一致性(连续性)hash算法(Consistent hashing)
Consistent hashing is a scheme that provides hash table functionality in a way that the addition or removal of one slot does not significantly change the mapping of keys to slots.
一致性哈希算法是分布式系统中常用的算法,为什么要用这个算法?
比如:一个分布式存储系统,要将数据存储到具体的节点(服务器)上, 在服务器数量不发生改变的情况下,如果采用普通的hash再对服务器总数量取模的方法(如key%服务器总数量),如果期间有服务器宕机了或者需要增加服务器,问题就出来了。 同一个key经过hash之后,再与服务器总数量取模的结果跟之前的结果会不一样,这就导致了之前保存数据的丢失。因此,引入了一致性Hash(Consistent Hashing)分布算法
算法的具体原理这里再次贴上:
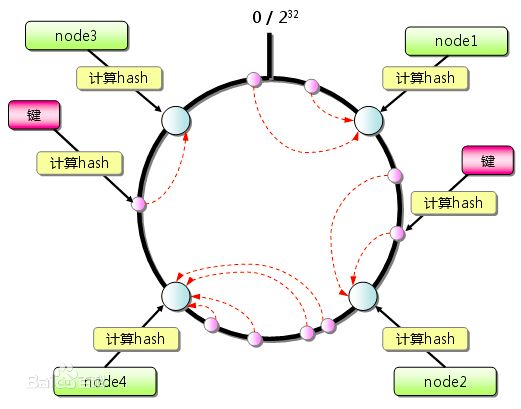
先构造一个长度为2^32的整数环(这个环被称为一致性Hash环),根据节点名称的Hash值(其分布为[0, 2^32-1])将服务器节点放置在这个Hash环上,然后根据数据的Key值计算得到其Hash值(其分布也为[0, 2^32-1]),接着在Hash环上顺时针查找距离这个Key值的Hash值最近的服务器节点,完成Key到服务器的映射查找。
这种算法解决了普通余数Hash算法伸缩性差的问题,可以保证在上线、下线服务器的情况下尽量有多的请求命中原来路由到的服务器。
不带虚拟节点的一致性Hash算法
/**
* 不带虚拟节点的一致性Hash算法
* @author 五月的仓颉http://www.cnblogs.com/xrq730/
*
*/
public class ConsistentHashingWithoutVirtualNode
{
/**
* 待添加入Hash环的服务器列表
*/
private static String[] servers = {"192.168.0.0:111", "192.168.0.1:111", "192.168.0.2:111",
"192.168.0.3:111", "192.168.0.4:111"};
/**
* key表示服务器的hash值,value表示服务器的名称
*/
private static SortedMap sortedMap =
new TreeMap();
/**
* 程序初始化,将所有的服务器放入sortedMap中
*/
static
{
for (int i = 0; i < servers.length; i++)
{
int hash = getHash(servers[i]);
System.out.println("[" + servers[i] + "]加入集合中, 其Hash值为" + hash);
sortedMap.put(hash, servers[i]);
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 使用FNV1_32_HASH算法计算服务器的Hash值,这里不使用重写hashCode的方法,最终效果没区别
*/
private static int getHash(String str)
{
final int p = 16777619;
int hash = (int)2166136261L;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++)
hash = (hash ^ str.charAt(i)) * p;
hash += hash << 13;
hash ^= hash >> 7;
hash += hash << 3;
hash ^= hash >> 17;
hash += hash << 5;
// 如果算出来的值为负数则取其绝对值
if (hash < 0)
hash = Math.abs(hash);
return hash;
}
/**
* 得到应当路由到的结点
*/
private static String getServer(String node)
{
// 得到带路由的结点的Hash值
int hash = getHash(node);
// 得到大于该Hash值的所有Map
SortedMap subMap =
sortedMap.tailMap(hash);
// 第一个Key就是顺时针过去离node最近的那个结点
Integer i = subMap.firstKey();
// 返回对应的服务器名称
return subMap.get(i);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String[] nodes = {"127.0.0.1:1111", "221.226.0.1:2222", "10.211.0.1:3333"};
for (int i = 0; i < nodes.length; i++)
System.out.println("[" + nodes[i] + "]的hash值为" +
getHash(nodes[i]) + ", 被路由到结点[" + getServer(nodes[i]) + "]");
}
}
带虚拟节点的一致性Hash算法
/**
* 带虚拟节点的一致性Hash算法
* @author 五月的仓颉 http://www.cnblogs.com/xrq730/
*/
public class ConsistentHashingWithVirtualNode
{
/**
* 待添加入Hash环的服务器列表
*/
