随着iPhone X发布,国内一些厂商也推出了刘海屏手机,即将发布的Android p也提供了对刘海屏的支持。so,我们的app也要提前做好适配。
什么是刘海屏?
屏幕的正上方居中位置(下图黑色区域)会被挖掉一个孔,屏幕被挖掉的区域无法正常显示内容,这种类型的屏幕就是刘海屏,也有其他叫法:挖孔屏、凹凸屏等等,这里统一按刘海屏命名。
目前国内厂商已经推出的刘海屏Android手机有华为P20 pro, vivo X21,OPPO R15。
如果没有适配刘海屏会有什么后果?
后果一:导航栏中title被遮挡
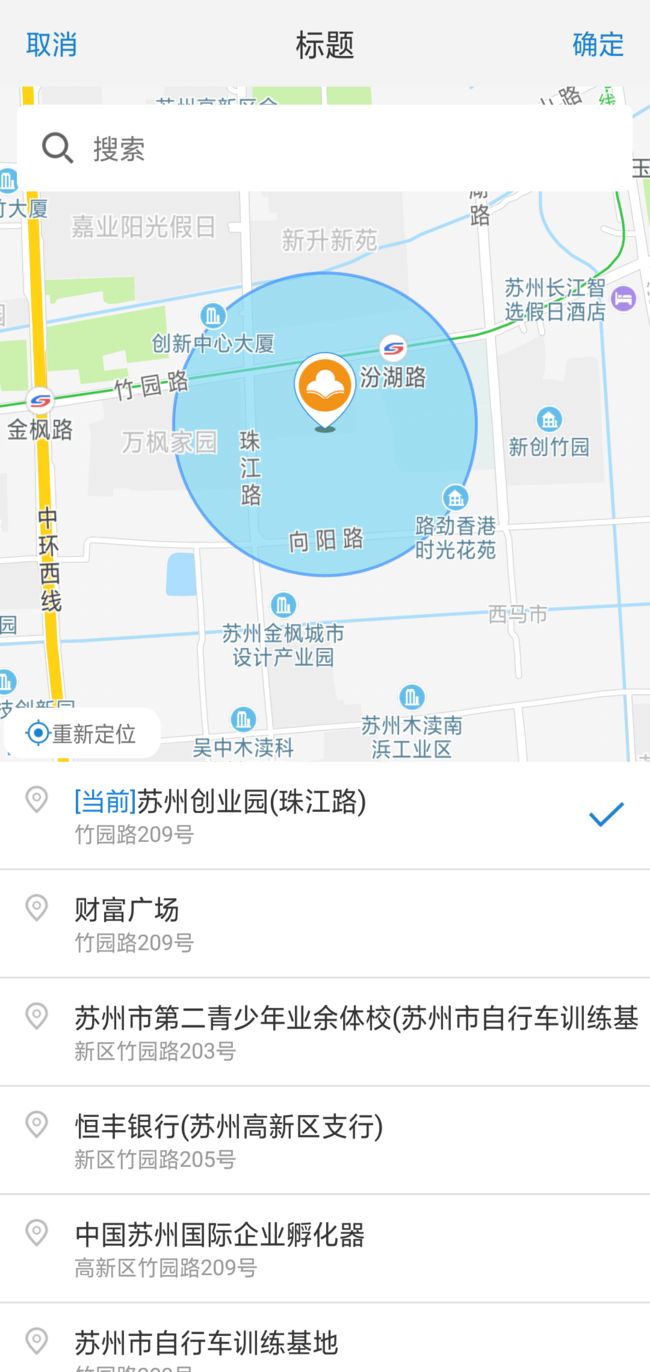
后果二:显示内容下移,头部出现黑条,底部出现遮挡
如何适配刘海屏?
