
- 进行回调进行回调onBootPhase(PHASE_LOCK_SETTINGS_READY)
- DevicePolicyManagerService类
- 3 PHASE_SYSTEM_SERVICES_READY(系统服务准备阶段):进入该阶段的服务能安全的调用核心系统服务。此时就不创建服务
- 进行回调onBootPhase(PHASE_SYSTEM_SERVICES_READY)
- AlarmManagerService类
- JobSchedulerService类
- NotificationManagerService类
- BackupManagerService类
- UsageStatsService类
- DeviceIdleController类
- TrustManagerService类
- UiModeManagerService类
- BluetoothService类
- BluetoothManagerService类
- EthernetService类
- WifiP2pService类
- WifiScanningService类
- WifiService类
- RttService类
- 各大服务执行systemReady()
- WindowManagerService.systemReady():
- PowerManagerService.systemReady():
- PackageManagerService.systemReady():
- DisplayManagerService.systemReady():
- 4 PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY(AMS准备就绪阶段):AMS准备就绪了,(其中AMS中的mSystemReady变量为true)。但是此时system_server主线程并没有准备就绪。
- 进行回调onBootPhase(PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY):
- MountService类
- TelecomLoaderService类
- UsbService类
- WebViewUpdateService类
- DockObserver类
- BatteryService类
- ActivityManagerService启动native crash监控,加载WebView,启动SystemUI等,顺序如下:
- mActivityManagerService.startObservingNativeCrashes();
- WebViewFactory.prepareWebViewInSystemServer();
- startSystemUi(context);
- networkScoreF.systemReady();
- networkManagementF.systemReady();
- networkStatsF.systemReady();
- networkPolicyF.systemReady();
- connectivityF.systemReady();
- audioServiceF.systemReady();
- Watchdog.getInstance().start();
- 5 PHASE_THIRD_PARTY_APPS_CAN_START(启动第三方应用阶段):
- 进行回调onBootPhase(PHASE_THIRD_PARTY_APPS_CAN_START):
- JobSchedulerService类
- NotificationManagerService类
- BackupManagerService类
- AppWidgetService类
- GestureLauncherService类
- DreamManagerService类
- TrustManagerService类
- VoiceInteractionManagerService类
- 接下来,各种服务的systemRunning的流程:
- WallpaperManagerService.systemRunning()
- InputMethodManagerService.systemRunning()
- LocationManagerService.systemRunning()
- CountryDetectorService.systemRunning()
- NetworkTimeUpdateService.systemRunning()
- CommonTimeManagementService.systemRunning()
- TextServicesManagerService.systemRunning()
- AssetAtlasService.systemRunning()
- InputManagerService.systemRunning()
- TelephonyRegistry.systemRunning()
- MediaRouterService.systemRunning()
- MmsServiceBroker .systemRunning()
- 6 PHASE_BOOT_COMPLETED(启动结束阶段):最后调用ActivityManagerService.finishBooting()时,则进入该阶段。至此,系统服务启动阶段完成就绪,system_server进程启动完成则进入Looper.loop()状态,随时待命,等待消息队列MessageQueue中的消息到来,则马上进入执行状态。
6、服务类别
system_server进程,从源码角度划分为引导服务、核心服务、普通服务3类(也就其他服务,因为源码上为other)。具体划分如下:
引导服务(7个):
ActivityManagerService
PowerManagerService
LightsService
DisplayManagerService
PackageManagerService
UserManagerService
SensorService核心服务(3个):
BatteryService
UsageStatsService
WebViewUpdateService其他服务(76个):
AlarmManagerService
VibratorService
....