private static String[] servers = {"192.168.0.0:111", "192.168.0.1:111", "192.168.0.2:111",
"192.168.0.3:111", "192.168.0.4:111"};
/**
* 真实结点列表,考虑到服务器上线、下线的场景,即添加、删除的场景会比较频繁,这里使用LinkedList会更好
*/
private static List realNodes = new LinkedList();
/**
* 虚拟节点,key表示虚拟节点的hash值,value表示虚拟节点的名称
*/
private static SortedMap virtualNodes =
new TreeMap();
/**
* 虚拟节点的数目,这里写死,为了演示需要,一个真实结点对应5个虚拟节点
*/
private static final int VIRTUAL_NODES = 5;
static
{
// 先把原始的服务器添加到真实结点列表中
for (int i = 0; i < servers.length; i++)
realNodes.add(servers[i]);
// 再添加虚拟节点,遍历LinkedList使用foreach循环效率会比较高
for (String str : realNodes)
{
for (int i = 0; i < VIRTUAL_NODES; i++)
{
String virtualNodeName = str + "&&VN" + String.valueOf(i);
int hash = getHash(virtualNodeName);
System.out.println("虚拟节点[" + virtualNodeName + "]被添加, hash值为" + hash);
virtualNodes.put(hash, virtualNodeName);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 使用FNV1_32_HASH算法计算服务器的Hash值,这里不使用重写hashCode的方法,最终效果没区别
*/
private static int getHash(String str)
{
final int p = 16777619;
int hash = (int)2166136261L;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++)
hash = (hash ^ str.charAt(i)) * p;
hash += hash << 13;
hash ^= hash >> 7;
hash += hash << 3;
hash ^= hash >> 17;
hash += hash << 5;
// 如果算出来的值为负数则取其绝对值
if (hash < 0)
hash = Math.abs(hash);
return hash;
}
/**
* 得到应当路由到的结点
*/
private static String getServer(String node)
{
// 得到带路由的结点的Hash值
int hash = getHash(node);
// 得到大于该Hash值的所有Map
SortedMap subMap =
virtualNodes.tailMap(hash);
// 第一个Key就是顺时针过去离node最近的那个结点
Integer i = subMap.firstKey();
// 返回对应的虚拟节点名称,这里字符串稍微截取一下
String virtualNode = subMap.get(i);
return virtualNode.substring(0, virtualNode.indexOf("&&"));
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String[] nodes = {"127.0.0.1:1111", "221.226.0.1:2222", "10.211.0.1:3333"};
for (int i = 0; i < nodes.length; i++)
System.out.println("[" + nodes[i] + "]的hash值为" +
getHash(nodes[i]) + ", 被路由到结点[" + getServer(nodes[i]) + "]");
}
}
另:
用线程池起了1000个线程,每个线程hash10000次,模拟一万次数据hash,并将测试结果上传。
/**
* 一致性hash代码
*
* @author shiguiming
*
* @param
*/
public class Shared {
// 真实节点对应的虚拟节点数量
private int length = 100;
// 虚拟节点信息
private TreeMap virtualNodes;
// 真实节点信息
private List realNodes;
public Shared(List realNodes) {
this.realNodes = realNodes;
init();
}
public List getReal() {
return realNodes;
}
/**
* 初始化虚拟节点
*/
private void init() {
virtualNodes = new TreeMap();
for (int i = 0; i < realNodes.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < length; j++) {
virtualNodes.put(hash("aa" + i + j), realNodes.get(i));
