django 类视图解析 -FormView一文中有小伙伴提问将POST来的数据写入模型中的业务逻辑,这样就有了本文,这里感谢这位小伙伴@huangkewen
Django编辑内容的通用视图包括
django.views.genetic.edit.FormView —与模型无关
django.views.genetic.edit.CreateView —与模型有关,创建模型实例
django.views.genetic.edit.UpdateView —与模型有关,修改模型实例
django.views.genetic.edit.DeleteView --与模型有关,删除模型实例
我们可以理解 CreateView、UpdateView、DeleteView 这三个通用视图是在 FormView 的基础上增加了对创建、修改、删除模型实例的方法。
那么,我们就先以 CreateView 为例一起来详细看看,它是怎么基于 FormView 来实现创建模型实例的,也就是怎么将 Post来的数据写入模型的。
CreateView 与 FormView 的区别
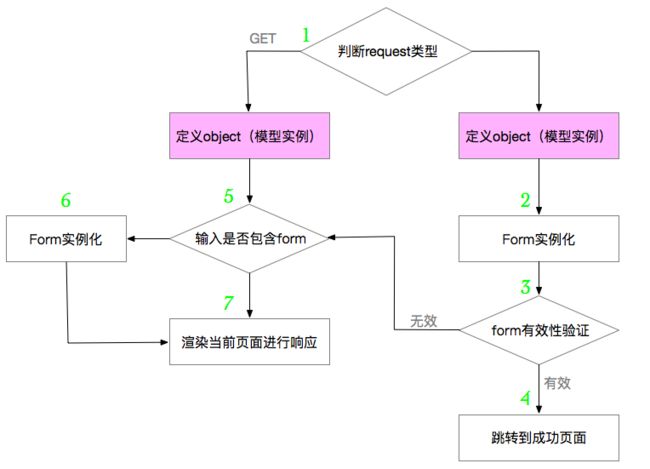
流程分析的差异
CreateView 与 FormView 的 流程相似,只是在 Get 和 Post 请求中定义了 object。那么 CreateView 如何实现数据与模型的联系呢?
原因在于 CreateView 依赖的 BaseCreateView 覆盖了FormView 依赖的 Base FormView 的 get_form_class() 方法,从而在 Form 实例化的过程中加入了与模型的交互。
对于 BaseFromView 而言,其 get_form_class() 函数为:
def get_form_class(self):
"""
Returns the form class to use in this view
"""
return self.form_class
对于 BaseCreateView 而言,其 get_form_class() 函数为:
def get_form_class(self):
"""
Returns the form class to use in this view.
"""
if self.fields is not None and self.form_class:
raise ImproperlyConfigured(
"Specifying both 'fields' and 'form_class' is not permitted."
)
if self.form_class:
return self.form_class
else:
if self.model is not None:
# If a model has been explicitly provided, use it
model = self.model
elif hasattr(self, 'object') and self.object is not None:
# If this view is operating on a single object, use
# the class of that object
model = self.object.__class__
else:
# Try to get a queryset and extract the model class
# from that
model = self.get_queryset().model
if self.fields is None:
raise ImproperlyConfigured(
"Using ModelFormMixin (base class of %s) without "
"the 'fields' attribute is prohibited." % self.__class__.__name__
)
return model_forms.modelform_factory(model, fields=self.fields)
这里要求要么设置 form_class,要么设置 fields,两者不能同时设置。对于处理模型的,要设置 fields,然后分别通过设置的 model、object、get_queryset() 获取使用的模型,这里,如果第一个满足条件则不会进行第二、第三个,如果有 model 属性则不再关心后两个。然后调用 modelforms的modelform_factory 创建模型实例。
代码结构的差异
既然前面说 CreateView 基于FormView,那么我们先来看看 CreateView 和 FormView 的继承关系:
上图中,黑色字为 CreateView 类及它继承的类,蓝色字为 FormView 继承的类,从图中可以看到 CreateView继承了 FormView 集成的所有类,此外还额外增加了一些内容。下面我们来具体看下:
SingleObjectTemplateResponseMixin 与 TemplateResponseMixin
这里,SingleObjectTemplateResponseMixin 继承 TemplateResponseMixin ,也就说在 CreateView 在模板响应这块儿与 FormView 更加了功能,那么,增加的是什么呢?