7、服务介绍
SystemServer启动了很多重要的系统服务,我们就来简单介绍下:
AccesssibilityManagerService:截取用户输入,并根据输入给用户一些额外的反馈,起到辅助效果的服务。
AccountManagerService:管理设备中所有账号的服务,有账号、密码、授权管理功能
ActivityManagerService:Android的核心服务,管理所有组件
AlarmManagerService:Android系统的闹钟服务
AppWidgetService:管理Laucher的用户Widget的服务
AsserAtlasService:把预加载的图片资源都打包成一张单一的图片,并跨进程共享由此产生的纹理,以降低总的内存使用情况的服务。
AudioService:提供应用设置音量、音效、铃声等接口的服务
BackupManagerService:备份和恢复应用数据的服务
BatteryService:监控电池状态的服务,当电池状态改变时会广播Intent。
BluetoothManagerService:管理系统蓝牙设备的服务
CertBlacklister:提供了一种简单的机制来更新系统SSL证书的公共密钥和序列号黑名单服务
ClipboardService:提供系统级别的剪贴板功能的服务
CommonTimeManagermentService:管理本地公共时间配置的服务
ConnectivityService:Android系统提供网络连接的服务
ContentService:管理Android中数据更新通知的服务,当ContentProvider中的内容发生变化时,它将发出广播通知这种变化
CountryDetectorService:检测当前用户所属国家的服务
DevicePolicyManagerService:提供系统配置管理的服务
DeviceStorageMonitorService:监控存储空间的服务,当存储空间低于10%的时候会广播警告
DiskStatsService:提供存储空间的统计服务
DisplayManagerService:管理心事设备的服务
DreamManagerService:管理屏幕保护的应用
DropBoxManagerService:产生和管理系统运行时的日志文件的服务。
EntroypyMixer:熵服务周期性地加载和保存随机信息,防止/dev/random 的状态编程可预知的,否则,这样一些需要随机数的应用程序得到将是重新的值。这个服务没有为应用程序提供接口
IdleMaintenanaceService:监视系统济宁idle服务。通过它可以获得系统计入idle通知
InputManagerService:管理键盘和触屏输入的服务
InputMethodManagerService:提供输入法管理功能的服务,包括disable/enable输入法,切换输入法等
LightsService:管理和控制光线传感器的服务
LocationManagerService:提供位置管理的服务
LockSettingService:管理锁屏服务
MountService:管理Android系统存储设备的服务
NetworkManagermentService:提供网络物理接口管理服务
NetworkPolicyManagerService:提供网络管理策略服务
NetworkStateService:管理网络连接状态的服务,当网络状态变化时,将发出广播
NetworkTimeUpdateService:提供根据网络时间更新本地时间的服务
NotificationManagerService:管理系统的Notifaction的服务
NsdService:基于苹果的Bonjour服务发现协议,提供远程的发现和零配置功能的服务
PackageManagerService:Android的包管理服务
PrintManagerService:提供打印管理的服务
RecognitionManagerService:身份识别服务
SamplingProfilerService:记录和分析系统启动性能的服务
SchedulingPolicyService:设置线程调度策略的服务
SearchManagerService:提供搜索功能的服务
SerialService:提供打开接串口设备的服务
StatusBarManagerService:提供更新stateBar上图标、动画接口的服务
TelephonyRegistry:监听和管理通话事件和状态的服务
TextServicesManagerService:提供拼写检查等文本功能的服务
TwilightService:根据用户的地理位置判断目前是否是黄昏时分的服务
UIModeManagerService:管理和设备系统的UI模式的服务
UsbService:管理USB设备和连接的服务
UserManagerService:管理Android用户的身份和信息的服务
VibratorService:管理和控制振动设备的服务
WallpaperManagerService:管理桌面背景的服务
WifiP2pService:管理WiFi点对点连接的服务
WifiService:管理和控制Wifi设备的服务
WindowManagerService:Android的核心服务,提供窗口管理功能。
至此SystemServer启动,我们已经讲解完毕了,有人会说,那没有启动Launcher呢,对的,其实启动Launcher不是在SystemServer,那它在哪里,它在ActivityManagerService里面,下面让我们来一起看一下ActivityManagerService的启动流程。
五、启动Launcher
(一)、启动Launcher的根源
在上面讲解启动各种服务时候,讲解到在SystemServer.java的startOtherServices()方法里面的1096行调用 mActivityManagerService.systemReady()方法如下:
代码在SystemServer.java 1096行
1091 // We now tell the activity manager it is okay to run third party
1092 // code. It will call back into us once it has gotten to the state
1093 // where third party code can really run (but before it has actually
1094 // started launching the initial applications), for us to complete our
1095 // initialization.