}
}
}
/**
* 获取一个结点
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T getNode(String key) {
Long hashedKey = hash(key);
// TODO judge null
Entry en = virtualNodes.ceilingEntry(hashedKey);
if (en == null) {
return (T) virtualNodes.firstEntry().getValue();
}
return (T) en.getValue();
}
/**
* MurMurHash算法,是非加密HASH算法,性能很高,
* 比传统的CRC32,MD5,SHA-1(这两个算法都是加密HASH算法,复杂度本身就很高,带来的性能上的损害也不可避免)
* 等HASH算法要快很多,而且据说这个算法的碰撞率很低. http://murmurhash.googlepages.com/
*/
private Long hash(String key) {
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.wrap(key.getBytes());
int seed = 0x1234ABCD;
ByteOrder byteOrder = buf.order();
buf.order(ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN);
long m = 0xc6a4a7935bd1e995L;
int r = 47;
long h = seed ^ (buf.remaining() * m);
long k;
while (buf.remaining() >= 8) {
k = buf.getLong();
k *= m;
k ^= k >>> r;
k *= m;
h ^= k;
h *= m;
}
if (buf.remaining() > 0) {
ByteBuffer finish = ByteBuffer.allocate(8).order(ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN);
// for big-endian version, do this first:
// finish.position(8-buf.remaining());
finish.put(buf).rewind();
h ^= finish.getLong();
h *= m;
}
h ^= h >>> r;
h *= m;
h ^= h >>> r;
buf.order(byteOrder);
return h;
}
/**
* 测试内部类
*
* @author shiguiming
*
*/
static public class Node {
private int name;
private int count = 0;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int i) {
this.name = i;
}
public int getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(int name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
// 同步方法,防止并发
synchronized public void inc() {
count++;
}
}
/**
* 测试方法
*
* @param args
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
List ndList = new ArrayList();
int i = 0;
while (true) {
ndList.add(new Node(i));
if (i++ == 9)
break;
}
final Shared sh = new Shared(ndList);
ExecutorService es = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final CountDownLatch cdl = new CountDownLatch(1000);
// 1000个线程
for (int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) {
es.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// Random rd = new Random(1100);
for (int k = 0; k < 10000; k++) {
sh.getNode(String.valueOf(Math.random())).inc();
}
cdl.countDown();
}
});
}
// 等待所有线程结束
cdl.await();
List nodeList = sh.getReal();
for (Node node : nodeList) {
System.out.println("node" + node.getName() + ":" + node.getCount());
}
}
}
测试结果:
一共10,000,000次 hash,基本算是较均匀投递到10个节点
使用Redis作为缓存服务器的,刚开始的时候会满足需要,随着项目的增大缓存数据的增多就会查询和插入更慢这时就要考虑Redis集群方案了