由于Android p正式版今日刚发布, 当前市面上的Android 刘海屏手机还不能用Android 官方提供的方案来解决,那怎么办呢?还好几个厂商自己给出了适配方案。我们先讲理论后上代码,如果您只想要代码就直接往下翻:
华为P20 pro
华为刘海屏适配官方文档
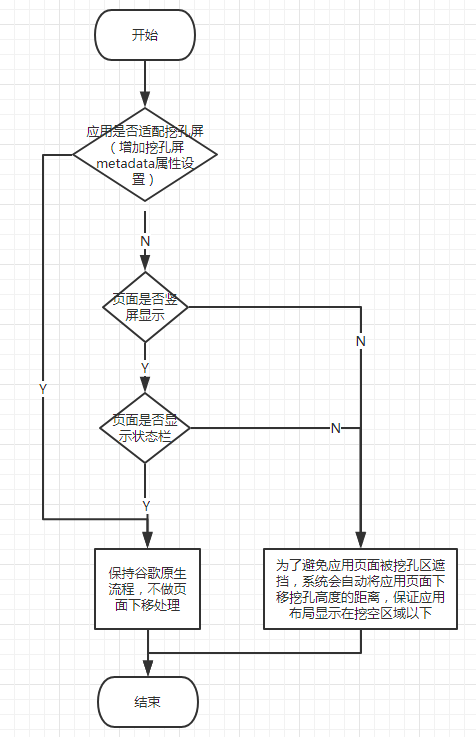
华为给出的文档最为详细(业界良心),P20 pro预装系统对未做刘海屏适配处理的app有一定处理,处理逻辑如下
可见,会被华为系统做偏移处理的有2种情况:
1.未设置meta-data值,页面横屏状态
2.未设置meta-data值,页面竖屏状态,不显示状态栏
这2种情况都会出现后果二。如果你的app中页面没有这两种情况,例如都是竖屏且显示状态栏,你就可以淡定地不做处理。
现在我们知道原因了就可以对症下药了,这里给出我推荐的解决方案(官方给出的解决方案不止一种,可以根据自己的需要采用) 分为4步:
1.配置meta-data
①对Application生效,意味着该应用的所有页面,系统都不会做竖屏场景的特殊下移或者是横屏场景的右移特殊处理:
② 对Activity生效,意味着可以针对单个页面进行刘海屏适配,设置了该属性的Activity系统将不会做特殊处理:
2.检测是否存在刘海屏
public static boolean hasNotchInScreen(Context context) {
boolean ret = false;
try {
ClassLoader cl = context.getClassLoader();
Class HwNotchSizeUtil = cl.loadClass("com.huawei.android.util.HwNotchSizeUtil");
Method get = HwNotchSizeUtil.getMethod("hasNotchInScreen");
ret = (boolean) get.invoke(HwNotchSizeUtil);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
Log.e("test", "hasNotchInScreen ClassNotFoundException");
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
Log.e("test", "hasNotchInScreen NoSuchMethodException");
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e("test", "hasNotchInScreen Exception");
} finally {
return ret;
}
}
3.获取刘海屏的参数
public static int[] getNotchSize(Context context) {
int[] ret = new int[]{0, 0};
try {
ClassLoader cl = context.getClassLoader();
Class HwNotchSizeUtil = cl.loadClass("com.huawei.android.util.HwNotchSizeUtil");
Method get = HwNotchSizeUtil.getMethod("getNotchSize");
ret = (int[]) get.invoke(HwNotchSizeUtil);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
Log.e("test", "getNotchSize ClassNotFoundException");
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
Log.e("test", "getNotchSize NoSuchMethodException");
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e("test", "getNotchSize Exception");
} finally {
return ret;
}
}
4. UI适配
没错,第1步仅仅是告诉EMUI系统不要瞎操作你的页面,真正适配的活还要你自己干。
①判断是否刘海屏,代码上面给出了
②如果是刘海屏手机需要应用自己调整布局避开刘海区,布局原则:保证重要的文字、图片和视频信息、可点击的控件和图标还有应用弹窗等等布局建议显示在状态栏区域以下(安全区域);不重要,遮挡不会出现问题的布局可以延伸到状态栏区域(危险区域)显示,按照这种布局原则修改,可以一次修改就能适配所有的刘海屏手机:
vivo & OPPO
OPPO刘海屏适配官方文档
vivo刘海屏适配官方文档
vivo 和 OPPO官网仅仅给出了适配指导,没有给出具体方案,简单总结为:
如有是具有刘海屏的手机,竖屏显示状态栏,横屏不要在危险区显示重要信息或者设置点击事件。
那怎么知道是不是刘海屏手机呢?