1096 mActivityManagerService.systemReady(new Runnable() {
1097 @Override
1098 public void run() {
1099 Slog.i(TAG, "Making services ready");
1100 mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(
1101 SystemService.PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY);
1102
1103 try {
1104 mActivityManagerService.startObservingNativeCrashes();
1105 } catch (Throwable e) {
1106 reportWtf("observing native crashes", e);
1107 }
1108
1109 Slog.i(TAG, "WebViewFactory preparation");
1110 WebViewFactory.prepareWebViewInSystemServer();
1111
1112 try {
1113 startSystemUi(context);
1114 } catch (Throwable e) {
1115 reportWtf("starting System UI", e);
1116 }
1117 try {
1118 if (networkScoreF != null) networkScoreF.systemReady();
1119 } catch (Throwable e) {
1120 reportWtf("making Network Score Service ready", e);
1121 }
1122 try {
1123 if (networkManagementF != null) networkManagementF.systemReady();
1124 } catch (Throwable e) {
1125 reportWtf("making Network Managment Service ready", e);
1126 }
1127 try {
1128 if (networkStatsF != null) networkStatsF.systemReady();
1129 } catch (Throwable e) {
1130 reportWtf("making Network Stats Service ready", e);
1131 }
1132 try {
1133 if (networkPolicyF != null) networkPolicyF.systemReady();
1134 } catch (Throwable e) {
1135 reportWtf("making Network Policy Service ready", e);
1136 }
1137 try {
1138 if (connectivityF != null) connectivityF.systemReady();
1139 } catch (Throwable e) {
1140 reportWtf("making Connectivity Service ready", e);
1141 }
1142 try {
1143 if (audioServiceF != null) audioServiceF.systemReady();
1144 } catch (Throwable e) {
1145 reportWtf("Notifying AudioService running", e);
1146 }
1147 Watchdog.getInstance().start();
1148
1149 // It is now okay to let the various system services start their
1150 // third party code...
1151 mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(
1152 SystemService.PHASE_THIRD_PARTY_APPS_CAN_START);
1153
1154 try {
1155 if (wallpaperF != null) wallpaperF.systemRunning();
1156 } catch (Throwable e) {
1157 reportWtf("Notifying WallpaperService running", e);
1158 }
1159 try {
1160 if (immF != null) immF.systemRunning(statusBarF);
1161 } catch (Throwable e) {
1162 reportWtf("Notifying InputMethodService running", e);
1163 }
1164 try {
1165 if (locationF != null) locationF.systemRunning();
1166 } catch (Throwable e) {
1167 reportWtf("Notifying Location Service running", e);
1168 }
1169 try {
1170 if (countryDetectorF != null) countryDetectorF.systemRunning();
1171 } catch (Throwable e) {
1172 reportWtf("Notifying CountryDetectorService running", e);
1173 }
1174 try {
1175 if (networkTimeUpdaterF != null) networkTimeUpdaterF.systemRunning();
1176 } catch (Throwable e) {
1177 reportWtf("Notifying NetworkTimeService running", e);
1178 }
1179 try {
1180 if (commonTimeMgmtServiceF != null) {
1181 commonTimeMgmtServiceF.systemRunning();
1182 }
1183 } catch (Throwable e) {
1184 reportWtf("Notifying CommonTimeManagementService running", e);
1185 }
1186 try {
1187 if (textServiceManagerServiceF != null)
1188 textServiceManagerServiceF.systemRunning();
1189 } catch (Throwable e) {
1190 reportWtf("Notifying TextServicesManagerService running", e);
1191 }
1192 try {
1193 if (atlasF != null) atlasF.systemRunning();
1194 } catch (Throwable e) {
1195 reportWtf("Notifying AssetAtlasService running", e);
1196 }
1197 try {
1198 // TODO(BT) Pass parameter to input manager
1199 if (inputManagerF != null) inputManagerF.systemRunning();
1200 } catch (Throwable e) {
1201 reportWtf("Notifying InputManagerService running", e);
1202 }
1203 try {
1204 if (telephonyRegistryF != null) telephonyRegistryF.systemRunning();
1205 } catch (Throwable e) {
1206 reportWtf("Notifying TelephonyRegistry running", e);
1207 }
1208 try {
1209 if (mediaRouterF != null) mediaRouterF.systemRunning();
1210 } catch (Throwable e) {
1211 reportWtf("Notifying MediaRouterService running", e);
1212 }
1213
1214 try {
1215 if (mmsServiceF != null) mmsServiceF.systemRunning();
1216 } catch (Throwable e) {
1217 reportWtf("Notifying MmsService running", e);
1218 }
1219 }
1220 });
我们来看下ActivityManagerService的systemReady(Runnable)方法
(二)、ActivityManagerService. systemReady(Runnable)方法解析
11719 public void systemReady(final Runnable goingCallback) {
11720 synchronized(this) {
11721 if (mSystemReady) {
11722 // If we're done calling all the receivers, run the next "boot phase" passed in
11723 // by the SystemServer
11724 if (goingCallback != null) {
11725 goingCallback.run();
11726 }
11727 return;
11728 }
11729
11730 mLocalDeviceIdleController
11731 = LocalServices.getService(DeviceIdleController.LocalService.class);
11732
11733 // Make sure we have the current profile info, since it is needed for
11734 // security checks.
