iOS 9.0之前 ,使用NSURLConnection比较多
iOS 7.0之后,苹果官方推出NSURLSession,并在9.0之后推荐使用且丢弃了NSURLConnection
因为NSURLSession在异步的处理上比NSURLConnection好很多
本文作为学习和了解,详解iOS9.0之前的NSURLConnection
NSURLConnection:
- 从 iOS 2.0 开始,已经有10多年的历史了
异步方法在 iOS 5.0 之后才有 ,
在 iOS 5.0 之后,是通过代理的方式,来实现网络开发
本例使用NSURLConnection、NSFileHandle、NSOutputStream
实现了从本地服务器下载一个700M视频的demo
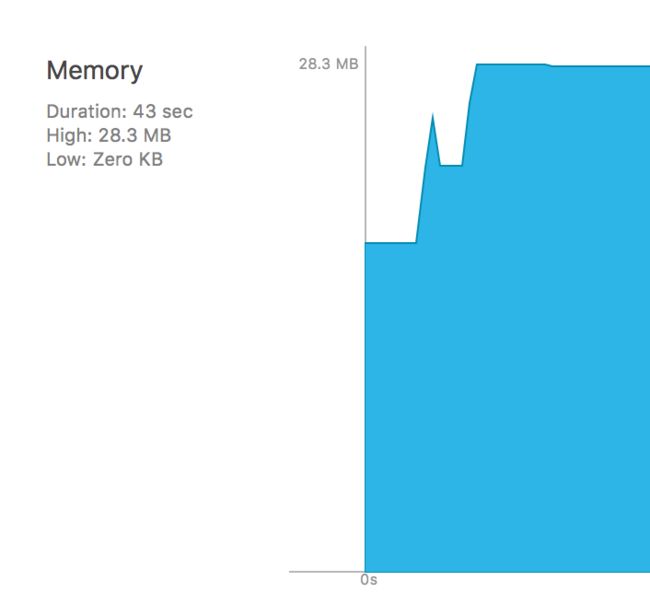
对内存进行了优化,内存一直保持在30M之内
并用GCD+NSRunloop进行异步下载
不影响UI主线程
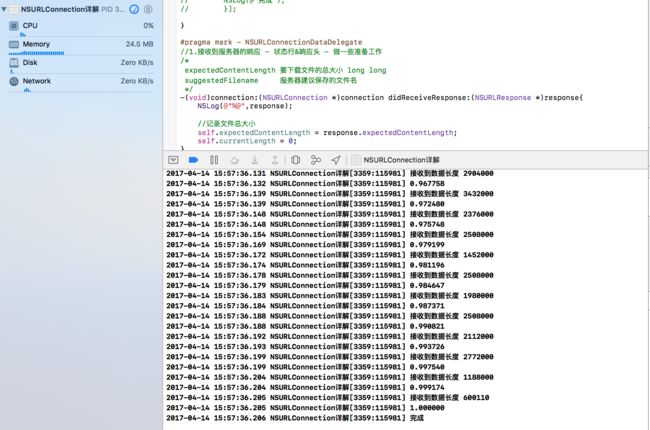
并在后台打印出下载完成进度百分比
Demo详解:
#import "ViewController.h"
// Newsstand Kit‘s 杂志包,是专门做杂志的,主要在国外使用,因为国内的书籍盗版太严重
// ISBN书号,电子书也必须是唯一的
// NSURLConnectionDownloadDelegate 方法主要针对杂志的下载提供接口
// 如果在开发中,使用 NSURLConnectionDownloadDelegate 代理方法下载,能够监听下载进度,但是无法找到下载的文件
@interface ViewController ()
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UIProgressView *Progress;
@property(nonatomic,assign)long long expectedContentLength; //要下载文件的总长度
@property(nonatomic,assign)long long currentLength; //当前下载的长度
//@property(nonatomic,strong) NSMutableData *fileData; //用来每次接受到数据,拼接数据使用
@property(nonatomic,copy) NSString *tartgetFilePath; //保存的目标路径
//@property(nonatomic,assign,getter=isFinished)BOOL finished;
@property(nonatomic,assign)CFRunLoopRef downloadRunloop; //下载线程的运行循环
/*
保存文件的输出流
- (void)open; 写入之前,打开流
- (void)close; 完成之后,关闭流
*/
@property(nonatomic,strong)NSOutputStream *fileStrem;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
}
/**
NSURLConnection - 从 iOS 2.0 开始,已经有10多年的历史了
异步方法在 iOS 5.0 之后才有 , 在 iOS 5.0 之后,是通过代理的方式,来实现网络开发
那时是iOS网络开发的黑暗史,网络开发很难
就因为这个黑暗史,才成就了一些第三方框架: AFN,ASI这些第三方框架
NS - NextStep 公司的缩写
- 开发简单的网络请求比较方便,可以采用异步方法
- 开发发杂的网络请求,例如:大文件下载,仍然需要使用代理来开发,非常繁琐!