使用Redis分布式要保证数据都能能够平均的缓存到每一台机器,首先想到的做法是对数据进行分片,因为Redis是key-value存储的,首先想到的是Hash分片,可能的做法是对key进行哈希运算,得到一个long值对分布式的数量取模会得到一个一个对应数据库的一个映射,没有读取就可以定位到这台数据库,那么速度但然会提升了。
但是取模的hash算法是有问题的如果集群数量不变的话没有什么问题,一旦增加一台机器或者一台机器挂掉,导致机器数量变化,就会导致计算的出的数据库映射乱掉,不能正确存取数据了。
因为这个问题引入我们说的一致性哈希算法,这个哈希算法具有的特征
1.均衡性:也有人把它定义为平衡性,是指哈希的结果能够尽可能分布到所有的节点中去,这样可以有效的利用每个节点上的资源。
2.单调性:对于单调性有很多翻译让我非常的不解,而我想要的是当节点数量变化时哈希的结果应尽可能的保护已分配的内容不会被重新分派到新的节点。
3.分散性和负载:这两个其实是差不多的意思,就是要求一致性哈希算法对 key 哈希应尽可能的避免重复。
一致性哈希就数据结构是创建一个排序的环形数据结构,有许多个区域,先让每一台服务器都分布环上,取每一个服务器的特效做哈希运行,得到的值放进环中,进行排序这样就能根据哈希特征找到对应的真是服务器,能够让把服务器平均的分布到环上。
第一个特征均衡性:就是尽量的让数据平均的分部到每一个服务器,不让某台机器压力特别打,或者干脆没活干,因为这个原因,我们的每一个服务器都添加几个虚拟服务器,比如真是服务器叫node1那么第一个服务器的虚拟服务器就叫node1-1,node1-2...,根据这些特征进行哈希运算也分布到环中,这样就能把服务器平均的分布到环中。
第二个特征单调性:因为服务器都在环中,数据的key进行哈希运算得到一个值,跟环中的服务器的哈希值进行比较,取离当前值最接近的哈希值对象的服务器,这样就是获取服务器的原理了,我们是做了一个偷懒的工作,服务器哈希进行排序,以顺时针方式得到一个刚好大于key哈希的服务器。
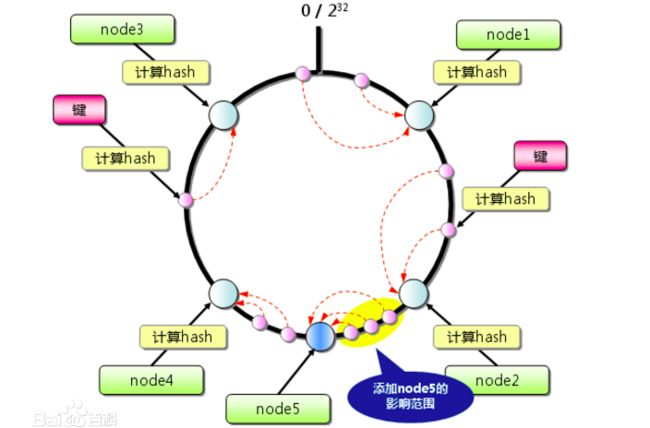
单调性是在不管添加节点还是删除节点,原来对应的服务器不变,因为这个环很大,服务器是零星分布的,这样增加或者删除一个节点只有受影响的都是当前节点,但是key对应的数据库是不变的,也不能说不变,是把变化变得尽可能的小。
第三个特征分散性和负载:指服务器在环中尽可能的分散,尽可能的让数据平均分布到不同的服务器,我们就是使用虚拟节点的方式解决的。
把代码放上来
1.Node对象,存放服务器的一些特征
重写toString()方法,使用这些特征生成服务器哈希码
public class Node {
// 节点名称
private String name;
// 节点IP
private String ip;
// 节点端口号
private int port;
// 节点密码
private String password;
public Node(String name, String ip, int port, String password) {
this.name = name;
this.ip = ip;
this.port = port;
this.password = password;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getIp() {
return ip;
}
public void setIp(String ip) {
this.ip = ip;
}
public int getPort() {
return port;
}
public void setPort(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [name=" + name + ", ip=" + ip + ", port=" + port
+ ", password=" + password + "]";
}
哈希算法实现,使用的是MurmurHash算法,是非加密的哈希算法速度比crc,md5更快
public final class MurmurHash {
public MurmurHash() {
}
private byte[] toBytesWithoutEncoding(String str) {
int len = str.length();
int pos = 0;
byte[] buf = new byte[len << 1];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char c = str.charAt(i);
buf[pos++] = (byte) (c & 0xFF);
buf[pos++] = (byte) (c >> 8);
}
return buf;
}
public int hashcode(String str) {
byte[] bytes = toBytesWithoutEncoding(str);
return hash32(bytes, bytes.length);
}
/**
* * Generates 32 bit hash from byte array of the given length and * seed.
* * * @param data byte array to hash * @param length length of the array
* to hash * @param seed initial seed value * @return 32 bit hash of the
* given array
*/
public int hash32(final byte[] data, int length, int seed) {
// 'm' and 'r' are mixing constants generated offline.