11735 updateCurrentProfileIdsLocked();
11736
11737 mRecentTasks.clear();
11738 mRecentTasks.addAll(mTaskPersister.restoreTasksLocked());
11739 mRecentTasks.cleanupLocked(UserHandle.USER_ALL);
11740 mTaskPersister.startPersisting();
11741
11742 // Check to see if there are any update receivers to run.
11743 if (!mDidUpdate) {
11744 if (mWaitingUpdate) {
11745 return;
11746 }
11747 final ArrayList doneReceivers = new ArrayList();
11748 mWaitingUpdate = deliverPreBootCompleted(new Runnable() {
11749 public void run() {
11750 synchronized (ActivityManagerService.this) {
11751 mDidUpdate = true;
11752 }
11753 showBootMessage(mContext.getText(
11754 R.string.android_upgrading_complete),
11755 false);
11756 writeLastDonePreBootReceivers(doneReceivers);
11757 systemReady(goingCallback);
11758 }
11759 }, doneReceivers, UserHandle.USER_OWNER);
11760
11761 if (mWaitingUpdate) {
11762 return;
11763 }
11764 mDidUpdate = true;
11765 }
11766
11767 mAppOpsService.systemReady();
11768 mSystemReady = true;
11769 }
11770
11771 ArrayList procsToKill = null;
11772 synchronized(mPidsSelfLocked) {
11773 for (int i=mPidsSelfLocked.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
11774 ProcessRecord proc = mPidsSelfLocked.valueAt(i);
11775 if (!isAllowedWhileBooting(proc.info)){
11776 if (procsToKill == null) {
11777 procsToKill = new ArrayList();
11778 }
11779 procsToKill.add(proc);
11780 }
11781 }
11782 }
11783
11784 synchronized(this) {
11785 if (procsToKill != null) {
11786 for (int i=procsToKill.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
11787 ProcessRecord proc = procsToKill.get(i);
11788 Slog.i(TAG, "Removing system update proc: " + proc);
11789 removeProcessLocked(proc, true, false, "system update done");
11790 }
11791 }
11792
11793 // Now that we have cleaned up any update processes, we
11794 // are ready to start launching real processes and know that
11795 // we won't trample on them any more.
11796 mProcessesReady = true;
11797 }
11798
11799 Slog.i(TAG, "System now ready");
11800 EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_AMS_READY,
11801 SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
11802
11803 synchronized(this) {
11804 // Make sure we have no pre-ready processes sitting around.
11805
11806 if (mFactoryTest == FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
11807 ResolveInfo ri = mContext.getPackageManager()
11808 .resolveActivity(new Intent(Intent.ACTION_FACTORY_TEST),
11809 STOCK_PM_FLAGS);
11810 CharSequence errorMsg = null;
11811 if (ri != null) {
11812 ActivityInfo ai = ri.activityInfo;
11813 ApplicationInfo app = ai.applicationInfo;
11814 if ((app.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM) != 0) {
11815 mTopAction = Intent.ACTION_FACTORY_TEST;
11816 mTopData = null;
11817 mTopComponent = new ComponentName(app.packageName,
11818 ai.name);
11819 } else {
11820 errorMsg = mContext.getResources().getText(
11821 com.android.internal.R.string.factorytest_not_system);
11822 }
11823 } else {
11824 errorMsg = mContext.getResources().getText(
11825 com.android.internal.R.string.factorytest_no_action);
11826 }
11827 if (errorMsg != null) {
11828 mTopAction = null;
11829 mTopData = null;
11830 mTopComponent = null;
11831 Message msg = Message.obtain();
11832 msg.what = SHOW_FACTORY_ERROR_MSG;
11833 msg.getData().putCharSequence("msg", errorMsg);
11834 mUiHandler.sendMessage(msg);
11835 }
11836 }
11837 }
11838
11839 retrieveSettings();
11840 loadResourcesOnSystemReady();
11841
11842 synchronized (this) {
11843 readGrantedUriPermissionsLocked();
11844 }
11845
11846 if (goingCallback != null) goingCallback.run();
11847
11848 mBatteryStatsService.noteEvent(BatteryStats.HistoryItem.EVENT_USER_RUNNING_START,
11849 Integer.toString(mCurrentUserId), mCurrentUserId);
11850 mBatteryStatsService.noteEvent(BatteryStats.HistoryItem.EVENT_USER_FOREGROUND_START,
11851 Integer.toString(mCurrentUserId), mCurrentUserId);
11852 mSystemServiceManager.startUser(mCurrentUserId);
