基于编程方式实现条件装配Spring Boot 自动装配
@Profile是3.1提出来的,但在4.0 发生了变化---通过注解调解
查看源码来看一下:
@Profile标注了@Conditional(ProfileCondition.class)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(ProfileCondition.class)//profile在4.0 发生了变化---通过ProfileCondition实现的
public @interface Profile {
/**
* The set of profiles for which the annotated component should be registered.
*/
String[] value();
}
ProfileCondition类,实现了Condition接口
ass ProfileCondition implements Condition {
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
MultiValueMap attrs = metadata.getAllAnnotationAttributes(Profile.class.getName());
if (attrs != null) {
for (Object value : attrs.get("value")) {
if (context.getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(Profiles.of((String[]) value))) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
Condition接口,是通过上下文,元数据类型的注解,来查看是否匹配,条件是否满足
注意:AnnotatedTypeMetadata接口--元信息,保留一些关于标注的信息,就是下面提到的一些属性方法等
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Condition {
/**
* Determine if the condition matches.
* @param context the condition context
* @param metadata metadata of the {@link org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata class}
* or {@link org.springframework.core.type.MethodMetadata method} being checked
* @return {@code true} if the condition matches and the component can be registered,
* or {@code false} to veto the annotated component's registration
*/
boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata);
}
再来看一个:SpringBoot的ConditionalOnProperty注解
观察到,这个注解也是标注了一个@Conditional({OnPropertyCondition.class}),OnPropertyCondition这个类最终也是实现的Condition接口
1、
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Documented
@Conditional({OnPropertyCondition.class})
public @interface ConditionalOnProperty {
String[] value() default {};
String prefix() default "";
String[] name() default {};
String havingValue() default "";
boolean matchIfMissing() default false;
}
2、
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 40)
class OnPropertyCondition extends SpringBootCondition {...}
3、
public abstract class SpringBootCondition implements Condition {...}
参照以上的源码实现一个小栗子,基于编程方式实现 - @ConditionalOnSystemProperty
【小栗子】
按照源码的提示,新建一个condition包名
1、新建一个注解ConditionalOnSystemProperty,定义属性方法
/**
* java系统属性 条件判断*
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Documented
@Conditional(OnSystemPropertyCondition.class)
public @interface ConditionalOnSystemProperty {
/**
* Java 系统属性名称
* @return
*/
String name();
/**
* Java 系统属性值
* @return
*/
String value();
}
2、实现OnSystemPropertyCondition
参照:OnPropertyCondition类继承SpringBootCondition ,
SpringBootCondition 是一个抽象的实现,最终还是实现Condition,所以这里就直接实现Condition接口
采用哪个都可以SpringBootCondition或者Condition都可以。
/**
* 系统属性条件判断
*/
public class OnSystemPropertyCondition implements Condition {
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
Map attributes = metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(ConditionalOnSystemProperty.class.getName());
//获取name,value
String propertyName = String.valueOf(attributes.get("name"));
String propertyValue = String.valueOf(attributes.get("value"));
//取到的值是不是和系统里的相匹配
String javaPropertyValue = System.getProperty(propertyName);
return propertyValue.equals(javaPropertyValue);
}
}
说明:
有很多获取metadata的方式,这里采用
getAnnotationAttributes(),返回值是Map
在这里也就是检索ConditionalOnSystemProperty里定义的是name和value的属性方法
3、创建引导类
bootstrap包下,新建引导类ConditionOnSystemPropertyBootstrap
引导类启动的时候@ConditionalOnSystemProperty注解会被激活
/**
* 系统属性条件引导类
*/
public class ConditionOnSystemPropertyBootstrap {
//定义一个bean:helloWorld
@Bean
@ConditionalOnSystemProperty(name = "user.name",value = "Lenovo")//进行条件装配,和系统的名字一样的话,就导入进来
public String helloWorld() {
return "Hello,World PK";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = new SpringApplicationBuilder(ConditionOnSystemPropertyBootstrap.class)
.web(WebApplicationType.NONE)
.run(args);
// 条件满足的话,通过名称和类型获取 helloWorld Bean,不满足无法获取
String helloWorld = context.getBean("helloWorld", String.class);
System.out.println("helloWorld Bean : " + helloWorld);
//关闭上下文
context.close();
}
}
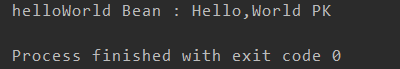
4、运行引导类
value的值和系统的名称相匹配,条件是满足的,返回了Hello,World PK
条件不满足的时候,会报错,bean找不到