**对NSURLConnection 的一些细节有所了解
问题:1.没有下载进度,会影响用户体验
2.有内存峰值,下载的文件有多大,NSData就会占用多大内存
解决方法:
- 通过代理的方式解决
1.进度跟进,解决思路:
1>在响应方法中获得文件总大小
2>每次接受到数据,计算获得数据的总长度,和总大小相比,计算出百分比
2.保存文件的思路
1>保存完成写入磁盘
测试结果:和异步方法执行一样,仍然存在内存峰值。
推测:苹果的异步方法的实现思路,和刚才的delegate实现思路一样
问题:下载的内存峰值依旧存在
2>下载一个写一个
1)NSFileHandle 彻底解决了内存峰值问题
2)NSOutputStream 输出流
- Socket 网络本质上,在客户端和服务器之间,数据的传递,都是以二进制流的方式传递的。
- 对数据流的操作,一定要有一些网络底层的思想之后,才容易理解
- 操作方式,比 FindHandle 更简洁
*/
-(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event{
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^{
//1.url
NSString *urlString = @"http://127.0.0.1/1.mp4";
urlString = [urlString stringByAddingPercentEscapesUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:urlString];
//2.request
NSURLRequest *request = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url];
//3.connection
//开始下载时的线程,是用 dispatch_async 创建的
NSLog(@"开始 %@",[NSThread currentThread]);
// For the connection to work correctly, the calling thread’s run loop must be operating in the default run loop mode.
//为了保证连接的工作正常,调用线程的run loop 必须运行在默认的运行循环模式下
NSURLConnection *conn = [NSURLConnection connectionWithRequest:request delegate:self];//使用代理
//设置代理工作的操作队列
[conn setDelegateQueue:[[NSOperationQueue alloc]init]];//新的问题 默认还在主线程工作,干扰主线程UI更新
//4.启动连接
[conn start];
// self.finished = NO;
//5.启动运行循环
// while (!self.isFinished) {
// //启动一个死循环,每次监听0.1秒
// [[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] runMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode beforeDate:[NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSinceNow:0.1]];
// }
//CoreFoundation框架(纯C语言,是Foundation的基础)中,提供了对运行循环更底层的操作
/*
CFRunLoopStop(rl) 停止当前的runloop
CFRunLoopGetCurrent()当前线程的runloop
CFRunLoopRun(); 直接运行当前线程的运行循环
以下代码,是最标准的 runloop 的操作方法
*/
//1.拿到当前线程的运行循环
self.downloadRunloop = CFRunLoopGetCurrent();
//2.启动运行循环
CFRunLoopRun();
NSLog(@"到我了吗?");
});
//直接下载视频
// [NSURLConnection sendAsynchronousRequest:request queue:[NSOperationQueue mainQueue] completionHandler:^(NSURLResponse * _Nullable response, NSData * _Nullable data, NSError * _Nullable connectionErro){
// [data writeToFile:@"/Users/Liu/Desktop/123.mp4" atomically:YES];
//
// NSLog(@"完成");
// }];
}
#pragma mark - NSURLConnectionDataDelegate
//1.接收到服务器的响应 - 状态行&响应头 - 做一些准备工作
/*
expectedContentLength 要下载文件的总大小 long long
suggestedFilename 服务器建议保存的文件名
*/
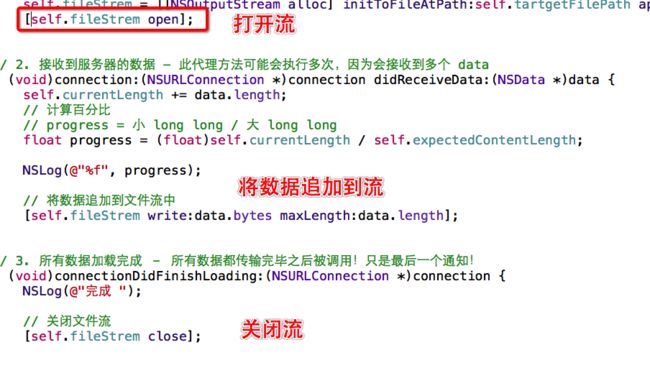
-(void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didReceiveResponse:(NSURLResponse *)response{
NSLog(@"%@",response);