11853
11854 synchronized (this) {
11855 if (mFactoryTest != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
11856 try {
11857 List apps = AppGlobals.getPackageManager().
11858 getPersistentApplications(STOCK_PM_FLAGS);
11859 if (apps != null) {
11860 int N = apps.size();
11861 int i;
11862 for (i=0; i 本文不是主要讲解ActivityManagerService,所以这里面的内容,我们在讲解ActivityManagerService启动流程的时候再详细讲解。
请看11878行startHomeActivityLocked(mCurrentUserId, "systemReady");
(三)、 startHomeActivityLocked(int,String)方法解析
代码在ActivityManagerService.java 3479行
3479 boolean startHomeActivityLocked(int userId, String reason) {
3480 if (mFactoryTest == FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL
3481 && mTopAction == null) {
3482 // We are running in factory test mode, but unable to find
3483 // the factory test app, so just sit around displaying the
3484 // error message and don't try to start anything.
3485 return false;
3486 }
3487 Intent intent = getHomeIntent();
3488 ActivityInfo aInfo =
3489 resolveActivityInfo(intent, STOCK_PM_FLAGS, userId);
3490 if (aInfo != null) {
3491 intent.setComponent(new ComponentName(
3492 aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName, aInfo.name));
3493 // Don't do this if the home app is currently being
3494 // instrumented.
3495 aInfo = new ActivityInfo(aInfo);
3496 aInfo.applicationInfo = getAppInfoForUser(aInfo.applicationInfo, userId);
3497 ProcessRecord app = getProcessRecordLocked(aInfo.processName,
3498 aInfo.applicationInfo.uid, true);
3499 if (app == null || app.instrumentationClass == null) {
3500 intent.setFlags(intent.getFlags() | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
3501 mStackSupervisor.startHomeActivity(intent, aInfo, reason);
3502 }
3503 }
3504
3505 return true;
3506 }
我们看到了在startHomeActivityLocked里面首选调用getHomeIntent来获取Launcher对应的Intent;其次调用resolveActivityInfo方法来获取对应的ActivityInfo,如果这个ActivityInfo不为null,则new一个ActivityInfo,最后调用mStackSupervisor的startHomeActivity来启动Launcher。所以这里面有两个重要方法是getHomeIntent和startHomeActivity这两个方法
(四)、 getHomeIntent()方法解析
代码在ActivityManagerService.java 3470行
3470 Intent getHomeIntent() {
3471 Intent intent = new Intent(mTopAction, mTopData != null ? Uri.parse(mTopData) : null);
3472 intent.setComponent(mTopComponent);
3473 if (mFactoryTest != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
3474 intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_HOME);
3475 }
3476 return intent;
3477
这个方法内部很简单就是构建一个Intent对象,并且返回。
(四)、 startHomeActivity(Intent,ActivityInfo,String)方法解析
908 void startHomeActivity(Intent intent, ActivityInfo aInfo, String reason) {
909 moveHomeStackTaskToTop(HOME_ACTIVITY_TYPE, reason);
910 startActivityLocked(null /* caller */, intent, null /* resolvedType */, aInfo,
911 null /* voiceSession */, null /* voiceInteractor */, null /* resultTo */,
912 null /* resultWho */, 0 /* requestCode */, 0 /* callingPid */, 0 /* callingUid */,
913 null /* callingPackage */, 0 /* realCallingPid */, 0 /* realCallingUid */,
914 0 /* startFlags */, null /* options */, false /* ignoreTargetSecurity */,
915 false /* componentSpecified */,
916 null /* outActivity */, null /* container */, null /* inTask */);
917 if (inResumeTopActivity) {
918 // If we are in resume section already, home activity will be initialized, but not
919 // resumed (to avoid recursive resume) and will stay that way until something pokes it
920 // again. We need to schedule another resume.
921 scheduleResumeTopActivities();
922 }
923 }
代码很简单,首先把Launcher的Activity移到最上面,然后开启。
上一篇文章 Android系统启动——5 zyogte进程(Java篇)
下一篇文章 Android系统启动——7附录1:Android属性系统