我们先来看看 TemplateResponseMixin 的代码,分析它实现了什么功能:
class TemplateResponseMixin(object):
"""
A mixin that can be used to render a template.
"""
template_name = None
template_engine = None
response_class = TemplateResponse
content_type = None
def render_to_response(self, context, **response_kwargs):
"""
Returns a response, using the `response_class` for this
view, with a template rendered with the given context.
If any keyword arguments are provided, they will be
passed to the constructor of the response class.
"""
response_kwargs.setdefault('content_type', self.content_type)
return self.response_class(
request=self.request,
template=self.get_template_names(),
context=context,
using=self.template_engine,
**response_kwargs
)
def get_template_names(self):
"""
Returns a list of template names to be used for the request. Must return
a list. May not be called if render_to_response is overridden.
"""
if self.template_name is None:
raise ImproperlyConfigured(
"TemplateResponseMixin requires either a definition of "
"'template_name' or an implementation of 'get_template_names()'")
else:
return [self.template_name]
TemplateResponseMixin
TemplateResponseMixin 这个类 定义了template_name、template_engine、response_class、content_type 四个属性以及 render_to_response 和 get_template_names 两个方法。
template_name 和 get_template_names 都用于返回模板名称,这里要么设置 template_name的名称,要么重新定义 get_template_names() 返回模板名称列表;其它类在获取模型名称时调用 get_template_names() 获取模板名称列表。
g
template_engine、response_class、content_type 三个属性以及 get_template_names() 都用于render_to_response() ,分别用于设定响应的 模板引擎、响应类型(TemplateResponse)、内容类型,render_to_response 用于渲染响应。
SingleObjectTemplateResponseMixin
我们再来看看 SingleObjectTemplateResponseMixin 的代码,分析它增加了什么功能:
class SingleObjectTemplateResponseMixin(TemplateResponseMixin):
template_name_field = None
template_name_suffix = '_detail'
def get_template_names(self):
"""
Return a list of template names to be used for the request. May not be
called if render_to_response is overridden. Returns the following list:
* the value of ``template_name`` on the view (if provided)
* the contents of the ``template_name_field`` field on the
object instance that the view is operating upon (if available)
* ``/.html``
"""
try:
names = super(SingleObjectTemplateResponseMixin, self).get_template_names()
except ImproperlyConfigured:
# If template_name isn't specified, it's not a problem --
# we just start with an empty list.
names = []
# If self.template_name_field is set, grab the value of the field
# of that name from the object; this is the most specific template
# name, if given.
if self.object and self.template_name_field:
name = getattr(self.object, self.template_name_field, None)
if name:
names.insert(0, name)
# The least-specific option is the default /_detail.html;
# only use this if the object in question is a model.
if isinstance(self.object, models.Model):
names.append("%s/%s%s.html" % (
self.object._meta.app_label,
self.object._meta.model_name,
self.template_name_suffix
))
elif hasattr(self, 'model') and self.model is not None and issubclass(self.model, models.Model):
names.append("%s/%s%s.html" % (
self.model._meta.app_label,
self.model._meta.model_name,
self.template_name_suffix
))
# If we still haven't managed to find any template names, we should
# re-raise the ImproperlyConfigured to alert the user.
if not names:
raise
return names
SingleObjectTemplateResponseMixin 在 TemplateResponseMixin 的基础上增加了template_name_field、template_name_suffix 用于设定 模板名称字段和模板名称后缀,用于定义 get_template_names()。
get_template_names() 重写 TemplateResponseMixin 的 get_template_names() ,这时如果类不定义模板名称不会像 TemplateResponseMixin 一样引发异常,而是尝试使用模型实例的名称定义模板名称。
BaseCreateView与BaseFormView
BaseCreateView 与 BaseFormView 相比增加了 object 属性的定义,object 用于定义模型实例。
class BaseCreateView(ModelFormMixin, ProcessFormView):
"""
Base view for creating an new object instance.