// They're not really 'magic', they just happen to work well.
final int m = 0x5bd1e995;
final int r = 24;
// Initialize the hash to a random value
int h = seed ^ length;
int length4 = length / 4;
for (int i = 0; i < length4; i++) {
final int i4 = i * 4;
int k = (data[i4 + 0] & 0xff) + ((data[i4 + 1] & 0xff) << 8)
+ ((data[i4 + 2] & 0xff) << 16)
+ ((data[i4 + 3] & 0xff) << 24);
k *= m;
k ^= k >>> r;
k *= m;
h *= m;
h ^= k;
}
// Handle the last few bytes of the input array
switch (length % 4) {
case 3:
h ^= (data[(length & ~3) + 2] & 0xff) << 16;
case 2:
h ^= (data[(length & ~3) + 1] & 0xff) << 8;
case 1:
h ^= (data[length & ~3] & 0xff);
h *= m;
}
h ^= h >>> 13;
h *= m;
h ^= h >>> 15;
return h;
}
/**
* * Generates 32 bit hash from byte array with default seed value. * * @param
* data byte array to hash * @param length length of the array to hash * @return
* 32 bit hash of the given array
*/
public int hash32(final byte[] data, int length) {
return hash32(data, length, 0x9747b28c);
}
public int hash32(final String data) {
byte[] bytes = toBytesWithoutEncoding(data);
return hash32(bytes, bytes.length, 0x9747b28c);
}
/**
* * Generates 64 bit hash from byte array of the given length and seed. *
* * @param data byte array to hash * @param length length of the array to
* hash * @param seed initial seed value * @return 64 bit hash of the
* given array
*/
public long hash64(final byte[] data, int length, int seed) {
final long m = 0xc6a4a7935bd1e995L;
final int r = 47;
long h = (seed & 0xffffffffl) ^ (length * m);
int length8 = length / 8;
for (int i = 0; i < length8; i++) {
final int i8 = i * 8;
long k = ((long) data[i8 + 0] & 0xff)
+ (((long) data[i8 + 1] & 0xff) << 8)
+ (((long) data[i8 + 2] & 0xff) << 16)
+ (((long) data[i8 + 3] & 0xff) << 24)
+ (((long) data[i8 + 4] & 0xff) << 32)
+ (((long) data[i8 + 5] & 0xff) << 40)
+ (((long) data[i8 + 6] & 0xff) << 48)
+ (((long) data[i8 + 7] & 0xff) << 56);
k *= m;
k ^= k >>> r;
k *= m;
h ^= k;
h *= m;
}
switch (length % 8) {
case 7:
h ^= (long) (data[(length & ~7) + 6] & 0xff) << 48;
case 6:
h ^= (long) (data[(length & ~7) + 5] & 0xff) << 40;
case 5:
h ^= (long) (data[(length & ~7) + 4] & 0xff) << 32;
case 4:
h ^= (long) (data[(length & ~7) + 3] & 0xff) << 24;
case 3:
h ^= (long) (data[(length & ~7) + 2] & 0xff) << 16;
case 2:
h ^= (long) (data[(length & ~7) + 1] & 0xff) << 8;
case 1:
h ^= (long) (data[length & ~7] & 0xff);
h *= m;
}
;
h ^= h >>> r;
h *= m;
h ^= h >>> r;
return h;
}
/**
* * Generates 64 bit hash from byte array with default seed value. * * @param
* data byte array to hash * @param length length of the array to hash * @return
* 64 bit hash of the given string
*/
public long hash64(final byte[] data, int length) {
return hash64(data, length, 0xe17a1465);
}
public long hash64(final String data) {
