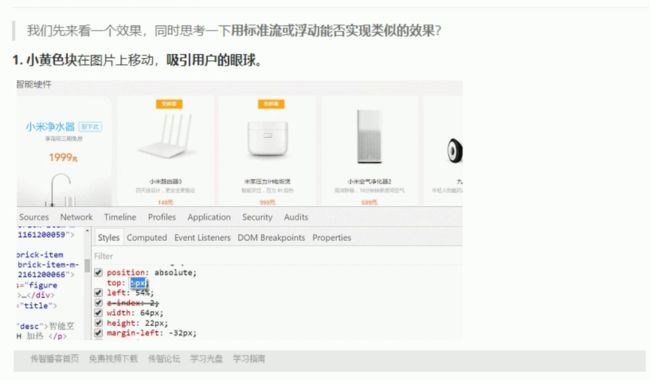
一 CSS布局的三种机制
1.标准流
2.浮动(盒子脱离标准流 浮起来 盒子水平排列)
3.定位(将盒子定在某一位置 自由的漂浮在其他盒子上面 css 离不开定位 特别是js特效)
二 为什么使用定位
要实现以上效果,不使用定位是非常困难的
将盒子定在某一个位置,自由的漂浮在其他盒子(包括标准流和浮动之上)
所以我们脑海中应该有三种布局机制的上下顺序
标准流(最底层) ->浮动的盒子在中间层->定位的盒子在最上层
三 定位详解
定位也是用来布局的,有两部分组成
定位 = 定位模式 + 边偏移
1> 边偏移
在CSS中 通过 top bottom right left 属性定义元素的边偏移
定位的盒子有了边偏移 才有价值 一般情况下 凡是有定位的地方都有边偏移
2> 定位模式(定位的分类)
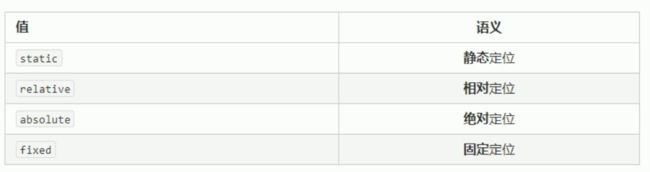
在CSS中 通过position属性定义元素的定位模式 语法如下
选择器 {position:属性值}
定位模式是有不同的分类的 在不同的情况下 我们使用不同的定位模式
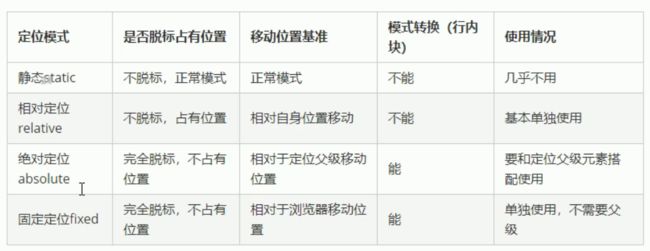
1:静态定位(static) 了解
静态定位 是元素默认的定位方式 无定位的意思 相当于 border 里面的none属性 就是无定位
静态定位 按照标准流特性摆放位置 没有边偏移
静态定位在布局时我们几乎是不用的
2:相对定位(relative) 重要
相对定位 是元素 相对于它 原来的位置 来说的
相对定位的特点:
相对于自己原来的位置移动
原来在标准流中 占有的位置 继续占有 后面的盒子仍然以标准流的方式对待它
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>相对定位title>
<style>
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
}
.two {
background-color: purple;
/* 定位 = 定位模式 + 边偏移 */
/* 虽然盒子走了 但是在标准流中仍然还有他的位置 没有脱标 */
position: relative;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div>div>
<div class="two">div>
<div>div>
body>
html>
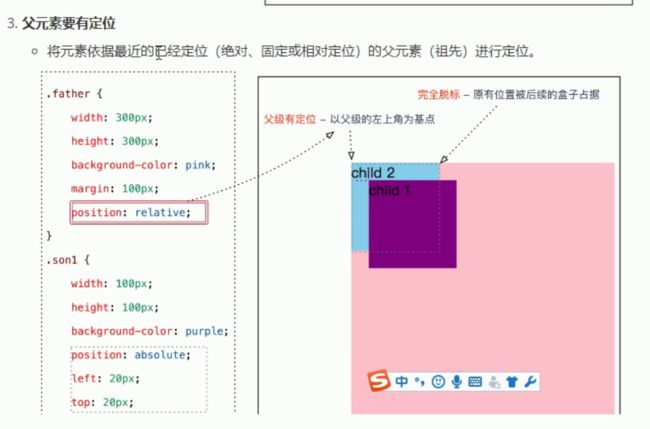
3:绝对定位(absolute)-重要
绝对定位是元素以带有定位的父级元素来移动位置
父级元素没有定位 就以浏览器为标准定位
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>绝对定位title>
<style>
.father {
width: 350px;
height: 350px;
background-color:pink;
margin: 100px;
/* 标准流的盒子 总是以父级为准移动位置 */
/* 绝对定位 如果父级没有定位 那么绝对定位的盒子 会以我们文档为准
浏览器为准移动位置 离自己最近的已经定位的为准 */
/* 如果有一下代码 则以父亲为准移动位置 */
/* position: relative; */
}
.son {
/* 如果父级没有定位 则以浏览器为标准 */
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: purple;
position: absolute;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son">
div>
div>
body>
html>
绝对定位的特点
是以带有定位的父级元素来移动位置 如果父级没有移动 则以浏览器文档为标准移动
不保留原来的位置 完全是脱标的
定位的口诀
子绝父相 :子级是绝对定位 父级要用相对定位
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>子绝父相title>
<style>
.up {
position: relative;
width: 1000px;
height: 90px;
background-color: pink;
}
.down {
width: 1000px;
height: 150px;
background-color: #000;
}
.arr-left {
position: absolute;
top: 25px;
left: 0;
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
background-color: purple;
}
.arr-right {
position: absolute;
top: 25px;
right: 0;
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
background-color: purple;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="up">
<img src="../images/img.jpg" alt="">
<div class="arr-left">div>
<div class="arr-right">div>
div>
<div class="down">div>
body>
html>
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Documenttitle>
<style>
.box {
width: 310px;
height: 190px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
margin: 100px auto;
padding: 10px;
position: relative;
}
.top {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
}
.bottom {
position: absolute;
bottom: 0;
right: 0;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<img class="top" src="../images/top_tu.gif" alt="">
<img src="../images/adv.jpg" alt="">
<img class="bottom" src="../images/br.gif" alt="">
div>
body>
html>
4:固定定位(fixed) 重要
固定定位时绝对定位的一种特殊形式。
1 完全脱标--完全不占位置
2 只认浏览器窗口+边偏移属性 来设置元素的位置
跟父元素没有任何关系 不随滚动条滚动
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>固定定位title>