Using this base class requires subclassing to provide a response mixin.
"""
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
self.object = None
return super(BaseCreateView, self).get(request, *args, **kwargs)
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
self.object = None
return super(BaseCreateView, self).post(request, *args, **kwargs)
BaseCreateView 继承 ModelFormMixin,BaseFormView继承 FormMixin。
class BaseFormView(FormMixin, ProcessFormView):
"""
A base view for displaying a form
"""
ModelFormMixin 与 FormMixin
ModelFormMixin 继承 FormMixin,此外还继承了 SingleObjecMixin ,SingleObjectMixin 定义了 model、queryset、context_object_name 等数据库查询的属性,此外还定义了 get_objetct()函数用于确定模型实例。
class SingleObjectMixin(ContextMixin):
"""
Provides the ability to retrieve a single object for further manipulation.
"""
model = None
queryset = None
slug_field = 'slug'
context_object_name = None
slug_url_kwarg = 'slug'
pk_url_kwarg = 'pk'
query_pk_and_slug = False
def get_object(self, queryset=None):
"""
Returns the object the view is displaying.
By default this requires `self.queryset` and a `pk` or `slug` argument
in the URLconf, but subclasses can override this to return any object.
"""
# Use a custom queryset if provided; this is required for subclasses
# like DateDetailView
if queryset is None:
queryset = self.get_queryset()
# Next, try looking up by primary key.
pk = self.kwargs.get(self.pk_url_kwarg, None)
slug = self.kwargs.get(self.slug_url_kwarg, None)
if pk is not None:
queryset = queryset.filter(pk=pk)
# Next, try looking up by slug.
if slug is not None and (pk is None or self.query_pk_and_slug):
slug_field = self.get_slug_field()
queryset = queryset.filter(**{slug_field: slug})
# If none of those are defined, it's an error.
if pk is None and slug is None:
raise AttributeError("Generic detail view %s must be called with "
"either an object pk or a slug."
% self.__class__.__name__)
try:
# Get the single item from the filtered queryset
obj = queryset.get()
except queryset.model.DoesNotExist:
raise Http404(_("No %(verbose_name)s found matching the query") %
{'verbose_name': queryset.model._meta.verbose_name})
return obj
def get_queryset(self):
"""
Return the `QuerySet` that will be used to look up the object.
Note that this method is called by the default implementation of
`get_object` and may not be called if `get_object` is overridden.
"""
if self.queryset is None:
if self.model:
return self.model._default_manager.all()
else:
raise ImproperlyConfigured(
"%(cls)s is missing a QuerySet. Define "
"%(cls)s.model, %(cls)s.queryset, or override "
"%(cls)s.get_queryset()." % {
'cls': self.__class__.__name__
}
)
return self.queryset.all()
def get_slug_field(self):
"""
Get the name of a slug field to be used to look up by slug.
"""
return self.slug_field
def get_context_object_name(self, obj):
"""
Get the name to use for the object.
"""
if self.context_object_name:
return self.context_object_name
elif isinstance(obj, models.Model):
return obj._meta.model_name
else:
return None
def get_context_data(self, **kwargs):
"""
Insert the single object into the context dict.
"""
context = {}
if self.object:
context['object'] = self.object
context_object_name = self.get_context_object_name(self.object)
if context_object_name:
context[context_object_name] = self.object
context.update(kwargs)
return super(SingleObjectMixin, self).get_context_data(**context)
这里的方法主要供 get_form_class() 方法调用。