byte[] bytes = toBytesWithoutEncoding(data);
return hash64(bytes, bytes.length);
}
}
一致性哈希ConsistentHash的实现
public class ConsistentHash {
/**
* 虚拟节点个数 用于复制真是节点进行负载均衡
*/
private final int virtualNodeNum;
//环形SortMap 用于存放节点并排序
private SortedMap circleMap = new TreeMap();
/**
* 构造,使用Java默认的Hash算法
* @param virtualNodeNum 虚拟化节点数量 复制的节点个数,增加每个节点的复制节点有利于负载均衡
* @param nodes 节点对象
*/
public ConsistentHash(int virtualNodeNum,Collection nodes){
this.virtualNodeNum = virtualNodeNum;
for(Node node:nodes){
addNode(node);
}
}
/**
* 构造
* @param virtualNodeNum 虚拟化节点数量 复制的节点个数,增加每个节点的复制节点有利于负载均衡
* @param nodes 节点对象
*/
public ConsistentHash(int virtualNodeNum,Node node){
this.virtualNodeNum = virtualNodeNum;
addNode(node);
}
/**
* 构造
* @param virtualNodeNum 虚拟化节点数量
*
*/
public ConsistentHash(int virtualNodeNum){
this.virtualNodeNum = virtualNodeNum;
}
/**
* 增加节点
* 每增加一个节点,就会在闭环上增加给定复制节点数
* 例如复制节点数是2,则每调用此方法一次,增加两个虚拟节点,这两个节点指向同一Node
* 由于hash算法会调用node的toString方法,故按照toString去重
* @param node 节点对象
*/
public void addNode(Node node) {
for (int i = 0; i < virtualNodeNum; i++) {
circleMap.put(HashUtils.murMurHash(node.toString() + i), node);
}
}
/**
* 移除节点的同时移除相应的虚拟节点
* @param node 节点对象
*/
public void remove(Node node) {
for (int i = 0; i < virtualNodeNum; i++) {
circleMap.remove(HashUtils.murMurHash(node.toString() + i));
}
}
/**
* 获得一个最近的顺时针节点
* @param key 为给定键取Hash,取得顺时针方向上最近的一个虚拟节点对应的实际节点
* @return 节点对象
*/
public Node get(Object key) {
if (circleMap.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
long hash = HashUtils.murMurHash(RText.toString(key));
if (!circleMap.containsKey(hash)) {
SortedMap tailMap = circleMap.tailMap(hash); //返回此映射的部分视图,其键大于等于 hash
hash = tailMap.isEmpty() ? circleMap.firstKey() : tailMap.firstKey();
}
//正好命中
return circleMap.get(hash);
}
}
这些是自己的实现,jedis 已经对分布式一致性哈希算法进行了封装
Jedis 添加服务器
JedisShardInfo jedisShardInfo1 = new JedisShardInfo(
bundle.getString("redis1.ip"), Integer.valueOf(bundle .getString("redis.port")));
JedisShardInfo jedisShardInfo2 = new JedisShardInfo(
bundle.getString("redis2.ip"), Integer.valueOf(bundle .getString("redis.port")));
List list = new LinkedList();
list.add(jedisShardInfo1);
list.add(jedisShardInfo2);
初始化ShardedJedisPool代替JedisPool:
ShardedJedisPool pool = new ShardedJedisPool(config, list);
测试
public void test() {
// 从池中获取一个Jedis对象
ShardedJedis jedis = pool.getResource();
String keys = "name";
String value = "snowolf";
// 删数据
jedis.del(keys);
// 存数据
jedis.set(keys, value);
// 取数据
String v = jedis.get(keys);
System.out.println(v);
// 释放对象池
pool.returnResource(jedis);
assertEquals(value, v);
}
这种分布式解决方案能解决只能最大程度的解决数据分布问题,但是还是会引起小范围的数据分布问题,增加节点的时候,当原来对应这台服务器的数据可能就会对应新加的数据库,但是读取的时候就会出问题了,会引起小范围的数据读取不到。
解决方案
1.Redis 的主从同步,同步下数据,这个可以参考资料。
2.使用java进行数据的重定向,使用定时任务对数据库进行扫描,得到所有的key进行一次哈希运算,如果是本服务器的数据不处理,如果运算的结果是别的服务器就对这条数据进行迁移,来保持数据的一致性。