<style>
.box {
position: relative;
width: 300px;
height: 300px;background-color: pink;
margin: 100px auto;
}
/* 逃出盒子 固定定位和父亲没关系 只认浏览器的可视区域*/
.box img {
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<img src="../images/sun.jpg" alt="" width="150px">
div>
body>
html>
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>新浪广告固定定位title>
<style>
.box {
width: 1002px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.ad-l {
position: fixed;
left: 0;
top: 180px;
}
.ad-r {
position: fixed;
right: 0;
top: 180px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<img class="ad-l" src="../images/ad-l.png" alt="">
<img class="ad-r" src="../images/ad-r.png" alt="">
<div class="box">
<img src="../images/box.png" alt="">
div>
body>
html>
5 定位(position)的扩展
>1 绝对定位的盒子居中
注意:绝对定位 固定定位的盒子不能通过设置 margin :auto 设置水平居中
在使用绝对定位中 要实现水平居中 可以使用 left:50% 在左移 自身宽度的一半来实现居中
第一步. left:50px 第二步margin-left: 负盒子的一半宽度
垂直居中
第一步 top:50% 第二步 margin-top 负盒子的一半高度
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>绝对定位盒子居中title>
<style>
.box {
position: absolute;
/* 第一步 */
left: 50%;
/* 第二步 */
margin-left: -100px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="box">div>
body>
html>
>2 堆叠顺序(z-index)
在使用定位布局时 可能会出现 盒子重叠的情况
加了定位的盒子 默认 后来者居上 后面出现的盒子 会压在 前面出现的盒子上
使用z-indexc层叠等级属性可以调整盒子的堆叠书序 如下图所示
z-index 的特性如下
1.属性值:正整数 负整数 或者 0 默认是0 数值越大 盒子越靠上
2.如果属性值相同 则按照书写顺序 后来居上
z-index 只能应用于 相对定位 绝对定位 固定定位 里面 其他标准流 浮动 静态定位 无效
3>定位改变display属性
display 是限时模式 可以改变下显示模式的方式如下
1.可以使用inline-block 转换为行内块元素
2.可以用浮动float默认转换为行内块元素 (类似 并不完全一样 浮动是脱标的)
3.绝对定位 和 固定定位也和浮动类似 默认转换特性 转换为行内块
所以说 一个行内元素 如果加了浮动固定定位 绝对定位 就可以接受宽高
练习
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>定位练习title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
li {
list-style: none;
}
.taobao {
width: 520px;
height: 280px;
background-color: #fff;
margin: 100px auto;
position: relative;
}
.arrow-r,.arrow-l {
position: absolute;
width: 20px;
height: 30px;
text-decoration: none;
line-height: 30px;
color: #fff;
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, .3);
}
.arrow-l {
left: 0;
top: 50%;
margin-top: -15px;
border-top-right-radius: 15px;
border-bottom-right-radius: 15px;
}
.arrow-r {
right: 0;
top: 50%;
margin-top: -15px;
/* border-top-left-radius: 15px;
border-bottom-left-radius: 15px; */
border-radius: 15px 0 0 15px;
text-align: right;
}
.arrow-l:hover,
.arrow-r:hover {
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, .5);
}
.taobao .circle {
position: absolute;
bottom: 15px;
left: 50%;
margin-left: -35px;
width: 70px;
height: 13px;
background-color:rgba(255, 255, 255, .3);
border-radius: 7px;
}
.circle li {
float: left;
width: 8px;
height: 8px;
background-color: #fff;
border-radius: 4px;
margin: 3px;
}
/* 有优先级的问题 */
.circle .current {
background-color: #f50000;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="taobao">
<a class="arrow-l" href="#"><a>
<a class="arrow-r" href="#">>a>
<img src="../images/taobao.jpg" alt="" width="100%">
<div class="xiaoyuandian">
<ul class="circle">
<li>li>
<li class="current">li>
<li>li>
<li>li>
<li>li>
ul>
div>
div>
body>
html>
定位小结
注意:
边偏移需要和定位模式联合使用 单独使用无效
top 和 bottom 不能同时使用
left 和 right 不能同时使用