//记录文件总大小
self.expectedContentLength = response.expectedContentLength;
self.currentLength = 0;
//生成目标文件路径
self.tartgetFilePath = [@"/Users/Liu/Desktop" stringByAppendingPathComponent:response.suggestedFilename];
//删除文件,removeItemAtPath 如果文件存在直接删除,如果文件不存在,什么也不做
[[NSFileManager defaultManager]removeItemAtPath:self.tartgetFilePath error:NULL];
//以追加的方式打开文件流
self.fileStrem = [[NSOutputStream alloc]initToFileAtPath:self.tartgetFilePath append:YES];
[self.fileStrem open];
}
//-(NSMutableData *)fileData{
// if(_fileData == nil){
// _fileData = [[NSMutableData alloc] init];
// }
// return _fileData;
//}
//2.接收到服务器的数据 - 此代理方法可能会执行多次 因为会收到多个data
-(void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didReceiveData:(NSData *)data{
NSLog(@"接收到数据长度 %tu",data.length);
self.currentLength +=data.length;
//计算百分比
//progress = 小 long long / 大 long long
float progress = (float)self.currentLength/self.expectedContentLength;
NSLog(@"%f %@",progress,[NSThread currentThread]);
//在主线程更新进度条
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
self.Progress.progress = progress;
});
//将数据追加到文件流中
[self.fileStrem write:data.bytes maxLength:data.length];
//拼接数据
//
// [self.fileData appendData:data];
}
//-(void)writeToFileWithData:(NSData *)data{
// // 文件操作
// /*
// NSFileManager :主要功能:创建目录,检查目录是否存在,遍历目录,删除文件。。。主要针对文件集的操作,类似于Finder
// NSFileHandle: 文件”句柄“, 如果在开发中,看到 Handle 这个单词,就意味着是对前面的单词“File”进行操作的对象
// 主要功能:对同一个文件进行二进制的读写操作的对象
// */
//
// //注意:如果文件不存在,fp 在实例化的结果是空
// NSFileHandle *fp = [NSFileHandle fileHandleForWritingAtPath:self.tartgetFilePath];
//
// //判断文件是否存在 - 如果存在,则追加数据;如果不存在,直接将数据写入磁盘
// if(fp == nil){
// [data writeToFile:self.tartgetFilePath atomically:YES];
// }else{
// //如果存在,将data“追加”到现有文件
// //1.将文件指针移动到文件的末尾
// [fp seekToEndOfFile];
//
// //2.写入文件
// [fp writeData:data];
//
// //3.关闭文件,在C语言的开发中,凡涉及到文件读写,打开和关闭通常是成对实现的
// [fp closeFile];
// }
//}
//3.所有数据加载完成 - 所有数据都传输完毕后调用,只是最后一个通知
-(void)connectionDidFinishLoading:(NSURLConnection *)connection{
//结束时代理工作的线程,是指定 NSOperationQueue 调度的
NSLog(@"完成 %@",[NSThread currentThread]);
//把数据写入磁盘
// [self.fileData writeToFile:self.tartgetFilePath atomically:YES];
// //释放 fileData
// self.fileData = nil;
[self.fileStrem close];
// //设置结束标记
// self.finished = YES;
//停止下载线程所在的运行循环
CFRunLoopStop(self.downloadRunloop);
}
//4.下载失败或者错误,提示:在正常商业应用开发中一定要做出错误处理
-(void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didFailWithError:(NSError *)error{
NSLog(@"失败 %@",error);
}
@end
PS:本文使用的下载源在本地服务器127.0.0.1,根据需要可以修改成其他下载源。