OPPO判断方法:
public static boolean hasNotchInOppo(Context context){
return context.getPackageManager().hasSystemFeature("com.oppo.feature.screen.heteromorphism");
}
vivo的判断方法:
public static final int NOTCH_IN_SCREEN_VOIO=0x00000020;//是否有凹槽
public static final int ROUNDED_IN_SCREEN_VOIO=0x00000008;//是否有圆角
public static boolean hasNotchInScreenAtVoio(Context context){
boolean ret = false;
try {
ClassLoader cl = context.getClassLoader();
Class FtFeature = cl.loadClass("com.util.FtFeature");
Method get = FtFeature.getMethod("isFeatureSupport",int.class);
ret = (boolean) get.invoke(FtFeature,NOTCH_IN_SCREEN_VOIO);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e)
{ Log.e("test", "hasNotchInScreen ClassNotFoundException"); }
catch (NoSuchMethodException e)
{ Log.e("test", "hasNotchInScreen NoSuchMethodException"); }
catch (Exception e)
{ Log.e("test", "hasNotchInScreen Exception"); }
finally
{ return ret; }
}
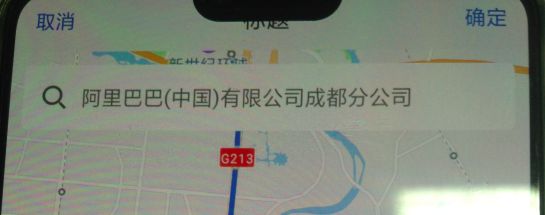
例如图一是在OPPO R15上出现的title被遮挡,显示状态栏后显示效果如下:
以上所讲的是各厂商提供的解决方案, 那么google官方对刘海屏做了什么样的支持呢?
google官方刘海屏适配方案
google从Android P开始为刘海屏提供支持,目前提供了一个类和三种模式:
一个类
The new DisplayCutout class lets you find out the location and shape of the non-functional areas where content shouldn't be displayed. To determine the existence and placement of these cutout areas, use thegetDisplayCutout() method
就是说可以用DisplayCutout这个类找出刘海(cutout)的位置和形状,调用getDisplayCutout()这个方法可以获取刘海(cutout)的位置和区域,我们看看这个类提供了什么方法:
所以我们可用这个类判断是否有刘海的存在以及刘海的位置
DisplayCutout cutout = mContext.getDisplayCutout();
三种模式
A new window layout attribute, layoutInDisplayCutoutMode, allows your app to lay out its content around a device's cutouts. You can set this attribute to one of the following values:
LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_DEFAULTLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_SHORT_EDGES-
LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_NEVER
第一种模式:
LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_DEFAULT : 仅仅当系统提供的bar完全包含了刘海区时才允许window扩展到刘海区,否则window不会和刘海区重叠
第二种模式:
LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_SHORT_EDGES :允许window扩展到刘海区(原文说的是短边的刘海区, 目前有刘海的手机都在短边,所以就不纠结了)
第三种模式:
LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_NEVER: 不允许window扩展到刘海区
我们可以设置是否允许window扩展到刘海区
WindowManager.LayoutParams lp =getWindow().getAttributes();
lp.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode
=WindowManager.LayoutParams.LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_NEVER;
getWindow().setAttributes(lp);
例如一个有状态栏的页面, 我们可以这样适配:
DisplayCutout cutout = getDisplayCutout();
if(cutout != null){
WindowManager.LayoutParams lp =getWindow().getAttributes();
lp.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode=WindowManager.LayoutParams.LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_NEVER;
getWindow().setAttributes(lp);
}
如果觉得有帮助, 点个赞再走可好啊~